A Method for Data Interaction of Large-Scale Distributed Battle ...
A Method for Data Interaction of Large-Scale Distributed Battle ...
A Method for Data Interaction of Large-Scale Distributed Battle ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
divided battlefield entity behaviors into six types: command<br />
and control entity, sensor entity, resource management entity<br />
and other entity. Based on the roles which the entities play in<br />
in<strong>for</strong>mation actions and the types <strong>of</strong> “Produced / Consumed”<br />
data, they divided entity into four types: plat<strong>for</strong>m entity,<br />
cognizing entity, communication entity and command entity.<br />
In a word, the purpose <strong>of</strong> sorting is to organize data<br />
interaction in class <strong>for</strong>m.<br />
1) Plat<strong>for</strong>m class entity: They indicate war plat<strong>for</strong>ms<br />
such as warship, plane, missile and ect. In simulation these<br />
entity main task is to simulate its behaviors such as plat<strong>for</strong>m<br />
maneuvering and etc. It mainly create the position, state and<br />
maneuvering and other data.<br />
2) Cognizing class entity: It also called sensor entity<br />
refers to various sensors with capabilities <strong>of</strong> detection,<br />
including radar, sonar, electronic surveillance and other<br />
equipment. In Simulation, the main task <strong>of</strong> such nodes is to<br />
<strong>for</strong>m a detection result in<strong>for</strong>mation fighting plat<strong>for</strong>m based<br />
on the objective situation in<strong>for</strong>mation generated by the war<br />
plat<strong>for</strong>m node. They subdivided into two types <strong>of</strong> cognizing<br />
entities: active and passive sensing entities. Active sensing<br />
entities affect objective environment when they are<br />
detecting, such as radar; while passive sensing entities work<br />
through analyzing objective environmental changes, such as<br />
electronic surveillance equipment.<br />
3) Command class entity: It refers to all kinds and levels<br />
<strong>of</strong> ommand posts such as <strong>for</strong>mate command posts, campaign<br />
group command posts, war zone command posts and so on.<br />
In simulation, the task <strong>of</strong> such nodes is to receive<br />
transmitted data from communication nodes and <strong>for</strong>m a<br />
decision-making situation <strong>for</strong> the commander。<br />
4) Communication class entity: It refers to the various<br />
communication links <strong>for</strong> data transmission, including cable<br />
links, satellite communication links, data links and so on. It<br />
is responsible <strong>for</strong> transferring data from one/several entities<br />
to another/several e entities. In simulation, such nodes’ task<br />
is transferring the detect result in<strong>for</strong>mation from the sensor<br />
nodes to the command post nodes and transferring situation<br />
in<strong>for</strong>mation between the command post node. For example,<br />
it transfers cognizing in<strong>for</strong>mation from a radar entity to a<br />
command entity. Modeling concerns communication<br />
bandwidth, communication capabilities and so on.<br />
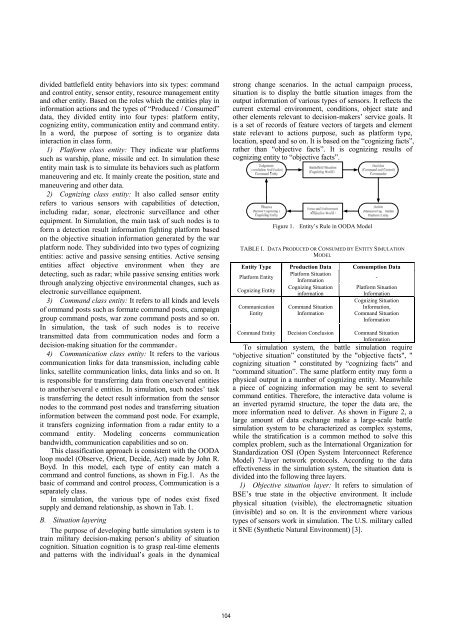
This classification approach is consistent with the OODA<br />
loop model (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act) made by John R.<br />
Boyd. In this model, each type <strong>of</strong> entity can match a<br />
command and control functions, as shown in Fig.1. As the<br />
basic <strong>of</strong> command and control process, Communication is a<br />
separately class.<br />
In simulation, the various type <strong>of</strong> nodes exist fixed<br />
supply and demand relationship, as shown in Tab. 1.<br />
B. Situation layering<br />
The purpose <strong>of</strong> developing battle simulation system is to<br />
train military decision-making person’s ability <strong>of</strong> situation<br />
cognition. Situation cognition is to grasp real-time elements<br />
and patterns with the individual’s goals in the dynamical<br />
strong change scenarios. In the actual campaign process,<br />
situation is to display the battle situation images from the<br />
output in<strong>for</strong>mation <strong>of</strong> various types <strong>of</strong> sensors. It reflects the<br />
current external environment, conditions, object state and<br />
other elements relevant to decision-makers’ service goals. It<br />
is a set <strong>of</strong> records <strong>of</strong> feature vectors <strong>of</strong> targets and element<br />
state relevant to actions purpose, such as plat<strong>for</strong>m type,<br />
location, speed and so on. It is based on the “cognizing facts”,<br />
rather than “objective facts”. It is cognizing results <strong>of</strong><br />
cognizing entity to “objective facts”.<br />
Figure 1. Entity’s Rule in OODA Model<br />
TABLE I. DATA PRODUCED OR CONSUMED BY ENTITY SIMULATION<br />
MODEL<br />
Entity Type Production <strong>Data</strong> Consumption <strong>Data</strong><br />
Plat<strong>for</strong>m Entity<br />
Plat<strong>for</strong>m Situation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
-<br />
Cognizing Entity<br />
Cognizing Situation Plat<strong>for</strong>m Situation<br />
in<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
Communication<br />
Entity<br />
Command Situation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
Cognizing Situation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation,<br />
Command Situation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
Command Entity Decision Conclusion Command Situation<br />
In<strong>for</strong>mation<br />
To simulation system, the battle simulation require<br />
“objective situation” constituted by the "objective facts", "<br />
cognizing situation " constituted by “cognizing facts” and<br />
“command situation”. The same plat<strong>for</strong>m entity may <strong>for</strong>m a<br />
physical output in a number <strong>of</strong> cognizing entity. Meanwhile<br />
a piece <strong>of</strong> cognizing in<strong>for</strong>mation may be sent to several<br />
command entities. There<strong>for</strong>e, the interactive data volume is<br />
an inverted pyramid structure, the toper the data are, the<br />
more in<strong>for</strong>mation need to deliver. As shown in Figure 2, a<br />
large amount <strong>of</strong> data exchange make a large-scale battle<br />
simulation system to be characterized as complex systems,<br />
while the stratification is a common method to solve this<br />
complex problem, such as the International Organization <strong>for</strong><br />
Standardization OSI (Open System Interconnect Reference<br />
Model) 7-layer network protocols. According to the data<br />
effectiveness in the simulation system, the situation data is<br />
divided into the following three layers.<br />
1) Objective situation layer: It refers to simulation <strong>of</strong><br />
BSE’s true state in the objective environment. It include<br />
physical situation (visible), the electromagnetic situation<br />
(invisible) and so on. It is the environment where various<br />
types <strong>of</strong> sensors work in simulation. The U.S. military called<br />
it SNE (Synthetic Natural Environment) [3].<br />
104