Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>47</strong> <strong>Ankle</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Foot</strong> 2295 <strong>47</strong><br />
Tarsal<br />
tunnel<br />
Flexor<br />
retinaculum<br />
B<br />
A<br />
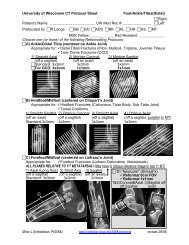
Figure <strong>47</strong>-99. Location <strong>of</strong> the tarsal tunnel. A, Illustration <strong>of</strong> the location <strong>of</strong> the tarsal tunnel (arrow), deep to the flexor retinaculum.<br />
(Artist, M. Schenk, MS, CMI.) B, Axial high-resolution T1-weighted image shows the medial neurovascular bundle (dotted ellipse) deep to the<br />
flexor retinaculum (arrows).<br />
Figure <strong>47</strong>-100. Tarsal tunnel containing a synovial<br />
cyst (arrow): axial (A) <strong>and</strong> sagittal (B) T2-weighted fatsuppressed<br />
images.<br />
A<br />
B<br />
(Fig. <strong>47</strong>-101A). These fractures tend to be the result <strong>of</strong><br />
repetitive injuries rather than a specific traumatic event. In<br />
our practice, such fatigue injuries are commonly seen in<br />
college athletes. Often the athlete’s prognosis <strong>and</strong> the<br />
length <strong>of</strong> time needed to rest the fatigue injury depend on<br />
whether the cortex is broken. When MRI demonstrates just<br />
bone marrow edema without a breach in the cortex, these<br />
will be radiographically occult, <strong>and</strong> our sports medicine<br />
physicians prefer we use the term stress reaction. We use<br />
stress fracture to refer to bones that exhibit a discrete line<br />
extending through the cortex by MRI, CT, or plain radiography<br />
(Figs. <strong>47</strong>-102 <strong>and</strong> <strong>47</strong>-103).<br />
Although navicular fatigue fractures may be suspected<br />
clinically, initial radiographs are <strong>of</strong>ten negative, <strong>and</strong> MRI<br />
is the next imaging study ordered to confirm the diagnosis.<br />
As with most stress fractures, MRI is more sensitive than<br />
CT for the detection <strong>of</strong> the bone marrow edema that develops<br />
before the cortex breaks (see Fig. <strong>47</strong>-101). But MRI,<br />
owing to its exquisite sensitivity to marrow edema, may be<br />
too sensitive to assess fracture healing. At the UW we have<br />
Ch0<strong>47</strong>-A05375.indd 2295<br />
9/9/2008 5:35:53 PM