Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulation (DTC-SVM) of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
DSP implementation <strong>of</strong> <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> control<br />
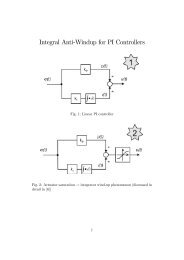
7.2 Steady state behaviour<br />
The experimental steady state no load operation at 25Hz stator frequency for<br />
conventional ST-<strong>DTC</strong> (Fig. 4.10) and <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> (Fig. 5.46b) control is presented in<br />
Fig. 7.5. The sampling time has been set at T = 200µ<br />
s for <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> and T = 25µ<br />
s for<br />
hysteresis based ST-<strong>DTC</strong> method, respectively.<br />
a)<br />
s<br />
s<br />
b)<br />
Figure 7.5. No load experimental steady state oscillograms at stator frequency 25Hz.<br />
(a) ST-<strong>DTC</strong> for T = 25µ<br />
s (b) <strong>DTC</strong>-<strong>SVM</strong> for T = 200µ<br />
s.<br />
s<br />
From the top: line to line voltage, phase current, amplitude <strong>of</strong> stator flux, motor torque.<br />
s<br />
As we can observed from Fig. 7.5a the motor phase current characterized by high<br />
current ripples. This is mainly because the inductances <strong>of</strong> the PMSM is smaller than an<br />
equivalent power induction motor IM. In order to reduce the current ripples the<br />
140














![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)