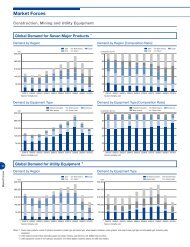
Annual Report 2007 - Komatsu
Annual Report 2007 - Komatsu
Annual Report 2007 - Komatsu
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS<br />
Service revenues from repair and maintenance and from transportation<br />
are recognized at the completion of service delivery.<br />
Revenues from long-term fixed price maintenance contracts are<br />
recognized ratably over the contract period.<br />
Certain of consolidated subsidiaries rent construction equipments<br />
to customers. Rent revenue is recognized on a straight-line<br />
basis over the rental period.<br />
Revenues are recorded net of discounts.<br />
(9) Income Taxes<br />
In accordance with SFAS No. 109, “Accounting for Income<br />
Taxes,” income taxes are accounted for under the asset and<br />
liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized<br />
for the future tax consequences attributable to differences<br />
between the financial statement carrying amounts of<br />
existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and<br />
operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets<br />
and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to<br />
apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary<br />
differences and carryforwards are expected to be realized or<br />
settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a<br />
change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that<br />
includes the enactment date.<br />
<strong>Komatsu</strong> uses a specific identification method to release the<br />
residual tax effects associated with components of accumulated<br />
other comprehensive income (loss) resulting from a change in<br />
tax law or rate.<br />
(10) Product Warranties<br />
<strong>Komatsu</strong> establishes a liability for estimated product warranty<br />
cost after sales. Estimates for accrued product warranty cost<br />
are primarily based on historical experience and are classified as<br />
other current liabilities.<br />
(11) Pension and Retirement Benefits<br />
The defined benefit plans are accounted for in accordance with<br />
SFAS No. 87, “Employers’ Accounting for Pensions” and SFAS<br />
No. 158, ”Employer’s Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension<br />
and Other Postretirement Plans-an amendment of SFAS No. 87,<br />
88, 106 and 132(R)” except for certain subsidiaries’ pension<br />
plans which in the aggregate are not significant. Certain domestic<br />
subsidiaries also have local severance payment plans under<br />
which accrued severance liabilities are stated on a vested benefit<br />
obligation basis, which is the amount required to be paid if all<br />
eligible employees voluntarily terminated their employment as of<br />
the balance-sheet date.<br />
Amortization of actuarial net gain or loss is included as a<br />
component of the Company’s net periodic pension cost for a<br />
year if, as of the beginning of the year, that unrecognized net<br />
gain or loss exceeds 10 percent of the greater of (1) the projected<br />
benefit obligation or (2) the fair value of that plan’s assets.<br />
In such case, the amount of amortization recognized is the<br />
resulting excess divided by average remaining service period of<br />
active employees expected to receive benefits under the plan.<br />
The expected return on plan assets is determined based on the<br />
historical long-term rate of return on plan assets. The discount<br />
rate is determined based on the rates of return of high-quality<br />
fixed income investments currently available and expected to be<br />
available during the period to maturity of the pension benefits.<br />
(12) Stock-Based Compensation<br />
Effective April 1, 2006, <strong>Komatsu</strong> adopted SFAS No. 123 (revised<br />
2004), “Share-Based Payment” (“SFAS No. 123R”) for<br />
the year ended March 31, <strong>2007</strong> using the modified prospective<br />
method. In accordance with SFAS No. 123R, <strong>Komatsu</strong> recognizes<br />
compensation expense using the fair value method.<br />
Compensation expense is measured at grant-date fair value of<br />
the stock option and charged to expense over the vesting period.<br />
For the years ended March 31, 2006 and 2005, <strong>Komatsu</strong><br />
had applied the intrinsic value method under Accounting<br />
Principles Board (APB) Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock<br />
Issued to Employees”. No compensation expense was recognized<br />
as the exercise price was at least equal to the market<br />
price on the date of grant.<br />
The following table summarizes pro forma net income of<br />
<strong>Komatsu</strong> if compensation expense for stock options granted<br />
under the plan had been determined in accordance with the<br />
fair value based method prescribed by SFAS No. 123R for the<br />
years ended March 31, 2006 and 2005:<br />
Millions of yen<br />
2006 2005<br />
Net income, as reported ¥114,290 ¥59,010<br />
Compensation expense 699 256<br />
Pro forma net income 113,591 58,754<br />
Yen<br />
Net income per share, basic and diluted: 2006 2005<br />
Basic earnings per share As reported ¥ 115.13 ¥ 59.51<br />
Pro forma 114.42 59.25<br />
Diluted earnings per share As reported 114.93 59.47<br />
Pro forma 114.23 59.21<br />
57 <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2007</strong>