Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Direct</strong> <strong>Torque</strong> <strong>Control</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>Space</strong> <strong>Vector</strong> <strong>Modulation</strong><br />
where:<br />
k<br />
s<br />
=<br />
2<br />
3<br />
R<br />
p<br />
= Ψ and Esy = ΩΨs Ψ<br />
s<br />
.<br />
s<br />
b<br />
Ψ , 2<br />
M<br />
e<br />
pb s<br />
Isy<br />
s<br />
3<br />
The above equations show that the<br />
U<br />
sx<br />
component has influence only on the change <strong>of</strong> stator<br />
flux magnitude<br />
Ψ<br />
s<br />
, and the component<br />
Ω<br />
U<br />
sy<br />
– if the term<br />
Ψs s<br />
Ψ is decoupled – can be<br />
used for torque adjustment. Therefore, the flux and torque quantities can be controlled as<br />
shown in Fig. 5.26.<br />
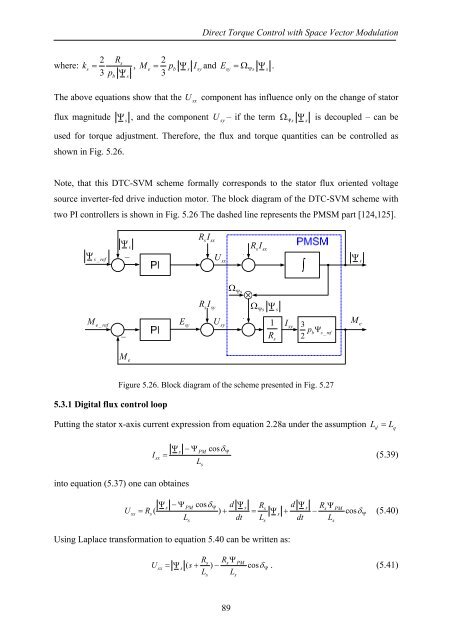
Note, that this <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> scheme formally corresponds to the stator flux oriented voltage<br />
source inverter-fed drive induction motor. The block diagram <strong>of</strong> the <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> scheme <strong>with</strong><br />
two PI controllers is shown in Fig. 5.26 The dashed line represents the PMSM part [124,125].<br />
Ψ s _ ref<br />
Ψ s<br />
_<br />
R I<br />
s<br />
sx<br />
U sx<br />
R I<br />
s<br />
sx<br />
∫<br />
Ψ s<br />
R I<br />
s<br />
sy<br />
Ω Ψs<br />
⊗<br />
Ω<br />
Ψ<br />
Ψs s<br />
M e _ ref<br />
_<br />
E sy<br />
U sy<br />
1 Isy<br />
R s<br />
3<br />
2<br />
p<br />
b<br />
Ψ<br />
s _ ref<br />
M e<br />
M e<br />
5.3.1 Digital flux control loop<br />
Figure 5.26. Block diagram <strong>of</strong> the scheme presented in Fig. 5.27<br />
Putting the stator x-axis current expression from equation 2.28a under the assumption Ld<br />
= L<br />
q<br />
into equation (5.37) one can obtaines<br />
U<br />
I<br />
sx<br />
Ψs<br />
−ΨPM<br />
cos<br />
= (5.39)<br />
L<br />
s<br />
δ Ψ<br />
Ψs −ΨPM cosδΨ<br />
d Ψs R d Ψ<br />
s s RsΨ<br />
PM<br />
= R ( ) + = Ψ + − cosδΨ<br />
(5.40)<br />
L dt L dt L<br />
sx s s<br />
s s s<br />
Using Laplace transformation to equation 5.40 can be written as:<br />
U<br />
sx<br />
Rs RsΨ<br />
PM<br />
=Ψ<br />
s<br />
( s+ ) − cosδ Ψ<br />
. (5.41)<br />
L L<br />
s<br />
s<br />
89













![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)