the RUSSIA oil & gas competitive intelligence report - Report Buyer
the RUSSIA oil & gas competitive intelligence report - Report Buyer the RUSSIA oil & gas competitive intelligence report - Report Buyer
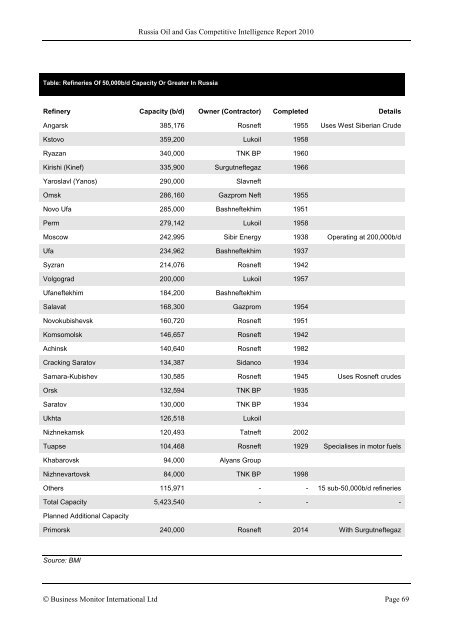
Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Intelligence Report 2010 Table: Refineries Of 50,000b/d Capacity Or Greater In Russia Refinery Capacity (b/d) Owner (Contractor) Completed Details Angarsk 385,176 Rosneft 1955 Uses West Siberian Crude Kstovo 359,200 Lukoil 1958 Ryazan 340,000 TNK BP 1960 Kirishi (Kinef) 335,900 Surgutneftegaz 1966 Yaroslavl (Yanos) 290,000 Slavneft Omsk 286,160 Gazprom Neft 1955 Novo Ufa 285,000 Bashneftekhim 1951 Perm 279,142 Lukoil 1958 Moscow 242,995 Sibir Energy 1938 Operating at 200,000b/d Ufa 234,962 Bashneftekhim 1937 Syzran 214,076 Rosneft 1942 Volgograd 200,000 Lukoil 1957 Ufaneftekhim 184,200 Bashneftekhim Salavat 168,300 Gazprom 1954 Novokubishevsk 160,720 Rosneft 1951 Komsomolsk 146,657 Rosneft 1942 Achinsk 140,640 Rosneft 1982 Cracking Saratov 134,387 Sidanco 1934 Samara-Kubishev 130,585 Rosneft 1945 Uses Rosneft crudes Orsk 132,594 TNK BP 1935 Saratov 130,000 TNK BP 1934 Ukhta 126,518 Lukoil Nizhnekamsk 120,493 Tatneft 2002 Tuapse 104,468 Rosneft 1929 Specialises in motor fuels Khabarovsk 94,000 Alyans Group Nizhnevartovsk 84,000 TNK BP 1998 Others 115,971 - - 15 sub-50,000b/d refineries Total Capacity 5,423,540 - - - Planned Additional Capacity Primorsk 240,000 Rosneft 2014 With Surgutneftegaz Source: BMI © Business Monitor International Ltd Page 69
Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Intelligence Report 2010 Oil Terminals/Ports The country's biggest Baltic Sea port is located in Primorsk, with additional ports in St. Petersburg and Vysotsk. Additional export capacity is located at the Black Sea port of Novorossiysk, Russia’s second largest oil export facility. The Pacific port of Kozmino was completed in December 2009, to become Russia's third largest oil export facility. Primorsk Primorsk, near St Petersburg, was completed in 2001 and exports around 1.5mn b/d, according to the EIA, although it claims export capacity of around 3mn b/d. The terminal exports refined products as well as crude, with Transnefteproduct beginning shipments in 2008. Novorossiysk The port of Novorossiysk is Russia’s main Black Sea port for oil, exporting Russian crude and oil delivered by pipeline from Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan. According to the EIA, around 1mn b/d of Russian crude is exported via the Black Sea (mainly through Novorossiysk), then sent through the Bosphorus to the Mediterranean. In June 2010, Transneft claimed that two plans had been developed to reduce or cease oil exports via the Bosphorus in order to provide customers for the Samsun-Ceyhan oil pipeline. Kozmino Russia's newest crude oil export terminal, the port of Kozmino, began operations in December 2009. The port sent its first cargo to Hong Kong, underlining its focus on catering for Asian demand. Kozmino exports East Siberian crude that is transported from the Meget railway terminal in the Irkutsk region to the Skovorodino oil terminal, which started operations in October 2009. The Kozmino terminal, which is operated by national oil midstream monopoly Transneft, is intended to be the terminus of the Eastern Siberia-Pacific Ocean (ESPO) pipeline, which is due to be completed in 2014-15. The Skovorodino oil terminal is the endpoint of Phase 1 of the ESPO pipeline, but Kozmino will receive oil delivered by rail from Skovorodino until the second phase has been completed. Each railway oil cargo will hold 4,600- 4,800 tonnes (33,700-35,200bbl), according to ESPO's website. Oil Pipelines The port of Kozmino is a vital part of Russia's Asia Pacific economic strategy. Located in the Sea of Japan, it offers links to the main regional consumers: Japan, South Korea and China. The port will provide an outlet to oil producers in East Siberia, including Rosneft, Surgutneftegaz and TNK-BP. Once the ESPO pipeline is extended to Kozmino, the port will play a major role in Russia's energy export sector. East Siberia Pacific Ocean (ESPO) Once completed, the 4,700km ESPO pipeline will overtake the Europe-bound Druzhba (Friendship), making it the world’s longest oil pipeline. Transneft’s ESPO will be the first Russian pipeline © Business Monitor International Ltd Page 70
- Page 19 and 20: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 21 and 22: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 23 and 24: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 25 and 26: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 27 and 28: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 29 and 30: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 31 and 32: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 33 and 34: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 35 and 36: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 37 and 38: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 39 and 40: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 41 and 42: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 43 and 44: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 45 and 46: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 47 and 48: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 49 and 50: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 51 and 52: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 53 and 54: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 55 and 56: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 57 and 58: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 59 and 60: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 61 and 62: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 63 and 64: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 65 and 66: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 67 and 68: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 69: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 73 and 74: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 75 and 76: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 77 and 78: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 79 and 80: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 81 and 82: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 83 and 84: Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Inte
- Page 85 and 86: Russia Oil & Gas Competitive Intell
- Page 87 and 88: Russia Oil & Gas Competitive Intell
- Page 89 and 90: Russia Oil & Gas Competitive Intell
Russia Oil and Gas Competitive Intelligence <strong>Report</strong> 2010<br />
Table: Refineries Of 50,000b/d Capacity Or Greater In Russia<br />
Refinery Capacity (b/d) Owner (Contractor) Completed Details<br />
Angarsk 385,176 Rosneft 1955 Uses West Siberian Crude<br />
Kstovo 359,200 Luk<strong>oil</strong> 1958<br />
Ryazan 340,000 TNK BP 1960<br />
Kirishi (Kinef) 335,900 Surgutneftegaz 1966<br />
Yaroslavl (Yanos) 290,000 Slavneft<br />
Omsk 286,160 Gazprom Neft 1955<br />
Novo Ufa 285,000 Bashneftekhim 1951<br />
Perm 279,142 Luk<strong>oil</strong> 1958<br />
Moscow 242,995 Sibir Energy 1938 Operating at 200,000b/d<br />
Ufa 234,962 Bashneftekhim 1937<br />
Syzran 214,076 Rosneft 1942<br />
Volgograd 200,000 Luk<strong>oil</strong> 1957<br />
Ufaneftekhim 184,200 Bashneftekhim<br />
Salavat 168,300 Gazprom 1954<br />
Novokubishevsk 160,720 Rosneft 1951<br />
Komsomolsk 146,657 Rosneft 1942<br />
Achinsk 140,640 Rosneft 1982<br />
Cracking Saratov 134,387 Sidanco 1934<br />
Samara-Kubishev 130,585 Rosneft 1945 Uses Rosneft crudes<br />
Orsk 132,594 TNK BP 1935<br />
Saratov 130,000 TNK BP 1934<br />
Ukhta 126,518 Luk<strong>oil</strong><br />
Nizhnekamsk 120,493 Tatneft 2002<br />
Tuapse 104,468 Rosneft 1929 Specialises in motor fuels<br />
Khabarovsk 94,000 Alyans Group<br />
Nizhnevartovsk 84,000 TNK BP 1998<br />
O<strong>the</strong>rs 115,971 - - 15 sub-50,000b/d refineries<br />
Total Capacity 5,423,540 - - -<br />
Planned Additional Capacity<br />
Primorsk 240,000 Rosneft 2014 With Surgutneftegaz<br />
Source: BMI<br />
© Business Monitor International Ltd Page 69