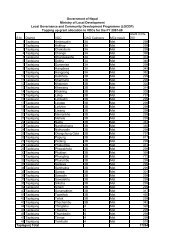
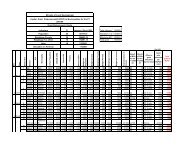
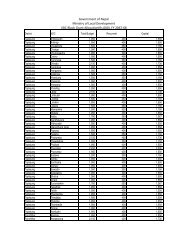
LGCDP M&E Framework
LGCDP M&E Framework
LGCDP M&E Framework
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Access to public goods/general<br />
Indicator: Average time for rural households to reach the nearest of 15 key facilities in<br />
minutes and hours<br />
Rationale: The indicator provides a broad overview of changes in access to public goods. It is an<br />
equally weighted average of 15 facilities (as tracked by the Nepal Living Standard Survey):<br />
primary school, health post, bus stop, paved road, dirt road (vehicle passable and<br />
impassable), local shop, haatbazar, market centre, agriculture centre, sajha/cooperatives,<br />
commercial bank, source of water, post office, telephone booth.<br />
Limits: • The indicator refers only to rural households. The data for both rural and urban<br />
together is currently not published.<br />
• Data for the indicator is very similar to the data for the poorest quintile of<br />
households. The reason can be that poor households tend to live in rural areas.<br />
• The indicator needs to be manually calculated based on the data published in the<br />
NLSS.<br />
• The interval between data collection of the Nepal Living Standard Survey is long<br />
with seven years. The next Living Standard Survey is planned for 2010.<br />
• The data is taken from the cross section (rather than from the panel) because it is<br />
available sooner. 2<br />
Baseline: 1 hour 59 minutes (2003/2004)<br />
Target: 1 hour 30 minutes (2012)<br />
Means of<br />
Nepal Living Standard Survey (cross section)<br />
Verification<br />
Frequency every 7 years<br />
Responsibility Central Bureau of Statistics<br />
Access to public goods/roads<br />
Indicator: % of rural households which have access to a dirt road (vehicle passable) within<br />
30 minutes<br />
Rationale: The construction of vehicle passable dirt roads is a typical service provided by local<br />
governments through <strong>LGCDP</strong>. This indicator focuses on the rural areas, where the gap is<br />
wider. The data refers to the time for one-way travel to the facility, irrespective of the<br />
mode of transport.<br />
Limits: • The interval between data collection of the Nepal Living Standard Survey is long<br />
with seven years. The next Living Standard Survey is planned for 2010.<br />
• To bridge the gap, the <strong>LGCDP</strong> Sample Surveys can collect data for this indicator<br />
in-between NLSS cycles. However, the data collected through these two tools<br />
might not be 100% comparable.<br />
Baseline: 67.6% (2003/2004)<br />
Target: 75% (2012)<br />
Means of<br />
Nepal Living Standard Survey (cross section) / <strong>LGCDP</strong> Sample Surveys<br />
Verification<br />
Frequency every 7 years / 2 years (2009, 2011, 2013)<br />
Responsibility Central Bureau of Statistics / M&E Section of MLD<br />
Indicator: Mean time taken by rural households to reach nearest dirt road (vehicle<br />
passable) in hours and minutes<br />
Rationale: The construction of vehicle passable dirt roads is a typical services provided by local<br />
governments through <strong>LGCDP</strong>. This indicator focuses on the rural areas, where the gap is<br />
wider (for urban areas, the average time is only 3 minutes). The data refers to the time for<br />
one-way travel to the facility, irrespective of the mode of transport.<br />
Limits: • see above<br />
Baseline: 3 hours 7 minutes (2003/2004)<br />
Target: 2 hours 30 minutes (2012)<br />
Means of<br />
Nepal Living Standard Survey (cross section) / <strong>LGCDP</strong> Sample Surveys<br />
Verification<br />
Frequency every 7 years / 2 years (2009, 2011, 2013)<br />
Responsibility Central Bureau of Statistics / M&E Section of MLD<br />
2 Cross section Living Standard data is published sooner than the data from the household panel. The cross section data from<br />
the NLSS 2003/2004, for example, was published in December 2004, while the analysis of panel households was published only<br />
in March 2006.<br />
5