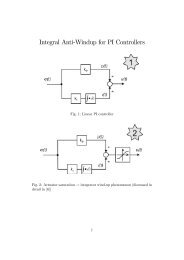
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Modeling and control modes <strong>of</strong> PM synchronous motor drives<br />
2 2 2 2 2 2<br />
d q s<br />
δI d PM s<br />
δI q s<br />
( L − L ) I cos + 2L Ψ I cos + L I = 0 (2.80)<br />
Solving for the torque angle δ<br />
I<br />
2 2 2 2 2 2<br />
d PM d PM s<br />
(<br />
d q<br />
)<br />
q<br />
−L Ψ ± L Ψ − I L −L L<br />
−1<br />
δ<br />
I<br />
= cos [ ]<br />
( L L ) I<br />
2 2<br />
d<br />
−<br />
q s<br />
(2.81)<br />
For givenδ I<br />
, the amplitude <strong>of</strong> stator voltage vector we can be calculated from equation<br />
(2.70) and amplitude <strong>of</strong> stator flux vector from (2.71). The active and reactive power<br />
and also the power factor can be obtained from equations (2.41),(2.46),(2.47),<br />
respectively for defined speed.<br />
Comparison study<br />
In order to compare the control strategies and to cancel dependence <strong>of</strong> machine power,<br />
per unit values defined as shown in Table 2.1 below have been introduced [3,9].<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> current vector:<br />
I<br />
sN<br />
= Is<br />
Is<br />
I<br />
= 2I<br />
(2.82)<br />
b<br />
srms( rated )<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> voltage vector: U<br />
s<br />
U<br />
s<br />
U<br />
sN<br />
= = (2.83)<br />
Ub ΩΨ<br />
b PM<br />
where: Ω b<br />
= 2 π f and b<br />
fb<br />
is rated frequency<br />
<strong>of</strong> the PM motor.<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> flux vector is: Ψ<br />
s<br />
Ψ<br />
s<br />
Ψ<br />
sN<br />
= =<br />
(2.84)<br />
Ψb<br />
ΨPM<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> torque is:<br />
Me<br />
Me<br />
M<br />
eN<br />
= =<br />
(2.85)<br />
M 3<br />
b pbΨ<br />
PMIb<br />
2<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> apparent power vector<br />
S S<br />
S = N<br />
S<br />
= 3<br />
(2.86)<br />
b UI<br />
b b<br />
2<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> active power<br />
P<br />
PN<br />
= (2.87)<br />
Sb<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> reactive power<br />
Q<br />
QN<br />
= (2.88)<br />
S<br />
b<br />
Table 2.1. Per unit values definition.<br />
In order to compare the steady state performance characteristic <strong>of</strong> the above discussed<br />
control strategies, for each <strong>of</strong> the control strategy some important quantities <strong>of</strong> the<br />
machine have been plotted as a function <strong>of</strong> the torque. The PMSM parameters, which<br />
are used for the calculations are given in Appendices.<br />
29














![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)