Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The Eurosystem Secures Price Stability<br />
Euro Area Key Interest<br />
Rates Unchanged in <strong>2004</strong><br />
Following two years of subdued<br />
growth (2002: 0.9%; 2003: 0.5%),<br />
euro area GDP expanded by 2.1%<br />
in <strong>2004</strong>. The growth momentum that<br />
gained a foothold in the second half of<br />
2003 was maintained at the beginning<br />
of <strong>2004</strong> but subsequently dampened<br />
by surging oil prices in the second<br />
half. Investment remained moderate<br />
throughout <strong>2004</strong>. Despite low interest<br />
rates and a pickup in profitability,<br />
investment in plant and equipment<br />
merely edged up. Construction investment,<br />
in fact, even diminished<br />
marginally. While consumer spendingpickedupsomewhattowardthe<br />
end of the year, it provided hardly<br />
any impulses. The revival in world<br />
trade lifted AustriaÕs current account<br />
surplus slightly compared with 2003,<br />
bringing it to 0.5% of GDP. The upturn<br />
hardly had a perceptible impact<br />
on the labor market yet in <strong>2004</strong>: Employment<br />
rose by 0.5% and unemployment<br />
persisted at 8.9% in <strong>2004</strong>.<br />
Euro area inflationary pressure<br />
remainedsubduedeventhoughdemand<br />
recovered in the first half of<br />
<strong>2004</strong>, above all because wage in-<br />
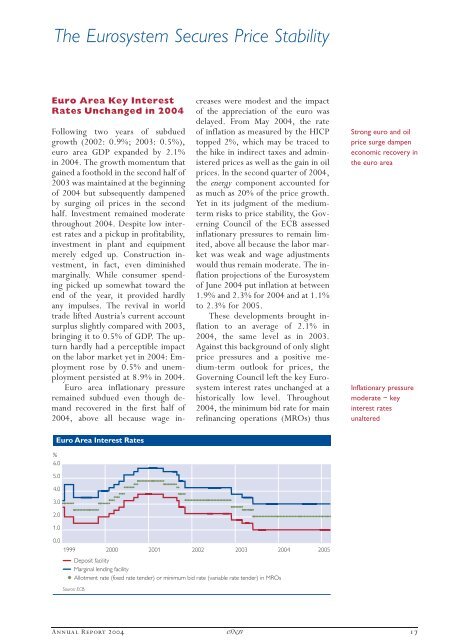
Euro Area Interest Rates<br />
%<br />
6.0<br />
5.0<br />
4.0<br />
3.0<br />
2.0<br />
1.0<br />
creases were modest and the impact<br />
of the appreciation of the euro was<br />
delayed. From May <strong>2004</strong>, the rate<br />
of inflation as measured by the HICP<br />
topped 2%, which may be traced to<br />
the hike in indirect taxes and administeredpricesaswellasthegaininoil<br />
prices. In the second quarter of <strong>2004</strong>,<br />
the energy component accounted for<br />
as much as 20% of the price growth.<br />
Yet in its judgment of the mediumterm<br />
risks to price stability, the Governing<br />
Council of the ECB assessed<br />
inflationary pressures to remain limited,<br />
above all because the labor market<br />
was weak and wage adjustments<br />
would thus remain moderate. The inflation<br />
projections of the Eurosystem<br />
of June <strong>2004</strong> put inflation at between<br />
1.9% and 2.3% for <strong>2004</strong> and at 1.1%<br />
to 2.3% for 2005.<br />
These developments brought inflation<br />
to an average of 2.1% in<br />
<strong>2004</strong>, the same level as in 2003.<br />
Against this background of only slight<br />
price pressures and a positive medium-term<br />
outlook for prices, the<br />
Governing Council left the key Eurosystem<br />
interest rates unchanged at a<br />
historically low level. Throughout<br />
<strong>2004</strong>, the minimum bid rate for main<br />
refinancing operations (MROs) thus<br />
0.0<br />
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 <strong>2004</strong><br />
Deposit facility<br />
Marginal lending facility<br />
Allotment rate (fixed rate tender) or minimum bid rate (variable rate tender) in MROs<br />
Source: ECB.<br />
2005<br />
Strong euro and oil<br />
price surge dampen<br />
economic recovery in<br />
the euro area<br />
Inflationary pressure<br />
moderate — key<br />
interest rates<br />
unaltered<br />
<strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2004</strong> ×<br />
17