BE Mechanical 2003 Structure - K. K. Wagh Education Society
BE Mechanical 2003 Structure - K. K. Wagh Education Society
BE Mechanical 2003 Structure - K. K. Wagh Education Society
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
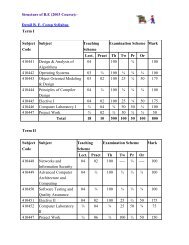
B.E. <strong>Mechanical</strong> <strong>2003</strong> <strong>Structure</strong> (w.e.f. July – 2006)<br />
FIRST TERM<br />
CODE SUBJECT TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME<br />
Lect. Pract/Dwg Paper TW Oral Pr Tota<br />
402041 <strong>Mechanical</strong> System Design 4 2 100** - 50 - 150<br />
402042 Dynamics of Machinery * 4 2 100 25 50 - 175<br />
402043 Mechatronics* 4 2 100 25 50 - 175<br />
402044 Gas Turbines & Jet Propulsion 4 - 100 - - - 100<br />
402045 Elective I 4 - 100 - - - 100<br />
402046 Project Work - 2 - - - - -<br />
Total of First Term 20 8 500 50 150 - 700<br />
SECOND TERM<br />
CODE SUBJECT TEACHING<br />
SCHEME<br />
EXAMINATION SCHEME<br />
Lect. Pract/Dwg Paper TW Oral Pr Tota<br />
402046 Project Work - 6 - 100 100 - 200<br />
402047 CAD/CAM & Automation* 4 2 100 25 50 - 175<br />
402048 Power Plant Engineering 4 2 100 25 50 - 175<br />
402049 Industrial Fluid Power 4 2 100 - 50 - 150<br />
402050 Elective II 4 - 100 - - - 100<br />
Total of First Term 16 12 400 150 200 - 750
Elective I<br />
Elective II<br />
402045 Product Design & Development 402050 Robotics<br />
402045 Non-Conventional Production Processes 402050 Computational Fluid Dynamics<br />
402045 Alternative Energy Sources 402050 Energy Conservation<br />
402045 Kinematic Analysis & Synthesis 402050 Rapid Prototyping<br />
402045 Operations Research 411050 Reliability Engineering<br />
402045 Costing & Cost control 402050 Automobile Engineering<br />
* Common with <strong>Mechanical</strong> sandwich course<br />
** Theory paper of 4 hours duration.<br />
Detailed Syllabus:<br />
(402041): Machine Design-III<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Drawing: 2 Hrs/Week (4 Hrs duration)<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
T/W: 25 Marks<br />
Oral: 50 Marks<br />
1. Bevel Gears:<br />
Straight tooth bevel gear terminology and geometric relationship-formative<br />
number of teeth-force analysis Design criteria of bevel gears-Beam and wear<br />
strengths-Dynamic tooth load-Effective load-Design of straight tooth bevel gears.<br />
Selection of materials for bevel gears. Introduction to design of spiral bevel gears
and hypoid gears and comparison with straight tooth bevel gears. Lubrication and<br />
Mounting of bevel gears. Bearing reactions. Types of failures in bevel gears.<br />
2. Worm gears:<br />
Worm and worm gear terminology and geometrical relationship-Types of worm<br />
and worm gears. Standard dimensions-force analysis of worm gear drive- Friction<br />
in Worm gears, efficiency-Worm and Worm wheel material-strength and wear<br />
ratings of worm gears- Thermal consideration in worm gear drive-Design of<br />
worm gear drive as per IS 7443 Types of failures in worm gearing. Methods of<br />
lubrication and selection of bearings.<br />
3. Cylinders and pressure vessels:<br />
Thick and thin cylinders-Thin cylindrical and spherical vessels-Lame’s equation-<br />
Clavarino’s and Birnie’s equations-Design of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders-<br />
Auto frettage and compound cylinders-Gasketed joints in cylindrical vessels.<br />
Modes of failures in pressure vessels.<br />
Unfired pressure vessels-Classification of pressure vessels as per I. S.: 2825-<br />
categones and types of welded joints-weld joint efficiency-Corrosion, erosion and<br />
protection of vessels, stresses induced in pressure vessels, materials of<br />
construction. Thickness of cylindrical and spherical shells and design of end<br />
closures as per code-Nozzles and Openings in pressure vessels-Reinforcement of<br />
openings in shell and end closures. Area compensation method-Types of vessel<br />
supports.<br />
4. Flywheel:<br />
Fundamental equation of motion-torque analysis-disk and rimmed flywheels-<br />
Stresses in flywheel rim and spokes-Design of disc and rimmed flywheels for<br />
various applications. Standard dimensions of flywheels.
5. Statistical consideration in design:<br />
Frequency distribution-Histogram and frequency polygon-Normal distribution-<br />
Units of measurement of central tendency and dispersion-Standard variablepopulation<br />
combinations- Design and natural tolerances-Design for assembly-<br />
Statistical analysis of tolerances-<strong>Mechanical</strong> reliability and factor of safety.
6. Design for manufacture:<br />
General principles of design for manufacture and assembly (DFM & DMFA).<br />
Principles of design of castings and forgings-Design for machining-Design for<br />
powder metallurgy-Design for welding.<br />
7. Optimum design:<br />
Objectives of optimum design- Johnson’s method of Optimum Design (MOD).<br />
Adequate and optimum design. Primary, subsidiary and limit equations- Optimum<br />
design with normal specifications of simple machine elements like tension bar,<br />
transmission shaft, helical spring-Introduction to optimum design with redundant<br />
specifications.<br />
8. Aesthetic and ergonomic considerations in design of products:<br />
Basic types of product forms-Designing for appearance-Shape, features, materials<br />
and finishes, proportions, symmetry, contrast etc.-Morgan’s colour code,<br />
Ergonomic considerations-Relation between man, machine and environmental<br />
factors. Design of displays and controls. Practical examples of products or<br />
equipments using ergonomic and aesthetic design principles.<br />
9. Design for quality assurance:<br />
Characteristics of product quality-Fitness for use-manufacturability-Reliability-<br />
Maintainability Safety-life cycle costs-Introduction to I.S.O. 9000 series-Design<br />
requirements of Clause 4.4. of I.S.O. 9001- Design input, output and verification-<br />
Design review and changes.<br />
Term Work:<br />
1. Term work shall consists of ONE design project. The design project shall<br />
consist of two imperial size sheets- one involving assembly drawing with a
part list and overall dimensions and the other sheet involving drawings of<br />
individual components, manufacturing tolerances, surface finish symbols and<br />
geometric tolerances should be specified so as to make it working drawing. A<br />
design report giving all necessary calculations of the design of components<br />
and assembly should be submitted in a separate file. Projects shall be in the<br />
form of design of mechanical systems involving design of Bevel/Worm gear<br />
box or design of pressure vessel using IS 2825 code.<br />
Three assignments based on any one of the following topics from each of the<br />
three groups.<br />
Group I : Sr. No.1 to 4, group II : Sr. No.5 to 8, Group III : Sr. No.9 to 12.<br />
1. Modem engineering materials and their applications/ evaluation methods for<br />
material selection.<br />
2. Piping design.<br />
3. Product design involving ergonomic and aesthetic considerations.<br />
4. Cost estimation of a product.<br />
5. Value engineering.<br />
6. Concurrent engineering.<br />
7. Reverse engineering.<br />
8. Design for manufacturing and assembly.<br />
9. Designing for environment.<br />
10. Designs in relation to patents, trade mark and copy right..<br />
11. Requirements of design office as per 1.5.0. 9000.<br />
12. Communicating the design.<br />
(Note: The above topics are restricted to assignment only and do not form part of<br />
syllabus of theory paper).<br />
Recommendation
As far as possible, preference should be given to prepare drawing sheet using<br />
computer. The manual drawing method using drawing board should be<br />
progressively discarded.<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Shigley J. E. and Mischke C. R. “<strong>Mechanical</strong> Engineering Design”,<br />
McGraw Hill Pub. Co. Ltd.<br />
2. Spotts M. F. and Shoup T. E.-“Design of Machine Elements”, Prentice Hall<br />
International.<br />
3. Bhandari V. B. “Design of machine Elements”, Tata- McGraw Hill Pub.<br />
Co. Ltd.<br />
4. Black P. H. and O. Eugene Adams,-“McGraw Hill Book Co. Inc.<br />
5. William C. Orthwein-“Machine Components Design”, West-Publishing<br />
Co. and Jail” I Pub. House.<br />
6. “Design Data” P. S. G. College of Technology, Coimbatore.<br />
7. Juvinal R. C. “Fundamentals of Machine Components . Design”,John<br />
Wiley and Sons.<br />
8. Hall A. S. Holowenko A. R. and Laughlin H. G. “Theory and problems of<br />
Machine Design”,Schaum’s outline series.<br />
9. I.S: 2825 Code for unfired pressure vessels.<br />
10. I.S: 7443-Method for load rating of worm gears.<br />
11. I.S. O. 9001 Quality systems model for quality assurance in<br />
Design/Development, Production Installation and Servicing.<br />
12. Johnson R. C.-<strong>Mechanical</strong> Design Synthesis with optimization applications,<br />
Von-Nostrand-Reynold Pub.<br />
13. Dieter G, E.-Engineering Design-McGraw Hill Inc.
(402042): Fluid Machinery<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Practicals: 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: 100 Marks<br />
Practicals : 50 Marks<br />
1. Momentum equation and its application:<br />
Impulse momentum principle, fixed and moving flat plates and curved vanes,<br />
series of plates and vanes, water wheels, Velocity triangles and their analysis,<br />
work done, efficiency etc.<br />
2. Hydrodynamic machine:<br />
Classification, general theory, centrifugal heads and fundamental equations,<br />
Euleren, degree of reaction etc, head on machines, various efficiencies, condition<br />
for maximum hydraulic efficienty.<br />
3. Impulse turbine:<br />
Main components and constructional features of Pelton wheel, velocity diagrams<br />
and analysis, number of buckets, jets, non-dimensional parameters like speed<br />
ratio, jet ratio, flow ratio, condition for maximum efficienty.<br />
4. Reaction Turbines:
Types of reaction turbines Francis, Kaplan, Deriaz, reversible, low head turbines,<br />
Main components and constructional features, draft tube, types, efficiency,<br />
limiations for use of draft tubes, cavitation.<br />
5. Governing performance and selection:<br />
Governing mechanism for Francis, Kaplan turbine, pelton wheel; safety devices<br />
of turbine, pressure regulators, surge tanks, forebay. Performance of water<br />
turbines: types of characteristic curves and related terms unit quantities specific<br />
speed and shape of runner. Selection of turbine considering various factors.<br />
6. Hydrodynamic Pumps:<br />
Classification, Components of centrifugal pumps. Its installation. Various terms<br />
associated with centrifugal pump, various heads, velocity triangles and their<br />
analysis, effect of outlet blade angle, cavitation, NPSH, Thomas cavitation factor,<br />
priming of punps, installation, specific speed and pump classification.<br />
Performance characteristics of centrifugal pump. Axial thrust, maintenance,<br />
troubles and remedies, series and parallel operation of pumps, system resistance<br />
curve, pump system interaction, water hammer problem in pumping system.<br />
7. Similarity (applied to turbines and pumps) :<br />
Model testing, scale effect.<br />
8. Special pumps:<br />
Airlift pump, Hydraulic ram, deep well pump, submersible pumps, vertical<br />
turbine pump, regenerative pump, screw pump, gear pump, reciprocating pump.<br />
Jet pumps, construction, principle of operation, energy analysis, performance<br />
characteristics.
9. Fluid coupling and torque converter:<br />
Construction, working, characteristics curves, applications.<br />
10. Hydraulic devices:<br />
accumulator, intensifier, press, jack, lifts, cranes etc.<br />
11. Hydro-Electric Plants:<br />
Classification, layout, components, Pump storage plants.<br />
List of Experiments<br />
Minimum 8 experiments shall be performed out of which experiments at serial<br />
number I and 2 and two experiments out of Sr. No.5, 6 and 7 are compulsory.<br />
Record of 8 experiments shall be submitted in the form of journal.<br />
1. Study and trial on a centrifugal pump to plot operating and variable speed<br />
characteristics.<br />
2. Study and trial on a gear pump and plotting of operating characteristics.<br />
3. Study and demonstration of different non conventional pumps such as air lift<br />
pump, jet pump, reciprocating pump, deepwell pump, hyd-ram etc.<br />
4. Verification of impulse momentum principle using flat, inclined and curved<br />
plates.<br />
5. Study and trial on a Pelton wheel and plotting of operating characteristics.<br />
6. Study and trial on a Francis turbine and plotting of main/operating characteristics.<br />
7. Study and trial on a Kaplan turbine and plotting of main/operating characteristics.<br />
8. Study and trial on a torque converter and plotting operating characteristics.<br />
9. Study of hydraulic accumulator, intensifier and press. .<br />
10. Visit to a Hydraulic electric power station and writing a report based on the visit.
11. Design of a complete pumping system installation using standard tables, charts<br />
supplied by pump manufactures.<br />
Assignments (Any Two)<br />
1. Cavitation and NPSH characteristics of centrifugal pump.<br />
2. Fault detection and remedial measures in pump operations.<br />
3. Use of Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. S. Ananthswamy, “Fundamentals on Hydraulic Machinery”, United Book<br />
Corporation, Pune.<br />
2. V. P. Vasandani, “Theory of Hydraulic machinery”, Khanna Publishers, Delhi.<br />
3. Dr. J. Lal, “Hydraulic Machines”, Metropolitan Book Co. Pvt. Ltd., Delhi.<br />
4. Karassik, “Hand Book of Pumps”, Tata McGraw Hills Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
5. R. K. Srivastava, Critical Aspects in Rotodynamic . Pumps and Systems, Techno<br />
Economic Research Institution, New Delhi.
(402043): Applied Thermodynamics –III<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Practicals : 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
Practicals: 50 Marks<br />
T/W: 25 Marks<br />
1. Compressible Fluid Flow:<br />
Static and stagnation properties, one-dimensional isentropic flow, property<br />
relations for isentropic flow.<br />
2. Nozzles:<br />
Flow of fluids through nozzle, subsonic, supersonic nozzles, and diffusers,<br />
continuity equation, variation of velocity, area and specific volume, mass of<br />
discharge through nozzle, maximum discharge and critical pressure ratio,<br />
chocking of nozzle, effect of friction, nozzle efficiency, velocity coefficients,<br />
steam nozzles, supersaturated flow, effect of variation in back pressure on flow<br />
characteristics.<br />
3. Steam Turbine:<br />
Types, constructional details, impulse turbine compounding of turbines, velocity<br />
diagrams, output, efficiency, effect of blade speed ratio on efficiency for impulse<br />
and reaction turbines, losses in turbines, reaction turbines-velocity diagrams,<br />
degree of reaction, reheat factor, stage efficiency, overall efficiency,<br />
constructional features of blades, governing of turbines, selection of turbines for
various applications, types of seals and packings to reduce leakage and lossed in<br />
turbines.<br />
4. Condensers:<br />
Necessity of condensers, types of condensers, Dalton’s law of partial pressures,<br />
condenser , vacuum and vacuum. Efficiency, condenser efficiency, air pumps,<br />
capacity of air extraction pumps, types of cooling towers, cooling water<br />
requirements.<br />
5. Gas Turbines:<br />
Theory and fundamentals of gas turbine, principles, classification,<br />
thermodynamic cycles, assumption for simple gas turbine cycle analysis, work<br />
ratio, concept of maximum and optimum pressure ratio, actual cycle, effect of<br />
operating variables on thermal efficiency, regeneration, intercooling, reheating<br />
and their effect on performance, closed cycle and semi closed cycle gas turbine<br />
plant, applications of gas turbines.<br />
6. Jet Propulsion:<br />
Introduction, theory of jet propulsion, types of jet engines energy flow through jet<br />
engines, thrust, thrust power, propulsive, thermal and overall efficiency, turbo jet,<br />
turbo prop, turbo fan and ducted fan engines, pulse jet and ram jet engines,<br />
applications of jet engine, methods of thrust augmentation, introduction to rocket<br />
engines (elementary treatment).<br />
7. High Pressure Boiler:
Principle and working of high pressure boilers, super critical boilers, fluidized<br />
bed combustion, general layout and specification of boilers used in thermal power<br />
plants.<br />
8. Thermodynamics of Vapour Power Cycle:<br />
Rankine cycle, theoretical and actual regenerative feed heating, types of feed<br />
water heaters, de-aerator, reheat cycle, parameters affecting Rankine cycle,<br />
reheating of steam, binary vapour cycle combined gas-steam power cycle, cogeneration.<br />
9. Economics of power generation:<br />
Load curves, load duration curve, Connected load, maximum load, peak load,<br />
base load and peak load power plants, load factor, plant capacity factor, plant use<br />
factor, demand factor, diversity factor, performance at variable load of power<br />
plants, heat rate and incremental heat rate curves, load sharing among generators<br />
and prime movers, load sharing between power stations, cost analysis, unit energy<br />
cost.<br />
10. Power Plants:<br />
Factors affecting selection of site for various types of power plants:<br />
Steam power plant: General arrangement, steam turbine arrangements, principles<br />
of water treatment.<br />
a) Diesel power plant:<br />
Layout, essential systems, advantages of diesel power plants over other power<br />
plants, application of diesel power plants.
) Nuclear power plants:<br />
Advantages over other types of plants, classification of nuclear power reactors.<br />
Boiling Water Reactor, Pressurized Water Reactor, Pressurized heavy water<br />
reactor, liquid metal cooled reactor, and gas cooled reactor systems. Nuclear<br />
power plants in India, waste disposal.<br />
c) Hydro-power plants:<br />
Important elements of hydro- power plant, classification of hydro-power plants,<br />
comparison with other power plants, hydro-power plants in India.<br />
d) Gas turbine power plant:<br />
Plant layout cooling of turbine blades, plant components and their arrangement,<br />
gas turbine plants in India.<br />
Term Work<br />
The term work shall consist of record of any three experiments from Group-I, any<br />
four experiments from Group-II and Group-III is compulsory.<br />
Group-I<br />
1. Study of steam turbines: Types of steam turbine, constructional details of<br />
impulse and reaction turbine.<br />
2. Study of steam turbine systems:<br />
(a) Methods of governing.
(b) Speed governor and oil servomotor relay mechanism.<br />
(c) Emergency trip gear mechanism and<br />
(d) Extraction pressure regulation system.<br />
3. Study of jet engines:<br />
(a) Turbojet.<br />
(b) Turbo prop.<br />
(c) Turbo fan, and<br />
(d) Ram jet and pulse jet.<br />
4. Study of cogeneration system preferably by visit to a plant.<br />
5. Study of high-pressure boilers.<br />
Group-II<br />
6. Trial on diesel generating set to determine the following characteristics:<br />
(a) Plant efficiency versus load.<br />
(b) Total fuel consumption versus load.<br />
(c) Rate of energy input versus load, and<br />
(d) Heat rate and incremental heat rate versus load.<br />
7. Study and trial on steam power plant to determine the following characteristics:<br />
(a) Plant Efficiency, Rankine Efficiencies, versus load.<br />
(b) Steam consumption specific steam consumption versus load.<br />
(c) Rate of energy input versus load, and
(d) Heat rate incremental heat rate versus load.<br />
8. Trial on subsonic. Steam nozzle (or air nozzle) to determine:<br />
(a) Variation of pressure along the length of the nozzle.<br />
(b) Discharge co-efficient and discharge Mach number.<br />
9. Trial on subsonic diffuser to determine the following:<br />
(a) Variation of pressure along the length.<br />
(b) Discharge coefficient.<br />
10. Trial on gas turbine power plant to determine the following characteristics:<br />
(a) Plant efficiency versus load.<br />
(b) Total fuel consumption versus load.<br />
(c) Rate of input energy versus load, and<br />
(d) Heat rate and ii1cremental heat rate versus load.<br />
Group-III,<br />
11. Study report on visit to one of the power plants listed in the syllabus above.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Arora S. C. and Domkundwar S., “A course in Power Plant Engineering”,<br />
Dhanpat Rai and Sons, New Delhi 1993.<br />
2. Morse F. T, “Power Plant Engineering”, Affiliated. East-West Press Private<br />
limited, New Delhi/Madras 1953.<br />
3. Ballaney P. L., “Thermal Engineering”, Khanna Publishers, Delhi 19990<br />
4. Nagpal G. R., “Power Plant Engineering”, S. K. Khanna Publishers, Third<br />
Edition, Delhi 1995.
5. Sharma P. C., “Power Plant Engineering”, S. K. Kataria and Sons, Fifth Edition,<br />
Delhi 1996.<br />
6. Rai G. D., “An Introduction to Power Plant technology”, Khanna Publishers, third<br />
Edition, Delhi 1996.<br />
7. A.W. Culp Jr., “Principles of Energy Conversion”, McGraw Hill Kogakusha Ltd.,<br />
Tokiyo.<br />
8. Harry Sorensen, “Energy Conversion Systems”, John Willey and Sons, New<br />
York.<br />
9. EI Vakil, “Power Plant Engineering”, McGraw Hill, New York.
(411044): Industrial Management-II<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: 100 Marks<br />
1. Workstudy: Method Study:<br />
Time Study-stopwatch, work sampling, PMTS: various methods, units of time<br />
measurement, breaking up of elements, time calculations. One of the methods like<br />
MOST or MTM to be covered in details.<br />
2. Plant Layout and Material Handling:<br />
Introduction, importance and relationship with organizational efficiency;<br />
systematic layout planning, use of computer software in layout planning; manual<br />
material handling; different types of trucks, hoists, belts, conveyors-flexibility,<br />
safety and cost aspects.<br />
3. Production Planning and Control:<br />
Forecasting; capacity estimation, planning, scheduling and controllingdifficulties,<br />
limitations and application of computers, CPM and PERT, expected<br />
time of completion of a project, probabilistic analysis, crashing of network and its<br />
costs.<br />
4. Materials Control:<br />
Types of inventory, inventory control through different analysis; Just in time,<br />
Kanban, MRP, MRP II-control procedure, advantage, limitations and<br />
applicability.
5. Operations Research:<br />
Linear Programming- Transportation problem, assignment problem, Sequencing,<br />
queuing fn,eory M/M/I.<br />
6. Job Evaluation and Merit Rating:<br />
Need, various methods.<br />
7. Value analysis and value engineering:<br />
Introduction, steps involved, applications in manufacturing and service industry.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Dewett K.K.Modern Economics Theory, Shyamlal. Charitable Inst, Delhi, 1995.<br />
2. Ghanekar A, Organisational behavior-concepts and causes, Everest Publication<br />
House, Pune, 1995.<br />
3. Lythans F., Organisational Behavior, 7 th Edition, McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 1995.<br />
4. Prasad N. K., Cost Accountacy.<br />
5. Gail Freeman Bell, Balkwill, Management Engineering-Principles and Practice,<br />
PIH, New Delhi.<br />
6. Introduction to Work Study~By International labour Organisation Geneva.<br />
7. Samuel Ei1on-Production Planning and Control, “Navneet Publications, Bomhay.<br />
8. Industrial Engineering handbook-Edition IV By H. B. Maynard.<br />
9. Hira and Gupta-Operations Research, S. Chand and Co. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
10. G. R. Terry, Principles of Management, Irwin Inc.
11. J. L. Riggs, production Systems-Planning, analysis and Control, John Wiley and<br />
Sons.
(402045): Refrigeration and Air conditioning (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: lOO Marks<br />
1. Air refrigeration system:<br />
Air as refrigerant, air craft refrigeration cycle, necessity, air cycle systems for air<br />
craft refrigeration such as bootstrap, regenerative, reduced ambient.<br />
2. Vapour compression system:<br />
Thermodynamic analysis, performance of system, actual vapour compression<br />
refrigeration cycle-effect of change of condenser and evaporator pressure, multi<br />
compressor-multi evaporator, and cascade systems.<br />
3. Refrigerants:<br />
Factors governing selection of refrigerants, alternative refrigerants for CFC’s and<br />
HCFC’s, ozone depletion, global-warming potential, Montreal and Kyoto<br />
protocol, total equivalent warming impact (TEWI), secondary refrigerants,<br />
refrigerant mixtures.<br />
4. Vapour Absorption Refrigeration:<br />
Aqua-ammonia and Li-Br systems, temperature-pressure concentration properties<br />
of Li-Br-water solutions, calculation of mass flow rates in the aborption cycle,<br />
enthalpy of Li-Br solution, thermal analysis of simple absorption system, actual
absorption system, double effect system, commercial absorption unit, solar<br />
absorption refrigeration systems.<br />
5. Applied psychrometry:<br />
Cooling and heating coils, bypass factor, air washers, evaporative cooling,<br />
adiabatic dehumidifier, water and steam injection, concept of SHF, RSHF, GSHF,<br />
ESHF, ADP.<br />
6. Heating and cooling load calculations:<br />
Health and comfort criteria, thermal comfort, air quality, design conditions,<br />
thermal transmission, infiltration and ventilation loads, internal loads, solar loads<br />
through transparent surfaces, solar loads on opaque surfaces.<br />
7. Duct System :<br />
Duct design considerations, methods of duct design equal friction method,<br />
velocity reduction method, static regain method, system balancing, air distribution<br />
system, inlet/outlet grills, diffusers and register, criteria for fan selection.<br />
8. Air Conditioning Systems:<br />
All air system, all water system, air water system, unitary and central air<br />
conditioning, instat1ation, charging, testing, and maintenance of window, split,<br />
packaged and central air conditioning system.
9. Components of refrigeration and air conditioning system:<br />
Compressors, condensers, evaporators, expansion devices such as capillary tubes,<br />
automatic expansion valves, thermostatic expansion valves and controls such as<br />
thermostats, humidystats, solonoid.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Arora C.P., Refrigeration and Air-conditioning, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing,<br />
New Delhi, 1998.<br />
2. Stocker W.F. and Jones J.W., Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, McGraw Hill<br />
International Editions, 1982<br />
3. Dossat Ray J., Principles of Refrigeration, S.I. Version Wiley Eastern Limited,<br />
1985.<br />
4. Manohar Prasad, Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, Wiley Eastern Limite.d,<br />
1983.<br />
5. Ballaney P.L., Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, Khanna Publishers, New<br />
Delhi, 1992.<br />
6. Arora S.C. and Domkundwar S., Refrigeration and Air-Conditionong, Dhanpat<br />
Rai and Sons publishing, New Delhi, 1994.<br />
7. Khurmi R.S. and Gupta J.K., refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, Eurasia<br />
publishing house (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 1994.<br />
8. Threlkeld J.L., Thermal Environmental Engineering, Prentice hall Inc. New<br />
Delhi.<br />
9. Manohar Prasad, Refrigeration and Air conditioning data book, wiley eastern Ltd.<br />
10. Survey of Indian Industries-The Hindu-Yearbook.
(402045): Non-Conventional Energy Sources (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures. : 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Solar Energy :<br />
Availability, limitations, energy efficiency by first and second law of<br />
thermodynamics, application of solar energy.<br />
2. Solar Radiation:<br />
<strong>Structure</strong> of the sun, energy radiated by the sun, angular relationship of earth and<br />
sun position, measurement of solar radiation.<br />
3. Flat Plate collectors:<br />
Types of constructional details of flat plate collector, energy balance for a flat<br />
plate collector, simple equation and performance curves, selection of flat plate<br />
collector.<br />
4. Solar concentrator:<br />
Limitations of flat plate collectors, various types of concentrators, their<br />
advantage, simple thermal energy balance equations, heliostats, selection of<br />
various materials for concentrators and reflecting surfaces.
5. Solar heating systems:<br />
Solar water and space heating systems, passive solar heating systems, solar<br />
heating economics, solar air heating systems.<br />
6. Solar distillation systems:<br />
various solar stills and selection, constructional details.<br />
7. Solar electric power:<br />
Solar photovoltaic system, - materials used and their performance, types of solar<br />
thermal power plant, working substance used, temperature required, various<br />
systems used, typical solar ponds.<br />
8. Wind Energy:<br />
Availability of wind, various types of wind mills and their constructional details<br />
and performance study.<br />
9. Geothermal Energy:<br />
Sources and application of Geothermal energy, various types of geothermal<br />
power plants.<br />
Tidal Energy: Tidal energy available in India, suitable locations, study of various<br />
tidal energy power plants, characteristics of turbines required.<br />
Ocean thermal energy: Comparison of various plants.<br />
10. Bio gas:
Chemistry of biogas generation variables affecting simple gas plants, types of<br />
digesteors thcir working and construction, application of biogas, use of bio-gas,<br />
case study of “pura village bio gas electricity generation”.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Krietn and Krieder, principles of solar engineering, Tata McGraw HilI Publishing<br />
Company Limited, New Delhi, .1994;<br />
2. Sukhatme S.P., Solar Energy, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited,<br />
New Delhi, 1994.<br />
3. Rai G.D., An Introduction to Power Plant Technology, Khanna Publishers, Third<br />
Edition, Delhi, 1996.<br />
4. Wakil M.M., Power Plant Technology, McGraw Hill International Book<br />
Company, 1984.<br />
5. Rai B.K., and Ramprasad M.S., Power generation through renewable sources of<br />
energy.<br />
6. Bansal and others, Non-conventional Energy sources.<br />
7. Garg H.P., and Prakash J., Solar Fundamental and Application, Tata McGraw Hill<br />
Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 1991.<br />
8. S.Rao and Dr.B.B. Parulekar, Energy Technology, Khanna Publishers, New<br />
Delhi.
(402045): Tribology (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme:<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Tribology:<br />
Introduction, tribology in design, Tribology in industry, Economic considerations.<br />
2. Friction:<br />
Introduction, Laws of friction, kinds of friction, causes of friction, friction<br />
measurement, theory of friction.<br />
3. Wear:<br />
Types of wear, various factors affecting wear, measurement of wear, wear<br />
between solids and flowing liquids, theory of wear.<br />
4. Lubricants and lubrication:<br />
Lubricant properties- physical and chemical. Lubrication-introduction, basic<br />
modes of lubrication. Flow of viscous fluid through rectangular slot. Seals-<br />
<strong>Mechanical</strong> and dynamic seals.<br />
5. Hydrostatic bearings:
Basic concept, operations, advantages and limitations. Hydrostatic conical and<br />
spherical bearings, load carrying capacity and flow of lubricants. Bearing power<br />
and film thickness, bearing temperature and power. Compensators and their<br />
action. Optimum design of step bearing.<br />
6. Hydrodynamic bearings:<br />
Theory of hydrodynamic lubrication. Mechanism of pressure development in oil<br />
film. Two-dimensional Reynolds eq1.lation. Infinite tapered shoe slider bearings<br />
and infinite long journal bearing; Short bearing theory applied to journal bearing.<br />
7. Friction and power losses in journal bearing:<br />
Ratio of heat conducted, temperature rise approximate and rapid methods, design<br />
considerations.<br />
8. Hydrodynamic Thrust bearing:<br />
Introduction, flat, plate thrust bearing, pressure equation, load, center of pressure.<br />
Tapered land thrust bearing, step thrust bearing, tilting pad thrust bearing.<br />
Friction in tilting pad thrust bearing.<br />
9. Hydrostatic squeeze film:<br />
Circular and Rectangular plates, impact conditions between lubricated solids,<br />
Application to journal bearing.<br />
10. Lubrication in special conditions:<br />
Forging, wire drawings extrusion, rolling. Lubricants used for wire ropes.
Reference Books<br />
1. Fuller D.D., Theory and Practice of Lubrication for Engineers. John Wiley and<br />
Sons.<br />
2. Halling J., Principles of Tribology, McMillan Press Ltd.<br />
3. Cameron A., Basic Lubrication Theory, Wiley Eastern Ltd.<br />
4. Neale M.J., Tribology hand Book”, Butterworths.<br />
5. B.C. Majumdar, Introduction to Tribology and Bearings, H. Wheeler and<br />
Company Pvt. Ltd.<br />
6. O.P. Qrlov, Fundamentals of Machine Design, Vol. IV, MIR.
(402045): Microprocessor Applications (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Introduction to semiconductor memories RAM/ROM/PROM/EPROM/<br />
EAPROM/ static and dynamic RAMs.<br />
2. 8 bit Micro controller (MCS-SI family-80S 1 as typical example), architecture,<br />
Instruction set, features, and Special stress on bit manipulation.<br />
3. RS-232C serial interface.<br />
4. ADC/DAC: Basic of ADC/DAC (Block level).<br />
5. Study of PC based data acquisition cards. Multiplexing of ilp of AID, scanning<br />
rates, using software for acquisition, manipulations and plotting of results like<br />
temperature monitoring along with pressure output relay driving capacity etc.<br />
6. Study of PLC applications in detail: Ladder Diagram development in detail.<br />
Application of PLC to CNC machine, boiler, cooling equipment as case studies.<br />
Furnaces.
7. Study or microprocessor based smart instruments, smart control valves and<br />
control systems. Explanation of smart features for two or three types of<br />
equipment like weighing machine, pH transmitter, differential pressure<br />
transmitter etc.<br />
(Note: It is necessary to demonstrate some of the concepts mentioned above).<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Intel Manuals.<br />
2. K.J. Ayala, “The 8051 Micro controller: Architecture, programming and<br />
Applications”, Penram International Published, India.<br />
3. S.Y. Boyer, “SCADA”, ISA Publications.<br />
4. John Webb, “PLC”, Otter.<br />
5. B. E. Noltingk, “Instrumentations Reference Book”, Butterworth International<br />
Edition.
(402045): Plant Engineering (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Organisation of Plant Engineering, Principles of Plant management functions.<br />
Classification of maintenance work-Routine maintenance, emergency work,<br />
service work, preventive maintenance. Project work, Corrective work,<br />
Assessment of maintenance work. Performance and productivity measurement;<br />
problem solving techniques. Statistical processes. Parato chart. Manpower<br />
planning and training for maintenance and safety staff.<br />
2. Basic Plant Facilities.<br />
(e) Sanitation.<br />
(a) Building: Types of Building structures, Ventilation and lighting, Roads<br />
and parking.<br />
(b) Electrical power generation, distributions, utilisation, stand by units.<br />
(c) Heating, ventilation and Air conditionong.<br />
(d) Water supply, Purification, use and disposal.<br />
(f) Planning and estimation of auxilliary services, such as water, steam,<br />
compressed air.<br />
(g) Layout of facilities-Types of layouts, selection of layout. Group<br />
technology aspect. P. Q. Analysis, PQRST analysis, material flow,<br />
REL charts, space requirements, space diagram. Use of computer for<br />
optimization of layouts.
3. Plant Operating Equipments. Selection and maintenance of-<strong>Mechanical</strong> power<br />
transmission systems, Hydraulic and Pneumatic systems, Piping and piping<br />
Seystems, Instrumentation and automatic control for plant equipment, noise and<br />
vibration control.<br />
Pollution control-Waste disposal, existing limiting norms. Recycling of waste.<br />
Plant safety-fire protection and prevention, safety against mechanical hazards,<br />
chemical hazards, accident prevention practices and codes.<br />
Energy conservation, management and audit. Material handling equipments.<br />
Principles of material handling, types of material handling equipmentclassification<br />
and selection.<br />
Unit load concept-Introduction to Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGV).<br />
4. Maintenance-Failure analysis-types and causes, types of maintenance-breakdown,<br />
preventive, predictive, condition monitoring-signature analysis, sound<br />
monitoring, Spectrometric oil Analysis Procedure (SOAP) and other<br />
contaminants’ monitoring techniques. Reliability and maintainability of<br />
equipment, lubrications and lubricants corrosion and wear, causes and its<br />
prevention, product life, cycle concept and spare part management. History cards<br />
for equipments, Computerised maintenance and house keeping, maintenance<br />
manuals.<br />
5. Maintenance problems occurring in product and process type industries and<br />
Power plants.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. R.A. Collacatt-<strong>Mechanical</strong> fault Diagnosis and Condition Monitoring-Chapman<br />
and Hall Ltd.
2. R.C. Rosaler-Handbook of Plant Engineering-McGraw Hill.<br />
3. Higgin-Handbook of Maintenance Engineering- McGraw Hill.<br />
4. Rudenko-Material, Handling equipment-MIR:- Publication.<br />
5. Jacob Fruchlboum-Bulk Material Handling, Handbook;<br />
6. CBS Publisher.<br />
7. Garg H.P.-Industrial Maintenance, S. Chand and Co. New Delhi.<br />
8. Edward Srivastava-Maintenance Management.<br />
9. Sushikumar Srivastava-Industrial Maintenance Management-S. Chand and<br />
Co.Ltd., New Delhi.
(402045): Analysis and Synthesis of Mechanisms (Elective I)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Review of Introduction to Mechanisms:<br />
Geometry of motion, plane and space mechanisms, terminology, definitions and<br />
assumption. Relative motion, degree of freedom for spatial mechanisms,<br />
kinematic inversions, mechanical advantage, transmission angle.<br />
2. Kinematic Analysis of Plane Mechanisms:<br />
Position and displacement analysis-position of a point, graphical and complexalgebra<br />
method for displacement. Rotatinal and translation displacement. Velocity<br />
analysis- relative motion, linear and angular velocity, Freudenstein’s theorem,<br />
velocity analysis and acceleration analysis-using auxiliary point method,<br />
Goodman’s indirect method. Computer-aided kinematics analysis.<br />
3. Curvature theory:<br />
Fixed and moving centrodes, envelopes-velocity and acceleration, inflection<br />
points and inflection circle. Euler-Savary equation, Bobillier’s theorem,<br />
Hartman’s construction, return circle, cusp points, cubic of stationary curvature,<br />
Ball’s point. Applications in dwell mechanism.<br />
4. Kinematic synthesis of Plane Mechanisms:
Type, number and dimensional synthesis, branch and order defects. Function<br />
generation and path generation, rigid body guidance. Chebychev spacing-three;<br />
four and five point synthesis, Burmester point theory, synthesis by analytical and<br />
graphical methods.<br />
5. Spatial Mechanisums:<br />
Position, velocity and accelerati9n analysis of RGGR mechanisms, Eulerian<br />
angles theorem on angular velocities and acceleration, DH parameters, DH matrix<br />
method, application of special mechanism to robotics. Kinematic analysis of an<br />
,industrial robot.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. J.E. Shigley and J.J., Vicker, Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, International<br />
Student Edition (McGraw Hill).<br />
2. G.N. Sandor and A.G. Erdman, Mechanism Design-Analysis and Synthesis, Vol.<br />
I and Vol. II, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., (Easter Economic Edition).<br />
3. Ghosh and A.K. Malik, Theory of Mechanisms and Machines, East-West Press<br />
Pvt. Ltd.<br />
4. A.S. Hall, Kinematic and linkage Design, Prentice Hall of India (Pvt.) Ltd.<br />
5. R. Beyer, Kinematic Synthesis of Mechanisms, McGraw Hill Book Co. New<br />
York.<br />
6. R.S. Hartenberg, J. Donavit, Kinematic Synthesis of Linkages, McGraw Hill<br />
Book Co.<br />
7. B.y. J. Duffy, Analysis of Mechanisms and Robot Manipulators, Edward Arnold<br />
Publishers Ltd., London, 1980.<br />
8. Rao J.S. and R.V. Dukkapati, Mechanics and Machine Theory, John Wiley.<br />
(402046) : Seminar<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Practicals: 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Oral: 50 Marks
Seminar should be based on deep study of any topic related to mechanical engg.<br />
Format of the seminar report should be as follows:<br />
1. Paper:<br />
The seminar report shall be typed/printed on white paper of A-4 size.<br />
2. Typing:<br />
The typing shall be in black colour with normal spacing and on one side of the<br />
paper.<br />
3. Binding:<br />
The seminar report should be submitted with front and back cover of card- paper<br />
neatly cut to size and bound together with, the text.<br />
4. Front Cover:<br />
The front cover shall have the following details in block capitals.<br />
(a) Title at the top.<br />
(b) Name of the candidate in the center, and<br />
(c) Name of the institute and the year of submission on separate lines, at the<br />
bottom.
5.Blank sheets:<br />
No blank sheets be left any where in the report.<br />
6. Title sheet:<br />
The title sheet shall be the first sheet and shall contain following details with<br />
proper spacing.<br />
A seminar report on<br />
(Title)<br />
By<br />
(Name)
(Examination No.)<br />
(Roll No.)<br />
Under the guidance of<br />
7. Seminar approval sheet:<br />
The approval sheet shall follow the title sheet and shall be as shown below with<br />
proper spacing.
This is to certify that the seminar entitled<br />
______________________________submitted by, _________________<br />
Examination No.__________________ for the partial fulfillment for the<br />
award of degree of B.E. (<strong>Mechanical</strong> Engineering) of university of Pune, Pune, is<br />
approved.<br />
(Guide)<br />
(Head of the Deptt.)<br />
(Examiner)<br />
8. The format of the text of the seminar reports:<br />
8.1 The report shall be presented in the form of a technical paper. After front cover,<br />
the title sheet and the seminar approval sheet, the introduction of the seminar<br />
work shall be given briefly (in about 10 lines) in the first paragraph of the text<br />
of the report.<br />
8.2 The introduction shall be followed by the literature survey.<br />
8.3 Report of any analytical or experimental work done should follow the 1iterature<br />
survey.<br />
8.4 Figures shall be drawn on separate sheets and inserted on the page on which the<br />
text is typed. The figures shall be either drawn in permanent I black ink or<br />
printed on paper. The figures shall be numbered.<br />
8.5 Tables shall be typed in text. A separate sheet may be used, if necessary. The<br />
tables shall be numbered.
1.6 Mathematical portion of the text shall be preferably typed. If this is not possible<br />
it shall be written in permanent black ink. Lengthy mathematical derivations shall<br />
not be included. Only the important steps and expressions shall be given.<br />
1.7 Discussions and conclusions shall form the last paragraph of the text. They<br />
shall be followed by nomenclature and symbols and then the acknowledgement.<br />
9. References:<br />
The references shall form the last section and shall be followed by ‘Appendix’ if<br />
any. They would contain list of works (papers, books, etc.) referred to in the body<br />
of the text and shall be arranged in the order in which they are cited in1he text.<br />
The numbering shall be done in numerals (e.g.1,2…) indicated as superscripts<br />
along with the author’s name il1the text. For any paper, the information shall<br />
contain the name of the author, the title of the paper, the name of the journals, the<br />
volume number, the page number and the year of publication in parenthesis. In<br />
case of references from journals and books in languages other than English the<br />
titles of the journals or books shall be transliterated into Latin script and not<br />
translated. For any book, the information shall contain the names of the authors,<br />
title, publisher and the year of publication in parenthesis. For papers and books<br />
with joint authorship the name of all the authors shall be introduced in the same<br />
order. The author’s name shall be with the last name followed bi initials.<br />
10. The total number of typed pages excluding the covers shall be from 15 to 20 only.<br />
All the pages shall be numbered.<br />
11. Two copies of seminar shall be submitted to the College. The students shall<br />
present the seminar before the examiners.
(402047): Project<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs/Week in Part I<br />
Practical: 6 Hrs/Week in Part II<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
T/W : 100 Marks<br />
Oral: 50 Marks<br />
1. Fabrication of models, machines OR prototypes based on new ideas, robots and<br />
machines based on hitech systems.Experimental set ups, energy<br />
audit/conservation studies of a department or a section in an organization/plant,<br />
Fabrication of testing equipment. Renovation of machines etc.<br />
Above work to be taken up individually or in groups. The group shall not be more<br />
than 4 students. A detailed report on the work done shall include project<br />
specifications, design procedure, drawings, process sheets, assembly procedure,<br />
test results, costing etc.<br />
2. Guidelines for project report:<br />
(a) Report shall be typed or printed.<br />
(b) Figures and tables shall be on separate pages and attached at. Respective<br />
positions.<br />
(c) Project title and approval sheets shall be attached at the beginning of the report<br />
followed by index and synopsis of the project.<br />
(d) References shall be mentioned at the end followed by appendices (if any).<br />
(e) When a group of students is doing a project, names of all the students shall be<br />
included on every certified report copy.
(f) Each group of students shall submit two copies of reports to the institute and<br />
one copy for each individual student.<br />
(g) In case of sponsored projects, the students shall obtain certificate from<br />
sponsor and attach it to the report.<br />
OR<br />
3. Computer based design/analysis or modeling/ simulation of product(s)<br />
mechanism(s) or system(s) and its validation or comparison with available bench<br />
marks/results.<br />
Oral shall be based on the project done by the students, jointly conducted by an<br />
internal and an external examiners appointed, at the end of Part II.
(402048): CAD/CAM and Automation<br />
Teaching Scheme.<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: 100 Marks<br />
Oral : 50 Marks<br />
Term Work: 25 Marks<br />
1. CAD/CAM Systems:<br />
CAD and CAM concepts, product cycle and CAD/CAM, application of<br />
computers in design, advantage’s 6f ~AD/CAM, hardware; and software for<br />
CAD/CAM, selection of CAD/CAM system.<br />
Computer Communications: Principle of net- working, classification of networks,<br />
transmission media and interfaces, local area network system.<br />
2. Computer Graphics:<br />
Two dimensional geometric and co-ordinate transformations, translation, rotation,<br />
scaling, mirror reflection, inverse co-ordinate transformation, matrix description<br />
of basic transformation. CAD/CAM Data Exchange-Introduction to Data<br />
Exchange formats, IGES/ PDES files, Graphics Standards.<br />
3. Geometric Modeling:<br />
Wire frame modelling, Surface modelling, Solid modelling, parametric solid<br />
modelling, Solid modelling based applications.
4. Finite Element Analysis:<br />
Fundamental concepts, introduction to PEA, stresses and equilibrium, boundary<br />
conditions, strain displacement relations, stress strain relations, temperature<br />
effects, Rayleigh Ritz method, Galerkin's method. principle of virtual work.<br />
One dimensional problems, finite element modelling, element division,<br />
numbering system, co-ordinates and shape functions, potential energy approach,<br />
Galerkin's approach, element. stiffness matrix force term, assembly of global<br />
stiffness matrix and ,load. Vector, finite element equations, types of boundary<br />
conditions, elimination approach, solution of equations, calculation of strains and<br />
stresses, temperature effects. Two dimensional problems using constant strain<br />
triangle.<br />
5. Simulation:<br />
Need of simulation, concept of a system, Model and its purpose, Types of<br />
simulation approaches-Event Scheduling Approach (ESA), Activity Scanning<br />
Approach (ASA), Process. Interaction Approach (PIA), Steps in a simulation<br />
study, advantages disadvantages and pitfall's of simulation, Simulation<br />
Languages.<br />
6. Computer Aided Manufacturing:<br />
CNC machine tools, principle of operation of CNC, steps in manufacturing,<br />
construction features including structure and drives, Direct numerical control<br />
(DNC) and its application, advantages and limitations of CNC systems.CNC part<br />
programming, axes of CNC machines, manual part programming using G code,<br />
use of subroutines, computer aided part programming using APT or any other<br />
language.<br />
7. Automation:
Concepts of automation, types of automation, computer integrated.<br />
Manufacturing, advantages and limitations of automation, automation strategies it<br />
manufacturing industries, flexible manufacturing system (FMS), types of FMS,<br />
machining centers.<br />
8. Robot Technology:<br />
Industrial robots, construction and operation of robots, robot axes and<br />
configuration, robot applications, robot select and economic justification.<br />
Term Work<br />
The term work shall consist of record of three assignments of problems based on<br />
following topics:<br />
1. (a) Construction of parametric solid model of anyone machine elements<br />
using software package.<br />
(b) Simulation of a simple <strong>Mechanical</strong> system.<br />
2. Stress and deflection analysis of any two machine elements using finite<br />
element package.<br />
3. Programming and making of two jobs on CNC or CNC Tutor involving<br />
turning, parting, taper turning and other turning operations.<br />
4. Part programming of one job on milling machines using APT language.<br />
Reference Books
1. Groover M.P. and Zimmers E.W.Computer Aided, Design and Manufacturing<br />
-Prentice Hall of India.<br />
2. Groover M.P., Automation, production systems and computer integrated<br />
manufacturing-Prentice Hall of India.<br />
3. Rogers D.F., Procedural elements for computer graphics-McGraw Hill Inc.<br />
4. Harrington Steven, Computer graphics-a programming, approach'-McGraw Hill<br />
Inc.<br />
5. Ibrahim Zeid-'CAD/CAM-theory and practice' Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co.<br />
6. Chandrupatla T.R. and Belegunda A.D. -Introduction to finite elements in<br />
engineering'-Prentice Hall of India.<br />
7. Segerling L.J., Applied finite elements analysis' John Wiley and Sons.<br />
8. Rao P.N., Tewari N.K. and Kundra T.K., Computer Aided Manufacturing'- Tata<br />
McGraw Hill Publishing Co.<br />
9. Radhakrishan P. and Subramanyan, CAD/CAM/CIM, Wiley Eastern Ltd.<br />
10. Bathe K. J., Finite element procedures, Prentice Hall of India.<br />
11. Ramamurti V., Computer aided mechanical design and analysis, Tata McGraw<br />
Hill Pub. Co.<br />
12. Nanua Singh-Systems Approach to Computer Integrated Design and<br />
Manufacturing-John. Wiley (1996)
(402049): Dynamics of Machinery<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
T/W: 25 Marks<br />
Oral: 50 Marks<br />
1. Governors:<br />
Governor function, inertia and centrifugal type governors, different types of<br />
centrifugal governors, controlling force analysis, governor effort and governor<br />
power, sensitivity, stability, isochronisms and hunting, friction, insensitiveness.<br />
2. Gyroscopes:<br />
Principles of gyroscopic action, precession and gyroscopic acceleration,<br />
gyroscopic couple, effect of gyroscopic couple on ships, aeroplane, vehicles,<br />
inclined rotating discs etc.<br />
3. Cam dynamics:<br />
Advance cam curves, cam dynamics, mathematical model, jump phenomenon,<br />
ramp of the cam-precam, polydyne cam.<br />
4. Balancing:
Balancing of rotating masses in one and several planes, balancing of.<br />
reciprocating masses in single and multicylinder engines-inclined, radial and vee<br />
type.Primary and secondary balancing analysis. Concept of, direct and reverse<br />
cranks. Static and dynamic balancing machines.<br />
5. Vibrations:<br />
Introduction, S.H.M., degrees of freedom.<br />
(a) Single degree of freedom system:<br />
(i) Undamped free vibrations, damped free vibrations, over damped,<br />
critically damped and underdamped vibrations, logarithmic decrement,<br />
viscous .damping and dry friction/Coloumbs damping.<br />
(ii) Forced vibrations: constant harmonic excitation, excitation due to<br />
reciprocating and rotating unbalance, vibration isolation and<br />
transmissibility and applications<br />
(iii) Torsional vibrations: Single degree of freedom system of free,<br />
undamped, damped and forced torsional vibrations. Study of two rotor<br />
systems, geared rotor system and three-rotor system.<br />
(b) Critical speed: Whirling of horizontal and vertical shafts carrying single rotor,<br />
damped and undamped systems.<br />
(c) Vibration measurements: Measurement of displacement, velocity,<br />
acceleration, frequency and damping. Different types of pick-ups, exciters,<br />
vibration meter and related instrumentation .<br />
Term Work :<br />
The term work shall consist of any 'eight' of the following experiments:<br />
1. To determine the 'characteristic curve of a centrifugal governor and to find its<br />
coefficient of insensitiveness and stability.
2. Verification of principle of gyroscope and gyroscopic couple, magnitude.<br />
3. Study of any two gyro controlled instruments.<br />
4. Verification of cam jump phenoml'l1on.<br />
5. To study the dynamic balancing machine and to balance a rotor (e.g. rotor of<br />
electric motor, flywheel, fan etc.)<br />
6. To determine the natural frequency of damped vibration of single degree<br />
freedom system and to find its ' damping coefficient.<br />
7. To verify natural frequency of torsional ,vibration of two rotor system and<br />
position of node.<br />
8. To determine critical speed of singl rotor system.<br />
9. To determine resonance frequency of transverse vibration of beams.<br />
10. To determine the frequency response curve under different damping<br />
conditions for single degree freedom, system of vibration.<br />
11. To study shock absorbers and to plot transmibility curve.<br />
Oral shall be based on the term work prescribed and presented in the form of a<br />
journal.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Beven T., "Theory of Machines".<br />
2. Jagdishlal, "Theory of Machines".<br />
3. Shigley J. E. and Vicker J. J., "Theory of Machines and Mechanisms",<br />
International Edition, McGraw Hill Inc.
4. Grover G. K., "<strong>Mechanical</strong> Vibrations", Nem Chand and Bros.<br />
5. Rao S. S., "<strong>Mechanical</strong> Vibratipns", Addison Wiley Publishing Co., World<br />
Student Series.<br />
6. Seto W. W., "<strong>Mechanical</strong> Vibrations", Schaum Publishing Co" New York. .1<br />
7. Hannah and Stephans, ':Mechanics of machines",Edward Aronold Publication.<br />
8. A. Gosh, Malik, "Theory of Mechanism and Machines", East-West'Pvt. Ltd.
(402050) : Industrial Fluid Power<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: 100 Marks<br />
T/W: 50 Marks<br />
1. Fluid power system: Components, advantages, application in the fields of<br />
machine tools, material handling, hydraulic pressess, mobile and stationary<br />
machines, clamping, devices etc. Transmission of power at static and dynamic<br />
states.<br />
2. Types of hydraulic fluids, petroleum based, synthetic and water based. Properties<br />
of fluids, selection of fluids, additives, effect of temperature and pressure on<br />
hydraulic fluid.<br />
3. Seals, sealing materials, compatibility of seal with fluids.<br />
4. Types of pipes, hoses, material, quick acting couplings Pressure drop in<br />
hoses/pipes.<br />
5. Fluid conditioning through filters, strainers, Sources of contamination, and<br />
contamination control, Heat Exchangers.
6. Power units and accessories: Types of power units, reservour assembly,<br />
constructional details, pressure gauges, pressure switches, temperature switches<br />
etc.<br />
7. Accumulators: Types, selection/design procedure, applications of accumulators.<br />
8. Pumps: Types, classification, principle of working and constructional details of<br />
vane pumps, gear pumps, radial and axial plunger pumps, screw pumps, power<br />
and efficiency calculations, characteristic curves, selection of pump for hydraulic<br />
power transmission.<br />
9. Control of fluid power:<br />
(i) Necessity of fluid control through pressure control, direction control, flow<br />
control valves.<br />
(ii) Principle of pressure control valves, direct operated and pilot operated relief<br />
valves, pressure reducing; valve, sequence valve.<br />
(iii) Principle of flow control valves, pressure compensated, temperature<br />
compensated flow control valves, meter in circuit, meter out circuits, flow<br />
through restrictor.<br />
(iv) Types of direction control valves: t two way two position, four way three<br />
position, four way two positions valves. Open centre, close centre, tandem<br />
centre valves, Cartridge valves. Manually operated, solenoid operated, pilot<br />
operated, direction control valves, check valve.
10. Actuators: (i) Linear and Rotary. (ii) Hydraulic motors- Types-vane, Gear, piston<br />
types, radial piston. (iii) Methods of control of acceleration, deceleration. (iv)<br />
Types of cylinders and mountings. (v) Calculation of piston velocity, thrust under<br />
static and dynamic applications, considering friction, inertia loads. (vi) Design<br />
considerations for cylinders.<br />
11. Selection of components and design of hydraulic circuit: (i) for linear circuit,<br />
regereration circuit, sequencing circuit with the use of electrical controls. (ii)<br />
Ladder diagram. (iii) Maintenance, troubleshooting, safety precautions of<br />
hydraulic circuit. (Students are advised to refer manufacturer's catalogues).<br />
12. JIC symbols/ISO symbols for hydraulic and pneumatic circuits.<br />
13. Principle of Pneumatics: (i) Laws of compression, types of compressors, selection<br />
of compressors. (ii) Comparison of Pneumatics with Hydraulic power<br />
transmissions. (iii) Types of filters, regulators, lubricators, mufflers, dryers. (iv)<br />
Pressure regulating valves, (v) Direction control valves, two way, three way, four<br />
way valves. Solenoid operated valves, push button, lever control valves.<br />
(vi)Speed regulating-Methods used in Pneumatics. (vii) Pneumatic actuators-<br />
Rotory, reciprocating. (viii) Air motors-Radial piston, vane, axial piston. (ix)<br />
Basic Pneumatic circuits, selection of components. (x) Application of Pneumatics<br />
in Low Cost Automation and in industrial automation.<br />
List of Experiments<br />
Minimum of 10 experiments shall be performed out of which 4 shall be from<br />
serial Nos. I to 8, .2 from serial Nos. 9 to 12 and 1 from serial numbers 14 and 15.<br />
Record / of experiments and assignment shall be submitted in the form of journal.
1. Study of Vane/ Piston pumps and determination of performance<br />
characteristics. Study of cavitation and aireation phenomenon.<br />
2. Study of pressure control valves and circuits using pressure control valves.<br />
3. Study of flow control valves and circuits using flow control valves.<br />
4. Study of Direction control and pilot operated check valves and circuits using<br />
Direction control and pilot operated check valves.<br />
5. Study of accumulators and charging procedure for accumulators.<br />
6. Study of Hydraulic Power units and different accessories.<br />
7. Study of Hydraulic systems for different applications (such as steel mill,<br />
presses, Injection moulding machines etc).<br />
8. Study of filters and determination of filtration rating.<br />
9. Study of compressed air generation and distribution system.<br />
10. Study of direction control valves used in pneumatics and circuits using<br />
manual and pilot operated valves.<br />
11. Study of shuttle valve/Quick exhaust valve/two pressure valve/Pneumatic<br />
clamp and circuits using these components.<br />
12. Study of Electro pneumatic valves and circuits using. Electrically operated<br />
valves.<br />
13. Study of simple hydraulic systems used in practice such as copy turning<br />
attachment, hydraulic clamps, Jack, dumper, forklift etc.<br />
14. Testing of a relief valve/flow control valve/direction control valve/hydraulic<br />
motor.<br />
15. Testing of a double acting hydraulic cylinder.
Assignment<br />
One design report of a hydraulic or pneumatic system using manufacture's<br />
catalogue.<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Pinches, "Industrial Fluid Power", Prentice Hall.<br />
2. D. A. Pease, "Basic Fluid Power", Prentice Hall.<br />
3. J. J. Pippenger, "Industrial Hydraulics", McGraw Hili Co.<br />
4. H. L. Stewart, "Hydraulics and Pneumatics", Industrial Press.<br />
5. A. Esposito, "Fluid Power with Application", Prentice Halt<br />
6. B. Lall, "Oil Hydraulics", International Literature Association.<br />
7. Yeaple, "Fluid Power Design handbook".<br />
8. Vicker's Manual on Industrial Hydraulics.<br />
9. Festo's Manual on Pneumatic Principle, Applications.<br />
10. ISO-1219, Fluid systems and components; graphic , symbols.
(402051): IC Engines and Automobile Engineering (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. General:<br />
Vehicle specifications, classification of vehicles and chassis, different layouts,<br />
chassis and frame, main components of an automobile, articulated vehicles.<br />
2. Fuel Supply Systems:<br />
(a) SI Engines: Carburation, air fuel requirements for SI engines under various<br />
operating conditions, essential parts of a modern carburettor, different<br />
circuits, carburettors used on automobiles, fuel injection in SI engines.<br />
(b) CI Engines: Functional requirements of an injection system, typical<br />
arrangment of solid injection system, individual pump and; nozzle system,<br />
unit injectors, distributor system, fuel injectors, types of nozzles, governing of<br />
IC engines.<br />
3. Cooling System:<br />
Temperature variation in various parts of IC engines, and their cooling, necessity<br />
of cooling, under cooling and overcooling, types of cooling systems.<br />
Components and working of pressurized forced thermostatic cooling system used<br />
in automobiles, coolant recovery, fan power and saving devices, additives
4. Lubrication System:<br />
Types of friction, functions and properties of lubricants, additives, pressure feed<br />
system used in automobiles, blow bye.<br />
5. Ignition Systems:<br />
Battery ignition system, magneto ignition system, electronic ignition systems,<br />
waste spark ignition system.<br />
6. Starting System:<br />
Different starting systems used in automobiles.<br />
7. Clutches:<br />
Types of clutches, single plate, multiplate, centrifugal clutches, clutch operating<br />
systems, wet clutches, fluid coupling, clutch plate material.<br />
8. Gear Box:<br />
Functions of gear box, various resistances to motion, rolling, air and gradient<br />
resistance, total resistance and tractive effort, variation of tractive effort with<br />
speed, power required for acceleration and gradiability, selection of gear ratio,<br />
sliding mesh, constant mesh and epicyclic gear boxes, synchromesh devices,<br />
automatic gear boxes, torque converters, overdrive, propeller shaft.
9. Spring and Suspension Systems:<br />
Objects of suspension, principles of suspension design, spring and unspring mass,<br />
types of springs, variable rate springs, torsion bars, rubber springs, shock<br />
absorbers, independent suspension, air suspension, interconnected suspension,<br />
hydro pneumatic suspension, self leveling suspension.<br />
10. Steering Systems:<br />
Requirements of good steering systems, steering geometry, camber, steering axis<br />
inclination, included angle, scrub radius, castor, toe in, toe out, turning radius,<br />
wheel balancing, steering linkages, steering gears, cornering force, slip angles,<br />
under steer, over steer, cross play and radial tyres, power steering.<br />
11. Braking Systems:<br />
Braking systems used in automobiles, layout and working, antiskid braking.<br />
12. Automobile Maintenance:<br />
Preventive maintenance, troubleshooting and diagnosis for systems mentioned at<br />
para 2 to 11 above.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Ganesan V., "Internal Combustion Engines", Tata McGraw Hill Pubvlishing<br />
Company Ltd, Ninth Edition, New Delhi, 1995.
2. Mathur M.L., and Sharma R. P., "A course in I.C. Engine", Dhanpat Rai<br />
Publication, Seventh Edition, New Delhi, 1999.<br />
3. Newton, Steeds and Garrett., "Motor Vehicle", The English Language Book<br />
<strong>Society</strong>, Ninth Edition, 1972.<br />
4. Crouse W. H., "Automotive mechanics", Tata McGraw Hill Publishing<br />
Company Ltd, New Delhi, Ninth Edition, Delhi, 1993.<br />
5. Singh Kirpal, "Automobile Engineering Vol. II", New Chand Jain", Seventh<br />
Edition, Delhi, 1996.<br />
6. Narang G. B. S., "Automobile Engineering", S. Chand and Company Ltd, Fifth<br />
Edition, Delhi, 1995.<br />
7. Joseph Heitner, "Automotive Mechanics" CBS Publishers and Distribution,<br />
Second Edition, Delhi, 1987.<br />
8. Ballancy P. L., "Internal Combustion Engines", Khanna Publishers, Third<br />
Edition, New Delhi, 1991.<br />
9. Gill P. W., Smith J. H., et.al, "Fundamental of I.C. Engines", Oxford and IBH<br />
Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., Fourth Edition, Delhi, 1959.<br />
10. Arkhangelsky V. et.al., "Motor Vehicle Engines", MIR Publishers, Mascow,<br />
1976.
(402051): Energy Conservation and Management (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Global and Indian energy market, Energy scenario in various sectors and Indian<br />
economy. Need and importance of energy conservation and management.<br />
2. Payback period. Return on Investment (ROI). Life Cycle Cost. Sankey Diagrams.<br />
Specific Energy consumption. Load Management.<br />
3. Energy Auditing-methodology, analysis and reporting. Portable and on-line<br />
instruments.<br />
4. Costing of utilities like steam, compressed air, electricity and water.<br />
5. Steam and Condensate Systems. Boilers (including packaged boilers), efficiency,<br />
testing, excess air and flue gas monitoring. Steam distribution. Steam traps.<br />
Condensate and flashsteam utilization. Thermal insulation. Economic Thickness<br />
of Insulation (ETI). Opportunities in Process Industries for Energy conservation.<br />
6. Electrial systems: Demand control, power factor improvement, benefits and ways<br />
of improvement. Load scheduling. Electric motors, losses, efficiency, energyefficient<br />
motors, motor speed control, variable speed drive.<br />
7. Lighting: Illumination levels, fixtures, timers, energy- efficient illumination.
8. Energy conservation in compressed air systems, refrigeration and air-conditioning<br />
systems and water systems. Elementary coverage of energy conservation in<br />
pumps and fans. .<br />
9. Cogeneration-concept, options (steam/gas turbine/DCT -based). Selection criteria.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. P. H. Henderson: India-The Energy Sector, Oxford university Press.<br />
2. Albert Thumann: Plant Engineers and managers Guide to Energy Conservation.<br />
3. D. A. ray: Industrial Energy Conservation. Pergamon Press.<br />
4. Callaghan: Energy Conservation.<br />
5. IGC Dryden, editor: The efficient use of Energy (Butterworths).<br />
6. W. C. Turner, editor: Energy Management handbook (Wiley).<br />
7. Patrick Steven R., Patric Dale R., Fordo Stephen: Energy Conservation Guide<br />
book, The fairmont Press Inc.<br />
8. Energy Conservation-related booklets published by National produ~tivity<br />
Council (NPC) & Petroleum Conservation research Assn. (PCRA).<br />
9. F. William Payne and Richard E. Thompson: Efficient Boiler Operation<br />
Source Book.
(402051): Advanced Machine Design (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Theory: 100 Marks<br />
1. Cams:<br />
Disk, cylindrical and three dimensional cams-selection of base curve-uniform<br />
acceleration base curve-harmonic base curve-cycloidal base curve-cam profile<br />
layout-polynomial cams-the 3-4-5 cam-analysis of cam and follower forces-cam<br />
design.<br />
2. Springs:<br />
Helical spring of rectangular cross section- Belleville spring-rubber springscylindrical<br />
rubber springs with shear and torsional loadings.<br />
3. Gears:<br />
Gear boxes for machine tool applications- determination of variable speed rangegraphical<br />
representation of speeds-structure diagram-deviation diagram-ray<br />
diagram-selection of optimum ray diagram- difference between number of teeth<br />
of successive gears in a change gear box-analysis of twelve speed gear boxcompound<br />
ray diagram.<br />
4. Design of Hoisting Equipments:
Design loads- hooks-wire ropes and chains-drums, sheaves and sprocketsarresting<br />
gear and brakes-drives of hoisting gear-jib and luffing mechanism.<br />
5. Shrink and Press fit Assemblies:<br />
Stresses due to interference fit-torque capacity of interference fit assembly axial<br />
load for assembly-temperature rise for assembly-stress concentration due to press<br />
fit-applications of shrink and press fitted assemblies.<br />
6. Friction Drives:<br />
<strong>Mechanical</strong> friction drives-face plate variators-cone variators without<br />
intermediate member- spheroidal and cone variators with intermediate membervariators<br />
with axially displaceable cones and intermediate members like belt, ring<br />
or chain.<br />
7. System Analysis:<br />
Systems approach-mathematical model-dynamic response of lumped and<br />
distributed systems- modeling of elasticities, masses, inertias, friction and<br />
damping-mathematical model for shock analysis-stress and deflection due to<br />
impact-application of systems approach to cam and gear mechanisms.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. J. E. Shigley-'<strong>Mechanical</strong> engineering design' McGraw Hill Inc.<br />
2. M. F. Sportts-'Design of machine elements' Prentice hall Inc.<br />
3. P. H. Black and O. E. Adams-'Machine design' McGraw Hill Inc.
4. A. S. Hall, A. R. Holowenko and H. G. Laughlin- 'Theory and problems of<br />
machine design' Schaum's outline series.<br />
5. N. Rudenko-'Materials handling equipment' M.I.R. Publishers, Moscow.<br />
6. M.P. Alexandrov-'Materials handling equipment' M.I.R. Publishers, Moscow.<br />
7. S. K. Basu and D. K. Pal-'Design of machine tools' oxford and IBH Pub. Co.<br />
8. N. K. Mehta-'Machine tool design' Tata McGraw Hill Pub. Co.
(402051): Costing and Cost Control (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week Paper: 100<br />
1. Introduction:<br />
Evolution of Management Accounting elements of costs; profitability and other<br />
objectives, product services and market mix, reporting for decision making.<br />
2. Cost Allocation:<br />
Cost accumulation and allocation, allocation of service department cost,<br />
allocating cost from other departments, methods of allocation.<br />
3. Joint cost and by-products:<br />
Introduction, method of allocating joints cost, accounting of by-products.<br />
4. Replacement cost and other models:<br />
Introduction , models including discounted cash flow.<br />
5. Cost volume Profit analysis:<br />
Assumptions and interrelationship between CV and P. Deterministic modelbreak-even<br />
point including multi-product situation, production constraints.
6. Pricing and Decision Process:<br />
Opportunity cost relevance and contribution approach; incremental cost; ROI;<br />
strategic princing of new products, Full cost pricing-advantages and<br />
disadvantages.<br />
7. Cost of Quality:<br />
Prevention, internal failure, external failure costs.<br />
8. Budgetary control and variance Analysis:<br />
Material, Labour, Overhead, Sales. Profit, Product-mix and Yield Variance.<br />
9. Cost control:<br />
Capital cost control-the nature of control, elements of cost control programme,<br />
project planning and scheduling, cost reporting and corrective action. Capital cost<br />
control-repeatitive operating cost, standard costs, cost reporting and corrective<br />
action.<br />
10. Estimating of cost:<br />
Estimating of material, machining, labour and overheads costs.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Drury Colin: Management Accounting.
2. Ashton Detal : Issues in Management Accounting.<br />
3. Elphic C. : New Approach to Cost Allocation.<br />
4. Gupta P. K. & Hira D. S. : Problems in Operations 4 Research.<br />
5. Prasad N. K. : Cost Accounting.<br />
6. Kanappan D., Augstine A. G., et.al. : <strong>Mechanical</strong> Estimating and costing,<br />
McGraw Hill, New Delhi.<br />
7. Jelan F. C., Cost and Optimisation Engineering, McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
8. Manufacturing Cost Engineering Handbook-Edited by E. M. Malstrom, Marcel<br />
Dekker Inc. New York 1984.<br />
9. B. K. Bhar : Cost Accounting, Academic Publishers, Calcutta.<br />
10. J. L. Riggs: Production Systems-Planning, Analysis and Control: John Wiley<br />
and Sons.<br />
11. C. T. Horngren : Cost Accounting-A Managerial emphasis: Prentice Hall<br />
Publication.
(402051): Machine Tool Design (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Introduction:<br />
Trend in designing machine tools, classification of various machine tools-general<br />
purpose, special purpose, NC-CNC on the basis of kinematics.<br />
2. Drives:<br />
Considerations in designing drives based on continuous or intermittent<br />
requirements of power, type and selection of motor for the drive, regulation and<br />
range of speed based on preferred number series/geometric progression, design of<br />
head stock gear box for spindle drive using ray diagram, structure diagram, nodal<br />
optimisation while designing compact gearbox.<br />
3. Stepless Regulation:<br />
Electromechanical System of regulation, frictrion, pressure and ball variations,<br />
P.I.V. drive (Kopp. Variator), Epicyclic drive.<br />
4. Elements of Machine Tools:<br />
Design of-beds, slideways, carriage, tables of lathes, milling machines based on<br />
force, frictional behaviour and different types of lubrication system. Design of<br />
Power Screws-sliding as well as rolling friction spindle units, supports for
spindles, bearings, preloaded supports. Rigidity and Vibration Analysis including<br />
stickslip sliding.<br />
5. Control System:<br />
Electrical Control, push button control, directional control relays, thermal relays,<br />
electrical brakes, automation in feed mechanism. Hydraulic Control in machine<br />
tool positional movement, power pack for lubrication system in hydrostatic drive.<br />
Control systems for, gear sliding and feed mechanism (open loop or closed loop)<br />
for NC-CNC machine using stepper motor or DC motor.<br />
6. NC-CNC Machine:<br />
Introduction, construction, operation, APT programming, transducers of various<br />
type, CPU block diagram, CAD-CAM Systems interfacing.<br />
7. Flexible manufacturing System:<br />
Definition, types, classification, equipment.<br />
8. Static and Dynamic testing of Machines as per Schlesinger's tests and Tobias's<br />
Stability Envelopes.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Pal, D.K. and Basu, S.K., "Design of Machine Tools", 4th Revised Ed.,<br />
Oxford-IBH.
2. Acherkan, N.S., et.al., "Machine Tool Design", Vol.I to Vol.IV, MIR<br />
Publications.<br />
3. Mehta, N. K., "Machine Tool Design", Tata McGraw Hill.<br />
4. Bhattacharya, A. and Sen, G. C., "Principles of -; Machine Tools", New<br />
Central Book Agency, Calcutta.<br />
5. T. Kundra, Rao, P.M. Tiwari, N.K., "Numerical Control and Computer Aided<br />
Manufacturing", Tata McGraw Hill.<br />
6. Martin, S.J., "Numerical Control of Machine Tools", ELBS.
(402051): Robotics (Elective II)<br />
Teaching Scheme<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs/Week<br />
Examination Scheme<br />
Paper: 100 Marks<br />
1. Planar Mechanisms:<br />
Advanced synthesis of planar mechanisms for ISP, MSP and FSP, Burmester<br />
theories and analytical techniques, Applications.<br />
Mechanism Dynamics: Newtonian and Lagrangian techniques, Energy methods.<br />
Spatial mechanisms. Axodes, kinematics of open and closed loop mechanisms.<br />
2. Basic Concepts in Robotics:<br />
Automation and robotics, robot anatomy, basic structure of robots, resolution,<br />
accuracy and repeatability.<br />
3. Classification and structure of robotic systems:<br />
Point to point and continuous path systems. Control loops of robotic systems, the<br />
mainpulators, the wrist motions and grippers.<br />
4. Drives and Control Systems:<br />
Hydraulic systems, DC servo motors, basic control systems concepts and models,<br />
control system analysis, robot activation and fed back components. Positional and<br />
velocity sensors, actuators. Power transmission systems, robot joint control<br />
design.
5. Robot arm kinematics and dynamics:<br />
The direct kinematics problem, the inverse kinematic solution, Lagrange-Euler<br />
formation, generalised D’Alembert equations of motion, Denavit Hartenberg<br />
convention and its applications.<br />
6. Sensors in Robotics:<br />
Tactile sensors, proximity and range sensors, force and torque sensors, uses of<br />
sensors in robotics.<br />
7. Vision Systems:<br />
Vision equipment, image processing, concept of low level and high level vision.<br />
8. Robot Programming:<br />
Methods of robot programming, lead through a programming methods, a robot<br />
program as a path in space, motion interpolation, WAIT, SIGNAL and DELAY<br />
commands, branching capabilities and limitations of lead through methods.<br />
9. Robot Language:<br />
The textual robot languages, generations of robot programming languages, robot<br />
language structure, constants, variables and other data objects. Motion commands,<br />
end effectors and senor commands, computations and operations, programme<br />
control and subroutines, communications and data processing, monitor mode<br />
commands. Introduction to artificial intelligence.
10. Robot applications in manufacturing:<br />
Material transfer and machine loading/unloading, processing operations assembly<br />
and inspection. Concept of safety in robotics.<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Yoram Koren, "Robotics for Engineers", McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
2. M. P. groover, M. Weiss, R. N. Nagel, N. G. Odrey, "Industrial Robotics<br />
Technology, Programming and Applications", McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
3. K. S. Fu, R. C. Gonzalex, C.S.G. Lee, "Robotics Control Sensing, Vision and<br />
intelligence", McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
4. Hartenberg and Denavit, "Kinematics and Synthesis of Linkages", McGraw<br />
Hill Book Co.<br />
5. A. S. Hall, "Kinematics and Linkage Design", Jr.Prentice Hall.<br />
6. J. Hirchhorn, "Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery", McGraw Hill Book<br />
Co.