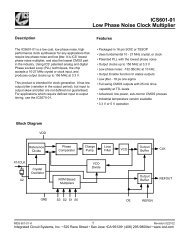
Intel PXA250 and PXA210 Applications Processors
Intel PXA250 and PXA210 Applications Processors
Intel PXA250 and PXA210 Applications Processors
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MultiMediaCard (MMC)<br />
Three other signals shown on the connector are COMM <strong>and</strong> the mechanical switches write protect<br />
(WP) <strong>and</strong> card detect (CD). WP <strong>and</strong> CD are both connected to COMM via a mechanical switch<br />
inside the socket when a device is inserted.<br />
Three other signals shown on the connector are COMM <strong>and</strong> the mechanical switches WP <strong>and</strong> CD.<br />
When a device is inserted in the example schematic (Figure 5-1), WP may be <strong>and</strong> CD is connected<br />
to COMM via a mechanical switch inside the socket<br />
SDCard devices have a write protect tab. Depending on the position of the tab, the WP signal may<br />
or may not be connected to the COMM signal. Connect the WP signal to a CPLD or other device<br />
capable of indicating to the driver software that the card is write protected. In this example,<br />
COMM is tied to a VCC <strong>and</strong> WP has a pull-down resistor. This causes a rising edge when the tab is<br />
in the write protect position <strong>and</strong> the WP signal remains low when the tab is in the read/write<br />
position.<br />
The CD signal, MMC_DETECT, indicates to the MMC controller when a card is installed. It is<br />
used for both an SDCard socket <strong>and</strong> an MMC socket. Since the MMC socket does not have the<br />
mechanical CD switch, other measures must be taken to produce a card detect. Thus, the SDCard<br />
<strong>and</strong> MMC cases are discussed separately.<br />
Note:<br />
While this schematic shows two ways to create a card detect, it is recommended that an SDCard<br />
socket be used if a card detect <strong>and</strong> write protection signal are desired even if only MMC devices<br />
are being used.<br />
5.1.2.1 SDCard Socket<br />
When using Figure 5-1, “<strong>Applications</strong> Processor MMC <strong>and</strong> SDCard Signal Connections” on<br />
page 5-3 as a template for your SDCard circuit design, all resistors labeled “DNI IF SD” should not<br />
be installed <strong>and</strong> all resistors labeled “DNI IF MMC” should be installed in the circuit. Removing<br />
R226 <strong>and</strong> inserting R225 causes the VSS2 signal on pin 6 to be tied to ground. Also, the SDCard<br />
needs a pull-down resistor in position R228.<br />
SDCard sockets have a card detect switch internal to the socket. The CD signal is physically<br />
connected to the COMM signal. Connect the CD signal to a CPLD or other device capable of<br />
indicating to the driver software that a card has been inserted in the socket. In this example,<br />
COMM is tied to a V CC <strong>and</strong> CD has a pull-down resistor. This causes a rising edge on CD when a<br />
card is inserted while the CD signal remains low if no card is in the socket.<br />
5.1.2.2 MMC Socket<br />
When using Figure 5-1, “<strong>Applications</strong> Processor MMC <strong>and</strong> SDCard Signal Connections” on<br />
page 5-3 as a template for your MMC circuit design, all resistors labeled “DNI IF MMC” should<br />
not be installed <strong>and</strong> all resistors labeled “DNI IF SD” should be installed in the circuit. This causes<br />
the VSS2 signal on pin 6 to be pulled-up through resistor R227.<br />
Unlike SDCard sockets, MMC sockets do not have a card detect or write protect switch. In order to<br />
implement this, a pull-up is placed on the VSS2 signal (pin 6 of the socket.) Since VSS2 <strong>and</strong> VSS1<br />
are connected internally on the MMC device, the signal called nMMC_DETECT on the schematic<br />
is driven low when the MMC device is inserted.<br />
5-4 <strong>PXA250</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>PXA210</strong> <strong>Applications</strong> <strong>Processors</strong> Design Guide