Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>47</strong> <strong>Ankle</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Foot</strong> 2241 <strong>47</strong><br />
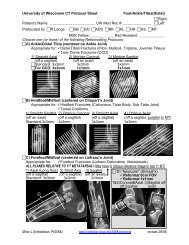
Figure <strong>47</strong>-44. Importance <strong>of</strong> weight-bearing view.<br />
A, Non–weight-bearing lateral view, obtained<br />
portably. On this image, the long axis <strong>of</strong> the talus<br />
(dashed white line) is parallel to the long axis <strong>of</strong> the<br />
first metatarsal (dashed black line), suggesting normal<br />
alignment. B, Same patient as in A, obtained upright at<br />
a follow-up clinic visit 3 months later. On this weightbearing<br />
lateral view, the long axis <strong>of</strong> the talus (solid<br />
white line) is now angled downward relative to the<br />
first metatarsal (solid black line). This indicates that<br />
the patient has a nonrigid flat-foot deformity (pes<br />
planus), demonstrable only with weight bearing.<br />
A<br />
B<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
Figure <strong>47</strong>-45. A, The patient is positioned supine on the CT table<br />
with her legs straight, feet together, toes pointing to the ceiling.<br />
B, Example <strong>of</strong> a foot holder we built to help keep patients’ feet<br />
centered in the CT scanner in neutral position. C, In lieu <strong>of</strong> a<br />
dedicated foot holder, we have used a box.<br />
metal, including it in the scanning field-<strong>of</strong>-view (FOV)<br />
does not cause excessive streak artifacts <strong>and</strong> does not<br />
increase the radiation exposure to organs in the torso.<br />
Securing the patient’s feet to a dedicated holder (Fig.<br />
<strong>47</strong>-45B) or to a box (Fig. <strong>47</strong>-45C) helps to hold the feet in<br />
neutral position <strong>and</strong> to prevent motion during the scan.<br />
Scout views are obtained in both the AP <strong>and</strong> lateral<br />
projections (Fig. <strong>47</strong>-46). The scanning FOV should be<br />
set wide enough to include both the right <strong>and</strong> left lateral<br />
malleoli; for most patients this is less than 25 cm. The<br />
coverage should begin superior to both syndesmoses<br />
<strong>and</strong> extend below the calcanei. In cases <strong>of</strong> pilon fractures,<br />
which are comminuted fractures involving the plafond,<br />
coverage is extended superiorly to include more <strong>of</strong> the<br />
distal tibia. We typically scan using 120 kVp at less than<br />
200 mA.<br />
Ch0<strong>47</strong>-A05375.indd 2241<br />
9/9/2008 5:34:22 PM