Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Ankle and Foot 47 - Department of Radiology - University of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
A<br />
C<br />
E<br />
B<br />
D<br />
F<br />
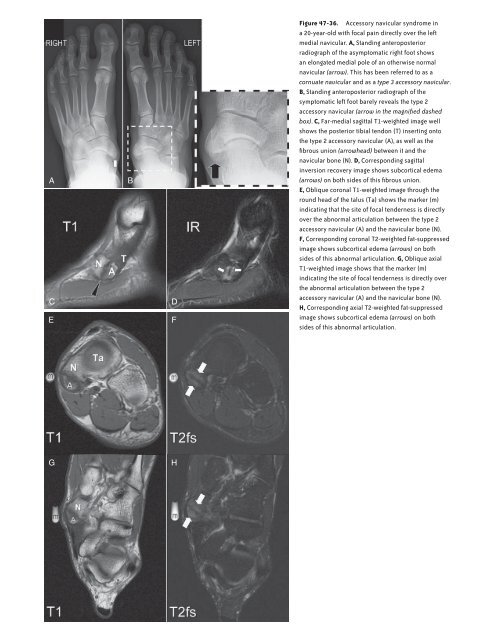
Figure <strong>47</strong>-36. Accessory navicular syndrome in<br />
a 20-year-old with focal pain directly over the left<br />
medial navicular. A, St<strong>and</strong>ing anteroposterior<br />
radiograph <strong>of</strong> the asymptomatic right foot shows<br />
an elongated medial pole <strong>of</strong> an otherwise normal<br />
navicular (arrow). This has been referred to as a<br />
cornuate navicular <strong>and</strong> as a type 3 accessory navicular.<br />
B, St<strong>and</strong>ing anteroposterior radiograph <strong>of</strong> the<br />
symptomatic left foot barely reveals the type 2<br />
accessory navicular (arrow in the magnified dashed<br />
box). C, Far-medial sagittal T1-weighted image well<br />
shows the posterior tibial tendon (T) inserting onto<br />
the type 2 accessory navicular (A), as well as the<br />
fibrous union (arrowhead) between it <strong>and</strong> the<br />
navicular bone (N). D, Corresponding sagittal<br />
inversion recovery image shows subcortical edema<br />
(arrows) on both sides <strong>of</strong> this fibrous union.<br />
E, Oblique coronal T1-weighted image through the<br />
round head <strong>of</strong> the talus (Ta) shows the marker (m)<br />
indicating that the site <strong>of</strong> focal tenderness is directly<br />
over the abnormal articulation between the type 2<br />
accessory navicular (A) <strong>and</strong> the navicular bone (N).<br />
F, Corresponding coronal T2-weighted fat-suppressed<br />
image shows subcortical edema (arrows) on both<br />
sides <strong>of</strong> this abnormal articulation. G, Oblique axial<br />
T1-weighted image shows that the marker (m)<br />
indicating the site <strong>of</strong> focal tenderness is directly over<br />
the abnormal articulation between the type 2<br />
accessory navicular (A) <strong>and</strong> the navicular bone (N).<br />
H, Corresponding axial T2-weighted fat-suppressed<br />
image shows subcortical edema (arrows) on both<br />
sides <strong>of</strong> this abnormal articulation.<br />
G<br />
H<br />
Ch0<strong>47</strong>-A05375.indd 2233<br />
9/9/2008 5:34:06 PM