Human Resources for Health in Maternal, Neonatal and - HRH ...
Human Resources for Health in Maternal, Neonatal and - HRH ... Human Resources for Health in Maternal, Neonatal and - HRH ...
Data source Keywords used in search No. Items retrieved Websites of Key Organisations Cambodia Reproductive and Child Health Resource Center http://rc.racha.org.kh/ ―traditional" and "birth" and "attendant‖ ―community" and "health" and "worker‖ "human" and "resources" "skilled" and "birth" and "attendant" 2 2 3 0 1 0 0 0 Sub total 1 Overall Sub Total 560 minus duplicates 512 Plus significant items uncovered in preliminary scoping, and 325 hand searching Minus duplicates 94 TOTAL included in the review 743 No. items included in review P a g e | 197
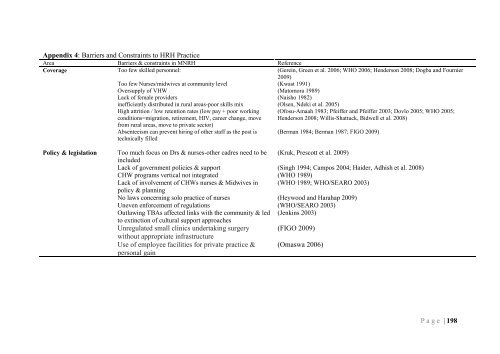
Appendix 4: Barriers and Constraints to HRH Practice Area Barriers & constraints in MNRH Reference Coverage Too few skilled personnel: Too few Nurses/midwives at community level Oversupply of VHW Lack of female providers inefficiently distributed in rural areas-poor skills mix High attrition / low retention rates (low pay + poor working conditions=migration, retirement, HIV, career change, move from rural areas, move to private sector) Absenteeism can prevent hiring of other staff as the post is technically filled (Gerein, Green et al. 2006; WHO 2006; Henderson 2008; Dogba and Fournier 2009) (Kwast 1991) (Matomora 1989) (Naisho 1982) (Olsen, Ndeki et al. 2005) (Ofosu-Amaah 1983; Pfeiffer and Pfeiffer 2003; Dovlo 2005; WHO 2005; Henderson 2008; Willis-Shattuck, Bidwell et al. 2008) (Berman 1984; Berman 1987; FIGO 2009) Policy & legislation Too much focus on Drs & nurses-other cadres need to be included Lack of government policies & support CHW programs vertical not integrated Lack of involvement of CHWs nurses & Midwives in policy & planning No laws concerning solo practice of nurses Uneven enforcement of regulations Outlawing TBAs affected links with the community & led to extinction of cultural support approaches Unregulated small clinics undertaking surgery without appropriate infrastructure Use of employee facilities for private practice & personal gain (Kruk, Prescott et al. 2009) (Singh 1994; Campos 2004; Haider, Adhish et al. 2008) (WHO 1989) (WHO 1989; WHO/SEARO 2003) (Heywood and Harahap 2009) (WHO/SEARO 2003) (Jenkins 2003) (FIGO 2009) (Omaswa 2006) P a g e | 198
- Page 147 and 148: although supplemented with epidemio
- Page 149 and 150: A technical meeting in Bangkok in 2
- Page 151 and 152: Development approach is an example
- Page 153 and 154: flexibility in order to overcome ge
- Page 155 and 156: up skilled birth attendance‖. The
- Page 157 and 158: Scaling up of the Navrongo service
- Page 159 and 160: conditions (Walt, Perera et al. 198
- Page 161 and 162: Figure 37 Critical success factors
- Page 163 and 164: Health system standards are explici
- Page 165 and 166: prevalence rate, however in order t
- Page 167 and 168: (Dieleman 2006) Selected key indica
- Page 169 and 170: In order to determine the answers t
- Page 171 and 172: Summary of findings This narrative
- Page 173 and 174: Health worker performance is theref
- Page 175 and 176: Discussion and Recommendations What
- Page 177 and 178: outlines how the HRH information ba
- Page 179 and 180: communities. A collaborative approa
- Page 181 and 182: Table 29 Examples of HRH performanc
- Page 183 and 184: Appendices Appendix 1. MDG5 Country
- Page 185 and 186: World Health Statistics http://www.
- Page 187 and 188: Appendix 3. Sources of all material
- Page 189 and 190: Data source Keywords used in search
- Page 191 and 192: Data source Keywords used in search
- Page 193 and 194: Data source Keywords used in search
- Page 195 and 196: Data source Keywords used in search
- Page 197: Data source Keywords used in search
- Page 201 and 202: Area Barriers & constraints in MNRH
- Page 203 and 204: Area Barriers & constraints in MNRH
- Page 205 and 206: Appendix 5 Literature that document
- Page 207 and 208: P a g e | 206
- Page 209 and 210: IMNCI PMTCT Perinatal Period Postna
- Page 211 and 212: Ambegaokar, M., Lush, L. (2004). "F
- Page 213 and 214: Barrett, B., J. Ladinsky, et al. (2
- Page 215 and 216: University South Africa with the Re
- Page 217 and 218: Cruse, D. (1997). Community Health
- Page 219 and 220: Elson, D., Evers, B. (1998). Sector
- Page 221 and 222: Flanagan, D., Williams, C., Mahler,
- Page 223 and 224: Greenwood, A. M., Bradley, A.K., By
- Page 225 and 226: Howard, G., Bogh, C., Goldstein, G.
- Page 227 and 228: Jhpeigo (1998). Participatory techn
- Page 229 and 230: Kroll, D., Dwyer, D. (1994). "Postn
- Page 231 and 232: Manandhar, D. S., D. Osrin, et al.
- Page 233 and 234: Morisky, D. E. (1985-86). "Evaluati
- Page 235 and 236: O‘Brien-Pallas, L., Irvine, D., P
- Page 237 and 238: Pfeiffer, J. and J. Pfeiffer (2003)
- Page 239 and 240: Replogle, J. (2007). "Training Trad
- Page 241 and 242: Shankar, A., S. Sebayang, et al. (2
- Page 243 and 244: Teela, K. C., L. C. Mullany, et al.
- Page 245 and 246: van Damm, W., et. al (2008). "Scali
- Page 247 and 248: WHO (2008). Global Standards for In
Appendix 4: Barriers <strong>and</strong> Constra<strong>in</strong>ts to <strong>HRH</strong> Practice<br />
Area Barriers & constra<strong>in</strong>ts <strong>in</strong> MNRH Reference<br />
Coverage<br />
Too few skilled personnel:<br />
Too few Nurses/midwives at community level<br />
Oversupply of VHW<br />
Lack of female providers<br />
<strong>in</strong>efficiently distributed <strong>in</strong> rural areas-poor skills mix<br />
High attrition / low retention rates (low pay + poor work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
conditions=migration, retirement, HIV, career change, move<br />
from rural areas, move to private sector)<br />
Absenteeism can prevent hir<strong>in</strong>g of other staff as the post is<br />
technically filled<br />
(Gere<strong>in</strong>, Green et al. 2006; WHO 2006; Henderson 2008; Dogba <strong>and</strong> Fournier<br />
2009)<br />
(Kwast 1991)<br />
(Matomora 1989)<br />
(Naisho 1982)<br />
(Olsen, Ndeki et al. 2005)<br />
(Ofosu-Amaah 1983; Pfeiffer <strong>and</strong> Pfeiffer 2003; Dovlo 2005; WHO 2005;<br />
Henderson 2008; Willis-Shattuck, Bidwell et al. 2008)<br />
(Berman 1984; Berman 1987; FIGO 2009)<br />
Policy & legislation<br />
Too much focus on Drs & nurses-other cadres need to be<br />
<strong>in</strong>cluded<br />
Lack of government policies & support<br />
CHW programs vertical not <strong>in</strong>tegrated<br />
Lack of <strong>in</strong>volvement of CHWs nurses & Midwives <strong>in</strong><br />
policy & plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
No laws concern<strong>in</strong>g solo practice of nurses<br />
Uneven en<strong>for</strong>cement of regulations<br />
Outlaw<strong>in</strong>g TBAs affected l<strong>in</strong>ks with the community & led<br />
to ext<strong>in</strong>ction of cultural support approaches<br />
Unregulated small cl<strong>in</strong>ics undertak<strong>in</strong>g surgery<br />
without appropriate <strong>in</strong>frastructure<br />
Use of employee facilities <strong>for</strong> private practice &<br />
personal ga<strong>in</strong><br />
(Kruk, Prescott et al. 2009)<br />
(S<strong>in</strong>gh 1994; Campos 2004; Haider, Adhish et al. 2008)<br />
(WHO 1989)<br />
(WHO 1989; WHO/SEARO 2003)<br />
(Heywood <strong>and</strong> Harahap 2009)<br />
(WHO/SEARO 2003)<br />
(Jenk<strong>in</strong>s 2003)<br />
(FIGO 2009)<br />
(Omaswa 2006)<br />
P a g e | 198