Ultrasound Blocks for the Anterior Abdominal Wall
Ultrasound Blocks for the Anterior Abdominal Wall
Ultrasound Blocks for the Anterior Abdominal Wall
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1. Anatomy <strong>for</strong> Anes<strong>the</strong>siologists | 15<br />
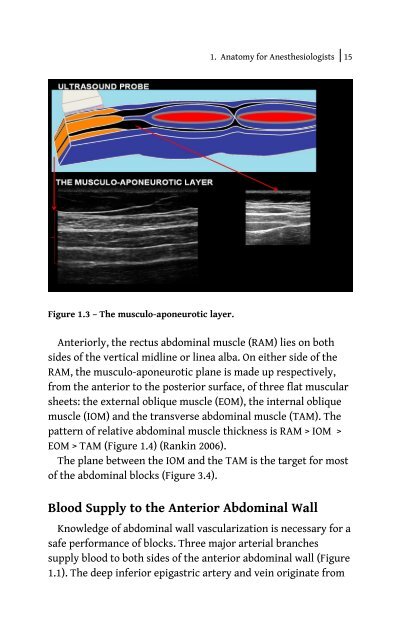
Figure 1.3 – The musculo-aponeurotic layer.<br />
<strong>Anterior</strong>ly, <strong>the</strong> rectus abdominal muscle (RAM) lies on both<br />
sides of <strong>the</strong> vertical midline or linea alba. On ei<strong>the</strong>r side of <strong>the</strong><br />
RAM, <strong>the</strong> musculo-aponeurotic plane is made up respectively,<br />
from <strong>the</strong> anterior to <strong>the</strong> posterior surface, of three flat muscular<br />
sheets: <strong>the</strong> external oblique muscle (EOM), <strong>the</strong> internal oblique<br />
muscle (IOM) and <strong>the</strong> transverse abdominal muscle (TAM). The<br />
pattern of relative abdominal muscle thickness is RAM > IOM ><br />
EOM > TAM (Figure 1.4) (Rankin 2006).<br />
The plane between <strong>the</strong> IOM and <strong>the</strong> TAM is <strong>the</strong> target <strong>for</strong> most<br />
of <strong>the</strong> abdominal blocks (Figure 3.4).<br />
Blood Supply to <strong>the</strong> <strong>Anterior</strong> <strong>Abdominal</strong> <strong>Wall</strong><br />
Knowledge of abdominal wall vascularization is necessary <strong>for</strong> a<br />
safe per<strong>for</strong>mance of blocks. Three major arterial branches<br />
supply blood to both sides of <strong>the</strong> anterior abdominal wall (Figure<br />
1.1). The deep inferior epigastric artery and vein originate from