Films minces à base de Si nanostructuré pour des cellules ...
Films minces à base de Si nanostructuré pour des cellules ...
Films minces à base de Si nanostructuré pour des cellules ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
multilayered conguration. Therefore, the (SRSO+SRSN) pattern thickness of the<br />
multilayer was calculated and found to be 8.8 nm.<br />
This value is close to the expected pattern thickness of 8.5 nm (3.5 nm + 5 nm)<br />
indicating that, the pattern thickness can be estimated from XRR technique to a<br />
high <strong>de</strong>gree of accuracy. Hence most of the MLs in this thesis were investigated by<br />
XRR.<br />
4.5.3 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy<br />
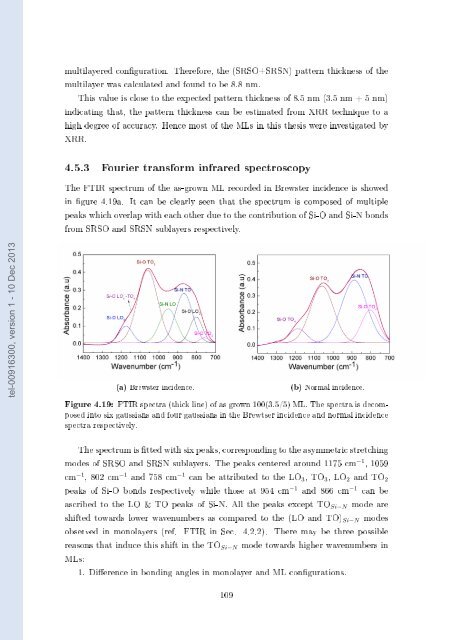
The FTIR spectrum of the as-grown ML recor<strong>de</strong>d in Brewster inci<strong>de</strong>nce is showed<br />
in gure 4.19a. It can be clearly seen that the spectrum is composed of multiple<br />
peaks which overlap with each other due to the contribution of <strong>Si</strong>-O and <strong>Si</strong>-N bonds<br />
from SRSO and SRSN sublayers respectively.<br />
tel-00916300, version 1 - 10 Dec 2013<br />
(a) Brewster inci<strong>de</strong>nce.<br />
(b) Normal inci<strong>de</strong>nce.<br />
Figure 4.19: FTIR spectra (thick line) of as grown 100(3.5/5) ML. The spectra is <strong>de</strong>composed<br />
into six gaussians and four gaussians in the Brewtser inci<strong>de</strong>nce and normal inci<strong>de</strong>nce<br />
spectra respectively.<br />
The spectrum is tted with six peaks, corresponding to the asymmetric stretching<br />
mo<strong>de</strong>s of SRSO and SRSN sublayers. The peaks centered around 1175 cm −1 , 1059<br />
cm −1 , 802 cm −1 and 758 cm −1 can be attributed to the LO 3 , TO 3 , LO 2 and TO 2<br />
peaks of <strong>Si</strong>-O bonds respectively while those at 954 cm −1 and 866 cm −1 can be<br />
ascribed to the LO & TO peaks of <strong>Si</strong>-N. All the peaks except TO <strong>Si</strong>−N mo<strong>de</strong> are<br />
shifted towards lower wavenumbers as compared to the (LO and TO) <strong>Si</strong>−N mo<strong>de</strong>s<br />
observed in monolayers (ref. FTIR in Sec. 4.2.2). There may be three possible<br />
reasons that induce this shift in the TO <strong>Si</strong>−N mo<strong>de</strong> towards higher wavenumbers in<br />
MLs:<br />
1. Dierence in bonding angles in monolayer and ML congurations.<br />
109