Supporting fulcrum axis
Supporting fulcrum axis
Supporting fulcrum axis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
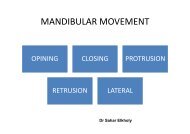
Definition<br />
Denture relation about<br />
an <strong>axis</strong><br />
Factors influencing<br />
effectiveness of<br />
indirect retainers<br />
Forms of indirect<br />
retainer
It is the component of RPD that<br />
assists direct retainers in<br />
preventing displacement of the<br />
distal extension denture base by<br />
creating resistance on the<br />
opposite side of the <strong>fulcrum</strong> line
It is the line about which the distal<br />
extension partial denture tends to<br />
rotate towards or away from the<br />
tissues.<br />
This <strong>axis</strong> is an imaginary line passing<br />
through the teeth(occlusal rests) and<br />
direct retainers( retentive tips)
The <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong> passes between<br />
the two main occlusal rests<br />
called (<strong>Supporting</strong> <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong>)<br />
This movements is resisted by<br />
the ridge& its overlying mucosa
The <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong> passes between<br />
most posterior and bilaterally<br />
located retentive terminals of<br />
primary direct retainer<br />
It is called (Retentive <strong>fulcrum</strong><br />
<strong>axis</strong>)<br />
This movements is resisted by<br />
Indirect retainers
1. Distance between the <strong>fulcrum</strong> line & the<br />
indirect retainer<br />
The greater the distance the more the<br />
effective will be the indirect retainer<br />
The indirect retainer must be<br />
perpendicular& midway to the <strong>fulcrum</strong><br />
<strong>axis</strong>
2.Effectiveness of tooth support<br />
Indirect retainer must be placed on a<br />
definite rest seat.<br />
It should be perpendicular to the<br />
long <strong>axis</strong> of tooth upon which it rest<br />
to prevent tooth movement<br />
Weak teeth should not be used to<br />
support indirect retainer
3.Effectiveness of direct retainer<br />
Unless the principle occlusal rests<br />
are held in their seats by the action<br />
of the direct retainers<br />
If displacement of the base away<br />
from the tissues will occur, Indirect<br />
retainer does not resist<br />
displacement
4.Rigidity of connectors supporting<br />
Indirect retainers<br />
All connectors must be rigid, to<br />
allow indirect retainer to be in<br />
function<br />
5. Indirect retainer must be rigid<br />
If arm of indirect retainer were to<br />
flex indirect retainer will not be<br />
effective
• - Occlusal rests .<br />
• - Canine extension from occlusal<br />
rest.<br />
• - Cingulum rest.<br />
• - Continuous bar<br />
• - Lingual plate
1. -Indirect retention.<br />
2. - Distribution of load over many teeth.<br />
3. -Give strength and rigidity to the<br />
appliance.<br />
4. "-Can form point of attachment for incisal<br />
rests
• - Palatally or lingually inclined teeth.<br />
• - Short clinical crown.
• Poor tolerance.<br />
• Interference with speech when used<br />
in the upper jaw.
-Palatal arm.<br />
-Anterior palatal bar<br />
-Posterior palatal bar<br />
-Extension of the palatal plate<br />
(horse shoe).