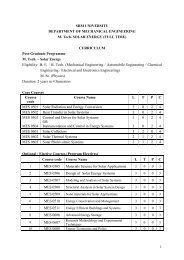
DRUG INDUCED KIDNEY DISEASE
DRUG INDUCED KIDNEY DISEASE
DRUG INDUCED KIDNEY DISEASE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>DRUG</strong> <strong>INDUCED</strong><br />
CHAPTER: 3<br />
<strong>KIDNEY</strong> <strong>DISEASE</strong><br />
BY<br />
Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM.,<br />
LECTURER<br />
DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE,<br />
SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
INTRODUCTION<br />
• Drug induced kidney disease or nephrotoxicity is a<br />
relatively common complication of several diagnostic<br />
and therapeutic agents.<br />
• TYPES :<br />
• 1. HAEMODYNAMIC CHANGES :<br />
• It leads to ARF , ATN ,Nephrotoxicity<br />
• ACE inhibitors<br />
• Angiotensin –II antagonists<br />
• NSAIDS
2INTRINSIC NEPHROTOXICITY <br />
TUCAE TUBULAR NECROSIS <br />
• Aminoglycosides<br />
• Cytotoxic drugs<br />
• Radiocontrast<br />
• ACUTE INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS<br />
• NSAID<br />
• Antibiotics<br />
• Diuretics<br />
• Proton pump inhibitors
• GLOMERULOPATHY:<br />
• NSAIDS<br />
• Gold<br />
• Pencillamide<br />
• OBSTRUCTIVE NEPHROPATHY:<br />
• Crystal uria<br />
• Cytotoxic drugs<br />
• Ciprofloxacin<br />
• sulphonamides
RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS:<br />
• Methysergide<br />
• Bromocriptine<br />
• methotrauxate
NSAID induced haemodynamic<br />
mechanisms:<br />
• phospholipid<br />
phospholipase A<br />
•<br />
• Arachidonic acid<br />
•<br />
5‐lipoxygenase cyclooxygenase‐I<br />
• 5HPETE<br />
• PGG II<br />
• 5HETE PGH synthesis<br />
• Leukotrienes PGH2 PGE2<br />
• LTA4,LTB4,LTC4 PGP2<br />
• LT receptor thromboxane synthase<br />
• thromboxane
• TREATMENT FOR HAEMODYNAMIC<br />
ARF:<br />
• With drawl of drug<br />
• Correct the renal blood flow<br />
• Treat the hyperkalemia<br />
• Serum potassium concentration should be carefully<br />
monitered
INTRINSIC NEPHROTOXICITY :<br />
• ACUTE INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS:<br />
• ETIOLOGY:<br />
• Idiosyncratic allergic drug interactions<br />
• Long term exposure of a drug<br />
• Because of hospitalization for longer period<br />
• This type of reactions occur after 2weeks of exposure<br />
• CLINICAL FEATURES:<br />
• Pyrexia<br />
• Rash<br />
• arthralgia
• IgE concentration in serum will be increased<br />
• Urine analysis – microscopical exam‐ shows the<br />
presence of leukocytes and neutrophils<br />
• Delayed renaluptake of gallium 67 on scintigraphy<br />
• Renal biopsy it shows inflammatory infilterate with<br />
variable number of eosinophils,lymphocytes,plasma cells<br />
• TREATMENT:<br />
• No need of renal replacement therapy and dialysis<br />
• Withdrawl of drug<br />
• Corticosteroids are helpful
<strong>DRUG</strong>S:<br />
• Beta‐lactam antibiotics:<br />
• Pencillin and cephalosporins<br />
• Other antibiotics:<br />
• Ciprofloxacin<br />
• Rifampicin<br />
• Sulphonamides<br />
• NSAIDS:<br />
• Ibuprofen<br />
• Selective COX II inhibitors‐ celecoxib
• DIURETICS:<br />
• Furosemide<br />
• Thiazide<br />
• PPI<br />
• Omeprazole<br />
• Lansoprazole<br />
• OTHERS:<br />
• Amodipine<br />
• Allopurinol, rifampicin<br />
• Dilthizem , phenytoin
Acute tubular necrosis :<br />
• ANTIBIOTICS:<br />
• Gentamycin<br />
• Vancomycin<br />
• ANTI‐VIRAL:<br />
• Cidofovir<br />
• Adefovir<br />
• Tenofovir<br />
• CYTOTOXIC <strong>DRUG</strong>S:<br />
• Cisplantin,cyclosporin,mitomycin
• Three phases:<br />
• Intiation phase<br />
• Maintenance phase<br />
• Recovery phase<br />
•<br />
• HYPOTENSION,<br />
VASOCONSTRICTORS<br />
• INCREASED NITRIC ACID SYNTHASE<br />
• Increased NO, cytokines( IL‐1 TNF‐@,free radicals)
Initiation phase:<br />
• Ischemia/nephrotoxins<br />
• Injury tubular epithelial cells<br />
• Cell death/detachment of basement membrane<br />
• Tubular necrosis<br />
Decreased blood volume/hypoperfusion<br />
• Decreased in GFR, increased serum creatinine,BUN concentration
MAINTENANCE PHASE :<br />
• Tubular necrosis<br />
• Tubular obstruction , increase in tubular<br />
permeability<br />
• Sustained reduction in GFR<br />
• azotemia,fluid retention,electrolyte<br />
imbalance,metabolic acidosis
RECOVERY PHASE:<br />
• RENAL FUNCTION<br />
Repair and regeneration of renal tissues<br />
Stimulation of growth factors<br />
Repair and promoting the proliferation of renal tubular cells<br />
Tubular function restored<br />
Increase in renal volume<br />
Gradual decrease in serum creatinine<br />
and urea level
PREVENTION:<br />
Nephrotic agents should be avoided in :<br />
Geriatric patients<br />
Heart failure<br />
Liver disease<br />
Existing renal disease<br />
Renal artery stenosis<br />
Diabetes mellitus<br />
TREATMENT<br />
Withdrawal of the drug that is responsible for ATN<br />
Monitor the fluid balance<br />
Hydration status and electrolyte
• Renal replacement therapy In emergency<br />
• IV dopamine 1‐3microgram /kg/minute is administered<br />
moa is selective vasodilation of renal disease<br />
• GLOMERULOPATHY:<br />
• NSAIDS cause glomerulopathy<br />
• Immune complex reactions<br />
• Immune complex gets deposited at the subepithelial<br />
space<br />
• Antigen is PLA2R binds to A2 receptor<br />
• OBSTRUCTIVE NEPHROPATHY:<br />
• Due to obstruction<br />
• Crystal and stone formation within uretic lumen
URATE NEPHROPATHY:<br />
• Accumulation of uric acid<br />
• Extensive cell lysis and purine catabolism results<br />
in rapid formation of uric acid