Urban Green Areas – their functions under a changing lifestyle of ...
Urban Green Areas – their functions under a changing lifestyle of ... Urban Green Areas – their functions under a changing lifestyle of ...
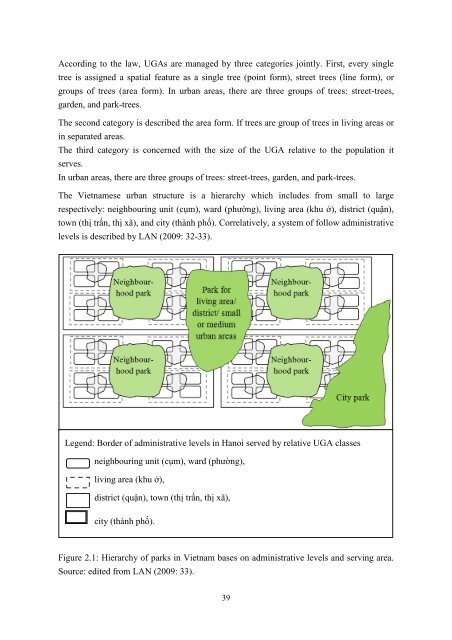
According to the law, UGAs are managed by three categories jointly. First, every single tree is assigned a spatial feature as a single tree (point form), street trees (line form), or groups of trees (area form). In urban areas, there are three groups of trees: street-trees, garden, and park-trees. The second category is described the area form. If trees are group of trees in living areas or in separated areas. The third category is concerned with the size of the UGA relative to the population it serves. In urban areas, there are three groups of trees: street-trees, garden, and park-trees. The Vietnamese urban structure is a hierarchy which includes from small to large respectively: neighbouring unit (cụm), ward (phường), living area (khu ở), district (quận), town (thị trấn, thị xã), and city (thành phố). Correlatively, a system of follow administrative levels is described by LAN (2009: 32-33). Legend: Border of administrative levels in Hanoi served by relative UGA classes neighbouring unit (cụm), ward (phường), living area (khu ở), district (quận), town (thị trấn, thị xã), city (thành phố). Figure 2.1: Hierarchy of parks in Vietnam bases on administrative levels and serving area. Source: edited from LAN (2009: 33). 39
As showing in the Figure 2.1, some single trees (Picture 2.7) and street-trees (green lines shown by the less green colour areas) improve local environment. In the higher level (the neighbourhood unit) most of UGAs are garden-trees. In the inner-city there are some street-trees which are not covered by the construction-law of Vietnam. Picture 2.7: Tree with name and registered number. Source: own picture (2012) Within a ward, there are also park-trees in addition to the street-trees, and garden-trees. Those UGAs’ have the functions of improving environmental quality and satisfying the recreational needs of the residents. The average area of each park is from one to six ha. In a district unit, there is a central park with multiple functions. This central park has elements of multi-functional parks, in terms of standard green area (5-7 m 2 / person), total area (40- 100 ha in district and small towns, 50-240 ha in larger district towns). Under such a structure, in large urban areas, city-parks play a multifunctional role of environmental improvement and recreation service for local people. The area of a city-park, which serves the city’s residents, is about 10-100 km 2 . Parks & gardens In this research, parks and gardens are mostly focused on. Very often parks and gardens are not distinguished by names. For example, Versailles sometimes is named as park, sometimes is named as garden. Parks are well defined by DUNNETT (2002: 51): “Park – the basic unit of urban recreational area, which is larger than 2 ha. Comprises the green space, together with a planned path structure and different organized leisure areas, is well equipped, able to receive large numbers of visitors and to accommodate public events. Park usually includes water features such as lakes, streams, fountains and diversified forms of greenery with different sized groups of trees shrubs, flower beds, meadows, laws, etc”. EVERT (2001: 463) gives an overview with clear definitions of parks & gardens. He indicates that in Europe, areas of open space are characterized by tree cover and extensive areas of lawn or meadow, which has been designated for preservation of natural features and/or for public or private recreational use. While in US, a natural or man-made area with trees and meadows is preserved and managed for its scenic and recreational benefit. A garden, in this view, is an area of land planted and cultivated with ornamental plants, fruits 40
- Page 9 and 10: Abstract Hanoi is a rapidly develop
- Page 11 and 12: Abstrakt Hanoi ist eine expandieren
- Page 13 and 14: Tóm tắt Hà Nội đang phát tr
- Page 15 and 16: List of Figure: Figure 1.1: Implica
- Page 17 and 18: (% of responding people)………
- Page 19 and 20: List of Pictures Picture 1.1a: Tran
- Page 21 and 22: n.n. Nov. No author November R- Rec
- Page 23 and 24: 1.1 Hanoi - the city under study Vi
- Page 25 and 26: Table 1.1: Climate indicators (2006
- Page 27 and 28: The administrative organization and
- Page 29 and 30: 1.2.1.4 Period 1964-1974 (see CHIEN
- Page 31 and 32: 10 BACH THAO PARK HOAN KIEM PARK TH
- Page 33 and 34: This “2020 Hanoi master plan” s
- Page 35 and 36: Figure 1.6: Organisation of Hanoi C
- Page 37 and 38: After that Hanoi citizens become mo
- Page 39 and 40: to predict the future demand of UGA
- Page 41 and 42: Figure 1.8: Sources of data Source:
- Page 43 and 44: Observations are systematically pla
- Page 45 and 46: (SUPPITAKSAKUL et al. 2006; VISSCHE
- Page 47 and 48: esearch fields in developed countri
- Page 49 and 50: 2 Urban green areas (UGAs) UGAS are
- Page 51 and 52: 2.1.1.7 Ancient Roman gardens Those
- Page 53 and 54: trees were not planted in rows whil
- Page 55 and 56: elements from earlier English, Fren
- Page 57 and 58: In the early modern period, the spr
- Page 59: esponsible administrative level, et
- Page 63 and 64: and quantity of the available trees
- Page 65 and 66: surround. That is most intensive fo
- Page 67 and 68: First, rubbish accumulates in ill m
- Page 69 and 70: There are several approaches to con
- Page 71 and 72: Table 2.3: Publications about urban
- Page 73 and 74: BINH 2012). In 1986, Vietnamese gov
- Page 75 and 76: impact on the thinking and behaviou
- Page 77 and 78: The resulting homogeneous social st
- Page 79 and 80: for further understanding of lifest
- Page 81 and 82: y religion, e.g.: catholic lifestyl
- Page 83 and 84: some aspects of their lifestyle as
- Page 85 and 86: low-income and immigrant communitie
- Page 87 and 88: observe is activity of people. Ther
- Page 89 and 90: eality, each activity is done to sa
- Page 91 and 92: 4 Recent utilization of parks and g
- Page 93 and 94: (% of the time) 70 60 50 40 30 20 1
- Page 95 and 96: area (m 2 ) The collected data by t
- Page 97 and 98: (% of the entire week) 4.1.5 Expert
- Page 99 and 100: share of park users every hour 16%
- Page 101 and 102: These findings can be understood by
- Page 103 and 104: Social statuses of the visitors mig
- Page 105 and 106: Others, 5.8% from work/ school/ uni
- Page 107 and 108: Share of means of transportation 10
- Page 109 and 110: Regarding the age of visitors it ca
According to the law, UGAs are managed by three categories jointly. First, every single<br />
tree is assigned a spatial feature as a single tree (point form), street trees (line form), or<br />
groups <strong>of</strong> trees (area form). In urban areas, there are three groups <strong>of</strong> trees: street-trees,<br />
garden, and park-trees.<br />
The second category is described the area form. If trees are group <strong>of</strong> trees in living areas or<br />
in separated areas.<br />
The third category is concerned with the size <strong>of</strong> the UGA relative to the population it<br />
serves.<br />
In urban areas, there are three groups <strong>of</strong> trees: street-trees, garden, and park-trees.<br />
The Vietnamese urban structure is a hierarchy which includes from small to large<br />
respectively: neighbouring unit (cụm), ward (phường), living area (khu ở), district (quận),<br />
town (thị trấn, thị xã), and city (thành phố). Correlatively, a system <strong>of</strong> follow administrative<br />
levels is described by LAN (2009: 32-33).<br />
Legend: Border <strong>of</strong> administrative levels in Hanoi served by relative UGA classes<br />
neighbouring unit (cụm), ward (phường),<br />
living area (khu ở),<br />
district (quận), town (thị trấn, thị xã),<br />
city (thành phố).<br />
Figure 2.1: Hierarchy <strong>of</strong> parks in Vietnam bases on administrative levels and serving area.<br />
Source: edited from LAN (2009: 33).<br />
39