worksheet packet
worksheet packet
worksheet packet
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
NAME<br />
.,-.~'<br />
~~~~·Wf*mfu1?%fMtWM.@.t~@~~NNf:H%t:-t~jt~~%':~H~t~M~~~&f:r:i~~1fr'1{ftN61~~W~~~1:t~W~%WG1~~r4~t:~f~f::tt~~9fm~~ffi<br />
- Use with Text Paqes 416-421<br />
r;t'- How Solutions Form<br />
In each of the follawing statements, a term has been scrambled. Unscramble the term and write it on the line provided.<br />
_____ ----:- 1. Solid solutions composed of metals usually are called loyals.<br />
_________<br />
__________<br />
__________<br />
2. When the particles of a mixture are evenly distributed throughout,<br />
the mixture is housenogeom.<br />
3. In a solution of sugar and water, the water is the noioels.<br />
4. In a solution of salt and water, the salt is the stoleu.<br />
___ --'- .,--5. Grinding a solid solute increases itsfarceus area.<br />
_________<br />
---,6. A gas dissolves best in a Hquid solvent when the solution is under<br />
high spursere.<br />
Circle the term in each set that is least related to the others. Then write a sentence explaining how the remaining<br />
terms are related. Compare your answers to those of your classmates. There may be more than one correct set of<br />
relationships.<br />
)<br />
1. solute, solution, ion, solvent _<br />
2. stir, grind, heat, hydrate<br />
3. dental amalgam, soda, sterling silver, brass<br />
4. metal, air, alloy, solid ---'-- _<br />
5. club soda, sugar water, vinegar, brass<br />
6. air, gas, nitrogen, carbon _<br />
Copyright e Glencoe/McGraw·HiII, a division of The McGraw·HiII Companies, Inc. 6
NAME<br />
DATE<br />
CLASS<br />
~mt.~:%f~W~1@t.~t@1~~W1~Wtm~}9~;H~ffiWTht1%tmWlj~%#~i~~~~Wtml*if~t.f:W§"lli~t~#$.t~7!~~**1:~}<br />
Use with Text Pages 416-421<br />
(<br />
/f,' How Solutions -Porm .<br />
Complete the table below by writing the missing information in the appropriate box. Then answer the<br />
following questions ...<br />
.Solution Type Solvent Solute Example<br />
gas<br />
gas<br />
solid<br />
saltwater<br />
solid.<br />
dental amalgam<br />
liquid<br />
liquid<br />
liquid<br />
clubsodo<br />
...<br />
, )<br />
solid<br />
brass<br />
-<br />
Study the information in your table carefully. What is true about the state of the solvent and<br />
the type of solution produced?<br />
_<br />
Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement true.<br />
1. A solid dissolves faster in a liquid if the temperature of the liquid is (increased, decreased).<br />
2.. A gas dissolves faster in a liquid if the temperature of the liquid is (increased, decreased).<br />
\<br />
3. The (larger, smaller) the surface area of a solid, the faster it will dissolve.<br />
4. When a gas is being dissolved in a liquid, stirring (speeds up, slows down) the dissolving<br />
process.<br />
5. When a solid is being dissolved in a liquid, stirring (speeds up, slows down) the dissolving<br />
.process.<br />
6. A gas dissolves faster ina liquid when under (high, low) pressure.<br />
Study your responses to the exercise above. Use your responses to answer the following question.<br />
7. How do the methods of speeding the rate of solution for dissolving a solid in a liquid compare<br />
to the methods of speeding the rate of solution when dissolving a gas in a liquid?<br />
Copyright ~ Glencoe/McGraw-Hili, a division of The McGraw-Hili Companies, Inc.<br />
61
NAME<br />
t. Solubility and<br />
,Concentration<br />
In the blank at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that cOfr~<br />
CLASS<br />
~f:~'f&t~tW~w~t%t¥mN1.m~ff:~f::~@W1fiHf@m%'~~1:~t~~®1$w..~~iWWim¥t~%fu~WW~:WfjNtWf.b~m*~~~~~K~tt'i%:"'ime~~f.m~~<br />
Use with Text Pages 424~29<br />
completes each statement.<br />
1. The maximum number of grams of solute that will dissolve in 100 g of solvent at a<br />
certain temperature is the __ of the solute.<br />
a. solubility b. dilution .<br />
2. Different substances have<br />
a. different<br />
solubilities.<br />
b.the same<br />
3. The concentration of a mixture of two or more liquids is expressed as a<br />
percentage by __ .<br />
a. mass b. volume<br />
4. A solution that has dissolved all the solute it can hold at a given temperature is __ .<br />
a. unsaturated b. saturated<br />
. -<br />
5. As the temperature of a liquid solvent increases, the amount of solid solute that can be<br />
dissolved in the solvent<br />
a. increases b. decreases<br />
6. Any solution that can hold more solute at a given temperature is __ .<br />
a. unsaturated b. saturated<br />
)<br />
7. Each time a saturated solution is heated to a higher temperature, it becomes __ .<br />
a. unsaturated b. supersaturated<br />
8. A solution that contains more solute than a saturated one at a given<br />
temperature is __ .<br />
a. unsaturated b. supersaturated<br />
9. Lines on a graph that show how much solute a solvent can hold at a given<br />
temperature are called __ .<br />
a. solution graphs b. solubility curves<br />
10. The concentration of a solid solute in a liquid solvent is expressed as a<br />
percentage by __ .<br />
a. mass b. volume<br />
11. A solution that has 4 g of KCI dissolved in 100mL of water is __ compared to a<br />
solution that has 30 g of KCI dissolved in 100mL of water.<br />
a. dilute b. concentrated<br />
12. One mL of water has a mass of<br />
a. one gram b. one kilogram<br />
)<br />
Copyright e Glencoe/McGraw-Hili, a division of The McGraw-Hili Companies, Inc. 63
NAME DATE CLASS<br />
~=.~~~~<br />
t"<br />
Use with Text Pages 424--431<br />
Solubility and<br />
Concentration<br />
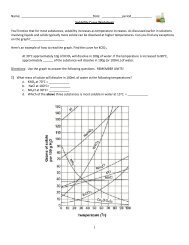
Use the information in the table to graph the solubility curves for barium hydroxide~ Ba(OH)2; copperill) sulfate,<br />
CuSO 4; potassium chloride, KCI; and sodium nitrate, NaN0 3<br />
. Use a different colored pencil for each compound.<br />
Solubility. in 9/100 9 water<br />
Compound<br />
Temperature<br />
.o-c 20°C 60°C 100°C<br />
Ba(OH)2 1.67 3.89 20.94 101.40<br />
CuS0 4 23.10 32.00 61.80 114.00<br />
KCI 28.0 34:2 45.8 56.30<br />
NaN0 3 73.0 87.6 122.0 180.00<br />
180.-----------------~---------------------------.<br />
160<br />
-.:-<br />
~ 140<br />
~<br />
'0 120<br />
~<br />
o 100<br />
o•...<br />
~ 80<br />
'-"<br />
g 60<br />
:0<br />
:l 40<br />
"'5<br />
VI<br />
20<br />
0+---+---1---1---;---~---r--~---r---r---r---r---;<br />
o 20 40 60 80 100 120<br />
Temperature<br />
(0C)<br />
Use the infonnation in the table and your graph to answer the following questions.<br />
1. At about what temperature will 100 g of water dissolve equal amounts of potassium chloride<br />
and barium hydroxide? __ ~ _<br />
2. At about what temperature will 37 g of both copper(ll) sulfate and potassium chloride dissolve<br />
in 100 g of w,ater? _---.:. -'-- _<br />
3. If 100 g of sodium nitrate are dissolved in 100 g of ~ater at 60°C is the solution formed<br />
saturated, unsaturated, or supersaturated? ------<br />
4. If 32 g of copper(ll) sulfate are dissolved in 100 g of water at 20 o e, is the solution produced<br />
saturated, unsaturated, or supersaturated? -".-- _<br />
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hili, a division of The McGraw-Hili Companies, Inc.<br />
63
NAME DATE CLASS<br />
11. Particles in Solution<br />
':.:;: ..•.<br />
Match the terms in Column II with the definitions in Column 1. Write the number of the correct term in the correct<br />
box in the grid. If you correctly complete the grid, the sum of the numbers in each horizontal and vertical row will be<br />
the same. Thefirst one is donefor you.<br />
Column I Column II<br />
a. homogenous mixture 1. mixture<br />
b. solution of metals 2. concentrated<br />
c. charged atom<br />
3. solution<br />
d. can dissolve polar solutes and ionic solutes<br />
e. substance being dissolved 4. solvent<br />
f. substance that dissolves a solute 5. supersaturated solution<br />
g. can dissolve only nonpolar solutes 6. unsaturated solution<br />
h. number of grams of solute that will dissolve<br />
7. dissocia tion<br />
in 100 g of solvent<br />
i. substance whose solutions do not conduct 8. nonelectrolyte<br />
electricity 9. solubility<br />
j. substance that separates into ions in a water 10. ion<br />
solution<br />
11.<br />
k. contains more solute than a saturated<br />
conductor<br />
solution does at a given temperature 12. ionization<br />
1. substance that allows electricity to pass 13. alloy<br />
through it<br />
r:<br />
14. solute<br />
solution that has all the solute it can hold at<br />
15.<br />
a given temperature<br />
dilute<br />
n. process by which ions split apart when dis- 16. nonpolar solvent<br />
solved 17. polar solvent<br />
o. process by which polar substances are pulled 18. saturated solution<br />
apart in water<br />
19.<br />
p.<br />
electrolyte<br />
any solution that can dissolve more solute at<br />
a given temperature<br />
Answer Box<br />
A3, B C D<br />
,<br />
E F G H<br />
Totals<br />
I J K L<br />
M N 0 P<br />
Totals<br />
.,<br />
~rrt IQ Gre~cGraw-Hili. a division of The. McGraw-Hili Companies, Inc.
NAME<br />
. DATE<br />
CLASS<br />
IJse wiIilTexl:Pa.ges 432-434<br />
Use the diagram below to answer questions 1-10 .<br />
Particles in Solution<br />
••<br />
1. Is water a polar molecule or a nonpolar molecule? How do you know? _<br />
2.IsHClpolarornonpolar?<br />
3. What is the general rule that determines how polar and nonpolar substances dissolve?<br />
_<br />
(<br />
4. Will HCl dissolve in water? ...,--~ _<br />
5. What happens to the HCI molecule when it is placed in water? _<br />
6. What happens to the hydrogen atom of the HCl molecule? " _<br />
7. What happens to the chlorine atom of the HCl molecule? _<br />
8. What is the process shown in the diagram called? _<br />
;<br />
9. Is HCl an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte? _<br />
10. Will the solution conduct electricity? --'- _<br />
64<br />
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hili, a division of The McGraw-Hili Companies, Inc.