Answer Key
Answer Key
Answer Key
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ANSWER KEY<br />
Part I- The Basics:<br />
1. Define the following terms:<br />
a. Solute – substance being dissolved<br />
(lower concentration)<br />
Worksheet – Introduction to Solutions<br />
c. Solution – homogenous mixture of 2 or<br />
more substances (solute + solvent)<br />
b. Solvent – substance doing the<br />
dissolving (higher concentration)<br />
d. Dissolution – the process of dissolving<br />
2. Identify the solute & solvent in each:<br />
a) Kool- aid b) ocean water c) your blood<br />
Kool-aid = solute Salt = solute Blood cells & nutrients = solute<br />
Water = solvent Water = solvent Water = solvent<br />
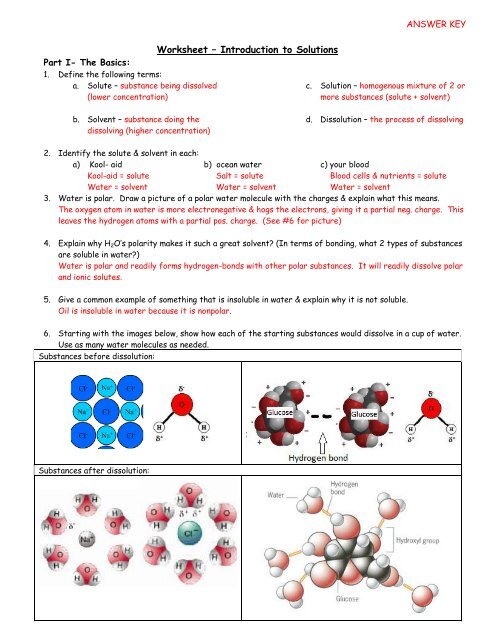
3. Water is polar. Draw a picture of a polar water molecule with the charges & explain what this means.<br />
The oxygen atom in water is more electronegative & hogs the electrons, giving it a partial neg. charge. This<br />
leaves the hydrogen atoms with a partial pos. charge. (See #6 for picture)<br />
4. Explain why H 2 O’s polarity makes it such a great solvent? (In terms of bonding, what 2 types of substances<br />
are soluble in water?)<br />
Water is polar and readily forms hydrogen-bonds with other polar substances. It will readily dissolve polar<br />
and ionic solutes.<br />
5. Give a common example of something that is insoluble in water & explain why it is not soluble.<br />
Oil is insoluble in water because it is nonpolar.<br />
6. Starting with the images below, show how each of the starting substances would dissolve in a cup of water.<br />
Use as many water molecules as needed.<br />
Substances before dissolution:<br />
Substances after dissolution:
7. The way NaCl and glucose dissolve in water is different from each other. Explain how & why.<br />
Glucose molecules (covalent) remain intact when dissolved in water. Each glucose molecule is surrounded by<br />
water molecules and forms hydrogen bonds with these water molecules.<br />
Salt compounds (ionic) dissociate in water. This means that the cations and anions separate. Each ion is<br />
surrounded by water molecules.<br />
8. a) Define the term dissociation.<br />
Dissociation - The separation of cations and anions in solution<br />
b) What types of compounds undergo dissociation during the dissolving process?<br />
Ionic compounds undergo dissociation during the dissolving process.<br />
9. How do you know when something is dissolved?<br />
Something is dissolved when you can no longer see it separately in the solution.<br />
10. a) Do solids dissolve in water? Give examples.<br />
Some solids dissolve in water, such as sugar and salt.<br />
b) Do liquids dissolve in water? Give examples.<br />
Some liquids dissolve in water, such as alcohol.<br />
c) Do gases dissolve in water? Give examples.<br />
Gases can dissolve in water if they are put under pressure. Ex: CO 2<br />
11. Does dissolving always involve water? Explain.<br />
No, other substances can also be solvents, such as gasoline, hexane, etc.<br />
12. What does the saying “like dissolves like” mean in chemistry?<br />
Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes.<br />
Part II- Real World Applications:<br />
1. A swim meet will not be cancelled due to rain, but it will be cancelled due to lightning. Explain.<br />
Water in the pool is not pure and contains many substances (such as salt from your body) that are<br />
electrolytes (will conduct an electrical current). If lightening strikes the pool, anyone in it would be<br />
electrocuted.<br />
2. Soap is able to dissolve and thus remove things like grease (non-polar) and sugar (polar). Do you think soap<br />
is polar, nonpolar, or both? Explain.<br />
Soap is both polar and nonpolar. The nonpolar regions of soap molecules surround things like grease<br />
(nonpolar) and the polar regions surround things like sugar (polar). Once these molecules are surrounded,<br />
they can be removed.<br />
3. Sharpie pens do not rub off in water. Do you think sharpie pen ink is polar or nonpolar? How could you<br />
remove sharpie pen?<br />
Sharpie pens are nonpolar since they do not dissolve in polar water.<br />
4. Auto mechanics will often use gasoline to clean grease off of their hands. Explain.<br />
Gasoline is a nonpolar solvent that will easily dissolve the nonpolar grease.<br />
Part III- Reading Questions: Read the article “Why Solubility Matters” and answer the following questions.<br />
1. a) What is the importance of vitamins in your body?<br />
Vitamins catalyze (speed up) the chemical reactions that occur in your body to keep you alive and<br />
healthy.
) What is the importance of minerals in your body?<br />
Minerals help promote certain chemical reactions or form structures in the body.<br />
2. What does the saying “like dissolves like” mean?<br />
Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes.<br />
3. a) How does your body absorb and store water soluble vitamins?<br />
Water soluble vitamins are dissolved in water when ingested, and then go into the blood stream to be used<br />
immediately.<br />
b) How is this different for fat soluble vitamins?<br />
Fat soluble vitamins are dissolved in the fats from food and stored in body tissues for future use.<br />
4. Why is it necessary to consume moderate amounts of fat in a healthy diet?<br />
These fats are essential for the proper absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.<br />
5. Are people more likely to become deficit in water soluble vitamins or fat soluble vitamins? Explain your<br />
reasoning.<br />
People are more likely to become deficit in water soluble vitamins because these are not stored in the body.