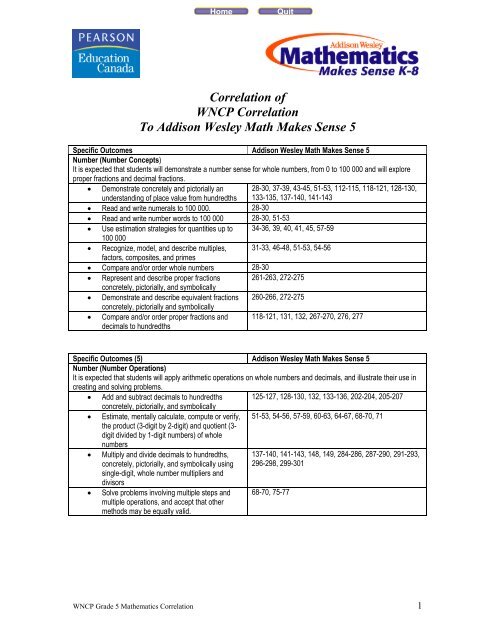
Correlation of WNCP Correlation To Addison Wesley Math Makes ...
Correlation of WNCP Correlation To Addison Wesley Math Makes ...
Correlation of WNCP Correlation To Addison Wesley Math Makes ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Correlation</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>WNCP</strong> <strong>Correlation</strong><br />
<strong>To</strong> <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Specific Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Number (Number Concepts)<br />
It is expected that students will demonstrate a number sense for whole numbers, from 0 to 100 000 and will explore<br />
proper fractions and decimal fractions.<br />
• Demonstrate concretely and pictorially an<br />
understanding <strong>of</strong> place value from hundredths<br />
28-30, 37-39, 43-45, 51-53, 112-115, 118-121, 128-130,<br />
133-135, 137-140, 141-143<br />
• Read and write numerals to 100 000. 28-30<br />
• Read and write number words to 100 000 28-30, 51-53<br />
• Use estimation strategies for quantities up to 34-36, 39, 40, 41, 45, 57-59<br />
100 000<br />
• Recognize, model, and describe multiples, 31-33, 46-48, 51-53, 54-56<br />
factors, composites, and primes<br />
• Compare and/or order whole numbers 28-30<br />
• Represent and describe proper fractions 261-263, 272-275<br />
concretely, pictorially, and symbolically<br />
• Demonstrate and describe equivalent fractions 260-266, 272-275<br />
concretely, pictorially and symbolically<br />
• Compare and/or order proper fractions and<br />
decimals to hundredths<br />
118-121, 131, 132, 267-270, 276, 277<br />
Specific Outcomes (5) <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Number (Number Operations)<br />
It is expected that students will apply arithmetic operations on whole numbers and decimals, and illustrate their use in<br />
creating and solving problems.<br />
• Add and subtract decimals to hundredths 125-127, 128-130, 132, 133-136, 202-204, 205-207<br />
concretely, pictorially, and symbolically<br />
• Estimate, mentally calculate, compute or verify,<br />
the product (3-digit by 2-digit) and quotient (3-<br />
digit divided by 1-digit numbers) <strong>of</strong> whole<br />
51-53, 54-56, 57-59, 60-63, 64-67, 68-70, 71<br />
numbers<br />
• Multiply and divide decimals to hundredths,<br />
concretely, pictorially, and symbolically using<br />
single-digit, whole number multipliers and<br />
divisors<br />
• Solve problems involving multiple steps and<br />
multiple operations, and accept that other<br />
methods may be equally valid.<br />
137-140, 141-143, 148, 149, 284-286, 287-290, 291-293,<br />
296-298, 299-301<br />
68-70, 75-77<br />
<strong>WNCP</strong> Grade 5 <strong>Math</strong>ematics <strong>Correlation</strong> 1
Specific Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Patterns and Relations (Patterns)<br />
It is expected that students will construct, extend, and summarize patterns, including those found in nature, using rules,<br />
charts, mental mathematics, and calculators.<br />
• Develop charts to record and reveal number 4, 5, 9-11, 352-355<br />
patterns<br />
• Describe how a pattern grows, using everyday 6-8, 9-11, 20, 21, 356<br />
language in spoken and written form<br />
• Construct and expand patterns in two and three 2, 3, 12-15, 23, 243-245, 256, 257, 354, 362-364<br />
dimensions, concretely and pictorially<br />
• Generate and extend number patterns from a 16-19, 352-355, 356-358, 360, 361<br />
problem-solving context<br />
• Predict and justify pattern extensions 8, 12-15, 354, 355<br />
Specific Outcomes (5) <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Shape and Space (Measurement)<br />
It is expected that students will use measurement concepts, appropriate tools, and the results <strong>of</strong> measurements to<br />
solve problems in everyday contexts.<br />
• Recognize and explain the meaning <strong>of</strong> length, 308, 309, 310-312, 313-315, 316, 317, 318<br />
width, height, depth, thickness, perimeter, and<br />
circumference<br />
• Evaluate the appropriateness <strong>of</strong> units and 311, 312, 216-218, 220, 221<br />
measuring tools in practical contexts<br />
• Estimate and measure the perimeter <strong>of</strong> irregular 318-320, 321-324, 325-327<br />
shapes<br />
• Estimate and measure the area <strong>of</strong> irregular 333-336, 337-339<br />
shapes by dividing them into parts<br />
• Estimate and measure the effect <strong>of</strong> changing 329-332<br />
one or more dimensions <strong>of</strong> a rectangle on its:<br />
• perimeter<br />
• area<br />
• Relate perimeter and area <strong>of</strong> rectangles, using 329-332<br />
manipulatives and diagrams<br />
• Estimate, measure, record, and order<br />
210-212, 213-215<br />
containers by volume using cm 3<br />
• Use concrete materials to relate cm 3 to mL 208, 209, 213-215<br />
• Construct objects <strong>of</strong> a specific volume, 212, 215<br />
expressed in cm 3<br />
• Solve problems involving mass (weight), using 216-218, 219-221<br />
g, kg, and t.<br />
• Read an analog clock to the nearest minute, 190-195<br />
and write the time<br />
• Read and write time on a 24-hour clock 193-196<br />
• Read and write SI notation for recording date<br />
and time<br />
190-192, 193-196<br />
<strong>WNCP</strong> Grade 5 <strong>Math</strong>ematics <strong>Correlation</strong> 2
Specific Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Shape and Space (3-D Objects and 2-D Shapes)<br />
It is expected that students will use visualization <strong>of</strong> 3-D objects and 2-D shapes to solve problems related to spatial<br />
relations.<br />
• Construct, analyze, and classify triangles 78, 79, 84-86,<br />
according to their side measures<br />
• Build, represent, and describe geometric 87-90, 91-94, 99-101, 102, 103, 106, 107, 108, 109<br />
objects and shapes<br />
• Identify and name polygons according to the 80-83<br />
number <strong>of</strong> sides, angles and vertices (3, 4, 5, 6,<br />
or 8)<br />
• Cover a given 2-D shape with tangram pieces 87-90<br />
• Complete the drawing <strong>of</strong> a 3-D object, on grid 95-98<br />
paper, given the front face<br />
• Determine, experimentally, the minimum<br />
information needed to draw a given 2-D shape<br />
91-94<br />
Specific Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Shape and Space (Transformations)<br />
It is expected that students will describe motion in terms <strong>of</strong> a slide, a turn, or a flip.<br />
• Recognize motion as a slide (translation), a turn 228-231, 232-235, 236-239<br />
(rotation), or a flip (reflection)<br />
• Recognize tessellations created with regular 226, 227, 243-245, 254, 255, 362-364, 371<br />
and irregular shapes in the environment<br />
• Cover a surface using one or more tessellating 226, 227, 243-245, 362-364, 365-367<br />
shapes<br />
• Create tessellations, using regular polygons 243-245, 362, 365-367<br />
• Identify planes <strong>of</strong> symmetry by cutting solids 99-101<br />
• Plot whole number ordered pairs in the first 248-251<br />
quadrant with intervals <strong>of</strong> 1, 2, 5, and 10<br />
• Identify a point in the first quadrant, using<br />
ordered pairs<br />
248-251<br />
<strong>WNCP</strong> Grade 5 <strong>Math</strong>ematics <strong>Correlation</strong> 3
Specific Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Statistics and Probability (Data Analysis)<br />
It is expected that students will develop and implement a plan for the collection, display, and interpretation <strong>of</strong> data to<br />
answer a question.<br />
• Identify a question to generate appropriate 175-177, 186, 187, 392, 393<br />
data, and predict results<br />
• Distinguish between a total population and a 175-177<br />
sample <strong>of</strong> that population<br />
• Use a variety <strong>of</strong> methods to collect and record 152, 154-157, 158-161, 164-166, 186, 187<br />
data<br />
• Evaluate the graphic presentation <strong>of</strong> the data to 154-157, 159-161, 164-166<br />
ensure clear representation <strong>of</strong> the results<br />
• Create classifications and ranges for grouping 155-157, 158-161, 164-166, 169-172<br />
data<br />
• Display data by hand or by computer in a<br />
variety <strong>of</strong> ways, including:<br />
- frequency diagrams<br />
- line plots<br />
- broken-line graphs<br />
• Discuss the reasonableness <strong>of</strong> the data and the<br />
results<br />
• Make inferences to generate a conclusion<br />
about the data<br />
154-157, 158-161, 162, 163, 164-166, 167, 168, 169-172,<br />
173, 174<br />
154, 158, 160, 161, 164-166<br />
178-181<br />
Specific Learning Outcomes <strong>Addison</strong> <strong>Wesley</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>Makes</strong> Sense 5<br />
Statistics and Probability (Chance and Uncertainty)<br />
It is expected that students will predict outcomes, conduct experiments, and communicate the probability <strong>of</strong> single<br />
events.<br />
• List all possible outcomes <strong>of</strong> an experiment 377-379<br />
involving a single event<br />
• Describe events, using the vocabulary <strong>of</strong> 372, 373, 374-376<br />
probability:<br />
- best/worst<br />
- probable/improbable<br />
- always/more likely/equally likely/less<br />
likely/never<br />
• Conduct probability experiments, and explain 377-379, 380-382, 383-385, 390, 391<br />
the results, using the vocabulary <strong>of</strong> probability<br />
• Conduct probability experiments to demonstrate<br />
that results are not influenced by factors such<br />
as the age, experience, or skill <strong>of</strong> the participant<br />
383-385, 389<br />
<strong>WNCP</strong> Grade 5 <strong>Math</strong>ematics <strong>Correlation</strong> 4