Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
©t t2r091r3e mKuuotNaQ jSYoRfHt1weaArve0 uL3LfCq.7 e WAhlclN 7r9iugrhUt0sW WrGe6s7eMrvvyeadg.J i nMla1diei pwOibtPho bIXnSf8iZn5iItAe1 iCVaglnctuxlnujsm.S Worksheet by <strong>Kuta</strong> <strong>Software</strong> LLC<br />
<strong>Kuta</strong> <strong>Software</strong> - Infinite Calculus<br />
Name___________________________________<br />
L'Hôpital's Rule<br />
Evaluate each limit using L'Hôpital's Rule.<br />
Date________________ Period____<br />
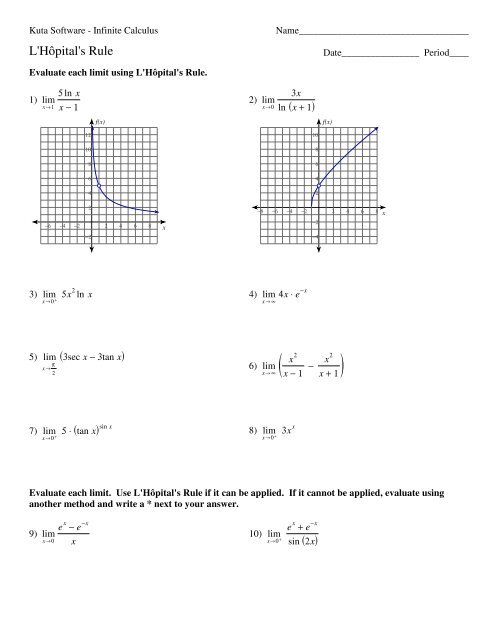
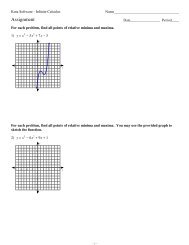
1) lim<br />
x →1<br />
5 ln x<br />
x − 1<br />
2) lim<br />
x →0<br />
3x<br />
ln (x + 1)<br />
f(x)<br />
f(x)<br />
12<br />
10<br />
10<br />
8<br />
8<br />
6<br />
6<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2<br />
2<br />
−6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8<br />
−2<br />
x<br />
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8<br />
−2<br />
−4<br />
x<br />
3) lim 5x 2 ln x 4) lim 4x ⋅ e −x<br />
x →0 + x → ∞<br />
5) lim<br />
x → π 2<br />
(3sec x − 3tan x)<br />
( 6) lim<br />
x2<br />
x → ∞ x − 1 − x 2<br />
) x + 1<br />
7) lim 5 ⋅ (tan x) sin x 8) lim<br />
x →0 + x →0 +<br />
3x x<br />
Evaluate each limit. Use L'Hôpital's Rule if it can be applied. If it cannot be applied, evaluate using<br />
another method and write a * next to your answer.<br />
9) lim<br />
x →0<br />
e x − e −x<br />
x<br />
10) lim<br />
x →0 +<br />
e x + e −x<br />
sin (2x)
©C o2E0O1Q37 BKsuEt2az cSBoefAtawmaKrcel pLqLHCt.9 F XAdlwl4 5rkiUgVhAt4sB jrWessmedrVvje9d0.1 1 nMjajdIeX zw7iwtUho lIPngfLienDiqtweB NCeanlzcHu0lCuwsY.k Worksheet by <strong>Kuta</strong> <strong>Software</strong> LLC<br />
<strong>Kuta</strong> <strong>Software</strong> - Infinite Calculus<br />
Name___________________________________<br />
L'Hôpital's Rule<br />
Evaluate each limit using L'Hôpital's Rule.<br />
Date________________ Period____<br />
1) lim<br />
x →1<br />
5 ln x<br />
x − 1<br />
2) lim<br />
x →0<br />
3x<br />
ln (x + 1)<br />
f(x)<br />
f(x)<br />
12<br />
10<br />
10<br />
8<br />
8<br />
6<br />
6<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2<br />
2<br />
−6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8<br />
−2<br />
x<br />
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8<br />
−2<br />
−4<br />
x<br />
5<br />
3<br />
3) lim<br />
x →0 +<br />
0<br />
5x 2 ln x<br />
4) lim 4x ⋅ e −x<br />
x → ∞<br />
0<br />
5) lim<br />
x → π 2<br />
0<br />
(3sec x − 3tan x)<br />
( 6) lim<br />
x2<br />
x → ∞ x − 1 − x 2<br />
) x + 1<br />
2<br />
7) lim<br />
x →0 +<br />
5 ⋅ (tan x) sin x<br />
8) lim<br />
x →0 +<br />
3x x<br />
5<br />
3<br />
Evaluate each limit. Use L'Hôpital's Rule if it can be applied. If it cannot be applied, evaluate using<br />
another method and write a * next to your answer.<br />
9) lim<br />
x →0<br />
2<br />
e x − e −x<br />
x<br />
10) lim<br />
x →0 +<br />
∞ *<br />
e x + e −x<br />
sin (2x)<br />
Create your own worksheets like this one with Infinite Calculus. Free trial available at <strong>Kuta</strong><strong>Software</strong>.com