MASTER'S THESIS - SuSanA
MASTER'S THESIS - SuSanA
MASTER'S THESIS - SuSanA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
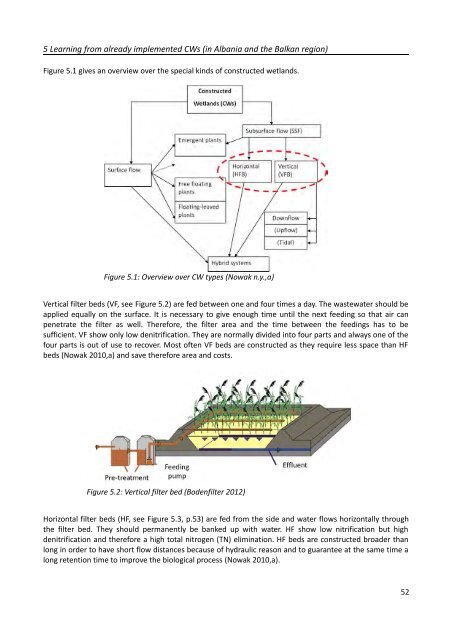
5 Learning from already implemented CWs (in Albania and the Balkan region)<br />
Figure 5.1 gives an overview over the special kinds of constructed wetlands.<br />
Figure 5.1: Overview over CW types (Nowak n.y.,a)<br />
Vertical filter beds (VF, see Figure 5.2) are fed between one and four times a day. The wastewater should be<br />
applied equally on the surface. It is necessary to give enough time until the next feeding so that air can<br />
penetrate the filter as well. Therefore, the filter area and the time between the feedings has to be<br />
sufficient. VF show only low denitrification. They are normally divided into four parts and always one of the<br />
four parts is out of use to recover. Most often VF beds are constructed as they require less space than HF<br />
beds (Nowak 2010,a) and save therefore area and costs.<br />
Figure 5.2: Vertical filter bed (Bodenfilter 2012)<br />
Horizontal filter beds (HF, see Figure 5.3, p.53) are fed from the side and water flows horizontally through<br />
the filter bed. They should permanently be banked up with water. HF show low nitrification but high<br />
denitrification and therefore a high total nitrogen (TN) elimination. HF beds are constructed broader than<br />
long in order to have short flow distances because of hydraulic reason and to guarantee at the same time a<br />
long retention time to improve the biological process (Nowak 2010,a).<br />
52