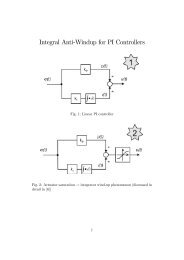
Introduction.
Introduction.
Introduction.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Workshop PG5<br />
Resources<br />
3.2.3 Constants<br />
32 bit value<br />
Integer: -2 147 483 648 to +2 147 483 647<br />
Floating decimal: -9.22337E+18 to +9.22337E+18<br />
Constants are fixed values that do not change during the program. They are<br />
written into a register.<br />
Example: fix coefficients like PI = 3.1415.<br />
The next example loads the register R 4 with a fixed value of ( 100 ). Then the<br />
register R 4 is divided by 0.25. Because the register R 4 contains an integer<br />
value and we want to divide it by a decimal value ( 0.25 ), you have to convert<br />
R4 into a decimal value. We copy R4 into R3500 (register we are sure is not<br />
being used), convert R3500 into a decimal value, and then divide R3500 by<br />
0.25. The result of the division is placed into R 5. R5 is then copied into R 6,<br />
and R6 is then converted into an integer value.<br />
How to use<br />
constants in<br />
your program:<br />
Instruction list program:<br />
FUPLA program:<br />
COB 0 ;Cyclic organization<br />
0 ; block<br />
LD R 4 ;load 100 into R 4<br />
100<br />
COPY R 4 ;convert the integer value<br />
R 3500 ;from integer to<br />
IFP R 3500 ;floating decimal<br />
0<br />
FDIV R 3500 ;divide the value by 0.25<br />
2.5e-1<br />
R 5 ; and place the result<br />
;into R5<br />
FBoxes: Integer: Move<br />
Converter: Int to float<br />
Floating decimal: Divide<br />
Converter: Float to Int<br />
COPY R 5<br />
R 6<br />
FPI R 6<br />
0<br />
ECOB<br />
;convert the result back to<br />
; integer<br />
© Saia-Burgess Controls Ltd. Page 3-6














![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)