On the Ecology of Mountainous Forests in a Changing Climate: A ...
On the Ecology of Mountainous Forests in a Changing Climate: A ...
On the Ecology of Mountainous Forests in a Changing Climate: A ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
90 Chapter 3<br />
ForClim-E<br />
Abiotic environment<br />
model<br />
ForClim-P<br />
Plant population<br />
dynamics model<br />
ForClim-S<br />
Soil organic matter<br />
dynamics model<br />
kLat<br />
kFC<br />
kSlAsp<br />
µ(T), µ(P)<br />
σ(T), σ(P)<br />
r<br />
uWiT<br />
uDD<br />
uDrStr<br />
uAET<br />
uWiT<br />
uDD<br />
uDrStr<br />
uAvN<br />
uXL<br />
uXL<br />
uAET<br />
uAvN<br />
ForestBase<br />
Site characteristics:<br />
latitude (kLat)<br />
soil field capacity (kFC)<br />
slope & aspect (kSlAsp)<br />
Climatic data:<br />
monthly µ and σ <strong>of</strong> T & P<br />
cross-correlation coefficients<br />
(r) between T & P<br />
Bioclimatic variables:<br />
W<strong>in</strong>ter temperature (uWiT)<br />
Annual sum <strong>of</strong> degree-days (uDD)<br />
Drought stress <strong>in</strong>dex (uDrStr)<br />
Actual evapotranspiration (uAET)<br />
Biotic data:<br />
Annual production <strong>of</strong> six<br />
types <strong>of</strong> litter (uXL)<br />
Soil data:<br />
Available nitrogen <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> soil<br />
(uAvN)<br />
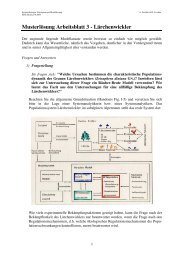
Fig. 3.13: Architecture <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> FORCLIM model. The three submodels FORCLIM-E,<br />
FORCLIM-P, and FORCLIM-S exchange data via <strong>the</strong> base module ForestBase, which<br />
warrants that all <strong>the</strong> output variables have a well-def<strong>in</strong>ed value all <strong>the</strong> time.<br />
FCPMon exports <strong>the</strong> procedures necessary for <strong>the</strong> monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> stem density distributions<br />
(histograms) and tree r<strong>in</strong>g chronologies, plus <strong>the</strong> animation <strong>of</strong> tree growth.<br />
FCPFileIO conta<strong>in</strong>s rout<strong>in</strong>es that perform file <strong>in</strong>put and output tasks, such as read<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong><br />
files with species parameters, writ<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> a matrix <strong>of</strong> limit<strong>in</strong>g factors for tree establishment<br />
and growth, and <strong>the</strong> read<strong>in</strong>g and writ<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> state vector <strong>of</strong> FORCLIM-P.<br />
FCPGrFact: Calculation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> three species-specific growth factors (gDDGF, gSMGF,<br />
gSNGF) and <strong>of</strong> total leaf area <strong>in</strong>dex, total biomass, and total tree number.<br />
FCPDynamic: This module conta<strong>in</strong>s <strong>the</strong> equations describ<strong>in</strong>g tree establishment, growth<br />
(except for three growth factors, cf. module FCPGrFact), mortality, and litter production.<br />
Moreover, it also conta<strong>in</strong>s <strong>the</strong> update procedure <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> state vector.<br />
ForClimP: model declaration <strong>in</strong> ModelWorks; it conta<strong>in</strong>s <strong>the</strong> ModelWorks procedures for<br />
model dynamics and ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>s <strong>the</strong> user <strong>in</strong>terface.