Supporting fulcrum axis
Supporting fulcrum axis
Supporting fulcrum axis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
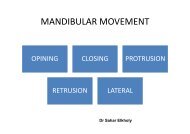
Definition<br />
Denture relation about<br />
an <strong>axis</strong><br />
Factors influencing<br />
effectiveness of<br />
indirect retainers<br />
Forms of indirect<br />
retainer
It is the component of RPD that<br />
assists direct retainers in<br />
preventing displacement of the<br />
distal extension denture base by<br />
creating resistance on the<br />
opposite side of the <strong>fulcrum</strong> line
It is the line about which the distal<br />
extension partial denture tends to<br />
rotate towards or away from the<br />
tissues.<br />
This <strong>axis</strong> is an imaginary line passing<br />
through the teeth(occlusal rests) and<br />
direct retainers( retentive tips)
The <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong> passes between<br />
the two main occlusal rests<br />
called (<strong>Supporting</strong> <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong>)<br />
This movements is resisted by<br />
the ridge& its overlying mucosa
The <strong>fulcrum</strong> <strong>axis</strong> passes between<br />
most posterior and bilaterally<br />
located retentive terminals of<br />
primary direct retainer<br />
It is called (Retentive <strong>fulcrum</strong><br />
<strong>axis</strong>)<br />
This movements is resisted by<br />
Indirect retainers
1. Distance between the <strong>fulcrum</strong> line & the<br />
indirect retainer<br />
The greater the distance the more the<br />
effective will be the indirect retainer<br />
The indirect retainer must be<br />
perpendicular& midway to the <strong>fulcrum</strong><br />
<strong>axis</strong>
2.Effectiveness of tooth support<br />
Indirect retainer must be placed on a<br />
definite rest seat.<br />
It should be perpendicular to the<br />
long <strong>axis</strong> of tooth upon which it rest<br />
to prevent tooth movement<br />
Weak teeth should not be used to<br />
support indirect retainer
3.Effectiveness of direct retainer<br />
Unless the principle occlusal rests<br />
are held in their seats by the action<br />
of the direct retainers<br />
If displacement of the base away<br />
from the tissues will occur, Indirect<br />
retainer does not resist<br />
displacement
4.Rigidity of connectors supporting<br />
Indirect retainers<br />
All connectors must be rigid, to<br />
allow indirect retainer to be in<br />
function<br />
5. Indirect retainer must be rigid<br />
If arm of indirect retainer were to<br />
flex indirect retainer will not be<br />
effective
• - Occlusal rests .<br />
• - Canine extension from occlusal<br />
rest.<br />
• - Cingulum rest.<br />
• - Continuous bar<br />
• - Lingual plate
1. -Indirect retention.<br />
2. - Distribution of load over many teeth.<br />
3. -Give strength and rigidity to the<br />
appliance.<br />
4. "-Can form point of attachment for incisal<br />
rests
• - Palatally or lingually inclined teeth.<br />
• - Short clinical crown.
• Poor tolerance.<br />
• Interference with speech when used<br />
in the upper jaw.
-Palatal arm.<br />
-Anterior palatal bar<br />
-Posterior palatal bar<br />
-Extension of the palatal plate<br />
(horse shoe).