Download PDF - pcaarrd - Department of Science and Technology
Download PDF - pcaarrd - Department of Science and Technology
Download PDF - pcaarrd - Department of Science and Technology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
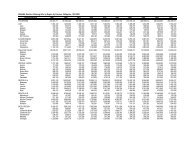
goes to waste (Fig. 3). On a per capita<br />
basis, consumption fell from 33 kg in 1980<br />
to only 24 kg in 1990 <strong>and</strong> 23 kg in 1998<br />
(DA-AMAS). This is because the prices <strong>of</strong><br />
locally sold banana have increased through<br />
the years. Table bananas found in<br />
supermarkets are mostly local (rejects)<br />
Cavendish <strong>and</strong> Lakatan (Gorrez, personal<br />
communication).<br />
Wastes<br />
15%<br />
Fresh (food)<br />
50%<br />
Processed<br />
into food<br />
product<br />
35%<br />
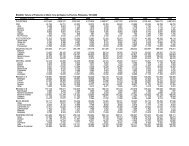
amounted to only 18,280 t valued at<br />
US$ 20.83 M in 1996–2000 (Tables 6 <strong>and</strong> 7).<br />
Of the total volume <strong>of</strong> chips exported from<br />
1999 to 2001, 38% went to Hongkong, 25%<br />
to Japan, 17% to Singapore, 11% to<br />
Netherl<strong>and</strong>s, <strong>and</strong> 9% to Korea (Fig. 5).<br />
The Philippines enjoys export advantage<br />
over its ASEAN neighbors in terms <strong>of</strong><br />
production <strong>and</strong> marketing because <strong>of</strong> its<br />
proximity to the major importing countries<br />
<strong>and</strong> technological advances in the<br />
production <strong>and</strong> h<strong>and</strong>ling systems. This is<br />
primarily because the infrastructure for<br />
export has long been established in<br />
Mindanao since the late 1960s. However,<br />
in most <strong>of</strong> the banana-growing areas<br />
especially the sites for Saba, Lakatan, <strong>and</strong><br />
Latundan, the necessary infra-support<br />
system is still lacking <strong>and</strong>/or insufficient to<br />
become competitive.<br />
Fig. 3.<br />
Domestic utilization <strong>of</strong> banana<br />
products, 1991–2000.<br />
Mango<br />
The Philippines ranked fifth among the<br />
world’s top major suppliers <strong>of</strong> banana in<br />
2000, with 3.56 M t or a share <strong>of</strong> 6.1% <strong>of</strong> the<br />
world production (FAO, 2000). India had the<br />
biggest share (18.9%), followed by Brazil<br />
(9.3%), China (8.9%), <strong>and</strong> Ecuador (8.6%).<br />
Indonesia occupied the sixth rank, while<br />
Thail<strong>and</strong> ranked ninth (Table 5).<br />
The major banana products being<br />
exported are fresh banana, chips/crackers,<br />
<strong>and</strong> catsup. The fresh bananas constitute<br />
the main bulk <strong>of</strong> our export representing<br />
almost 98% <strong>of</strong> the total volume exported. In<br />
1996-2000, the average volume exported<br />
reached to about 1.31 M t valued at<br />
US$ 261 M (Tables 6 <strong>and</strong> 7). Figure 4 shows<br />
the major importing countries <strong>of</strong> the fresh<br />
banana in 1999-2000 where Japan occupies<br />
the biggest share (61%), followed by China<br />
(16%), Korea (8%), Taiwan (6%), <strong>and</strong> United<br />
Arab Emirates (UAE) (6%). On the other<br />
h<strong>and</strong>, the average exported chips/crackers<br />
Mango is grown practically all over the<br />
Philippines. It ranks second among the<br />
important fruit crops in terms <strong>of</strong> areas <strong>and</strong><br />
production. In 2001, the total volume <strong>of</strong><br />
production reached 879,737 t (Table 8).<br />
Several mango cultivars are grown in the<br />
country but the most important are<br />
‘Carabao’ <strong>and</strong> ‘Pico.’ The Carabao mango,<br />
which accounts for 70% <strong>of</strong> total production,<br />
is recommended for both local <strong>and</strong> foreign<br />
markets. Other varieties such as ‘Pahutan’<br />
<strong>and</strong> ’Katchamita’ are also grown in<br />
considerable quantity.<br />
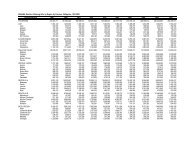
In 2001, the Philippines ranked seventh<br />
among the largest mango producers, with<br />
884,272 t or 4% <strong>of</strong> the total global output <strong>of</strong><br />
25.1 M t (Table 9). The largest mangoproducing<br />
country was India with 11.5 M<br />
(52%), followed by China with 3.21 M t (14%),<br />
Mexico with 1.46 M t (6.6%), Thail<strong>and</strong> with<br />
1.35 M t (6.19%), Indonesia with .95 M t<br />
(4.3%), <strong>and</strong> Pakistan with .94 M t (4.3%).<br />
10 ............................................................................................................. R&D Status <strong>and</strong> Directions