MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Design rules<br />
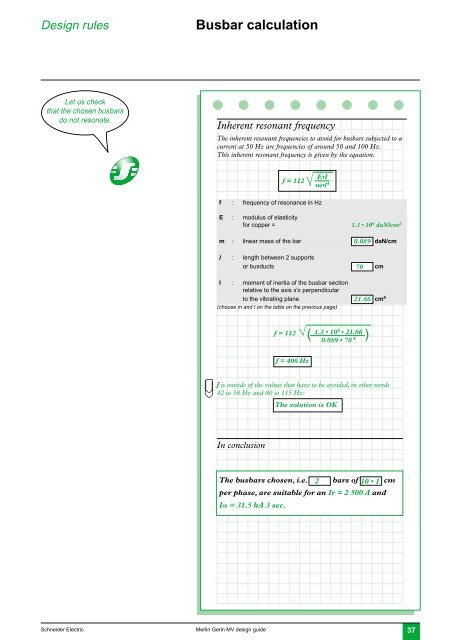
Busbar calculation<br />
Let us check<br />
that the chosen busbars<br />
do not resonate.<br />
Inherent resonant frequency<br />
The inherent resonant frequencies to avoid for busbars subjected to a<br />
current at 50 Hz are frequencies of around 50 and 100 Hz.<br />
This inherent resonant frequency is given by the equation:<br />
f = 112<br />
E•I<br />
m•l 4<br />
f : frequency of resonance in Hz<br />
E : modulus of elasticity<br />
for copper = 1.3 • 10 6 daN/cm 2<br />
m : linear mass of the bar 0.089 daN/cm<br />
l : length between 2 supports<br />
or busducts 70 cm<br />
I : moment of inertia of the busbar section<br />
relative to the axis x'x perpendicular<br />
to the vibrating plane 21.66 cm 4<br />
(choose m and I on the table on the previous page)<br />
f = 112 1.3 • 10 6 • 21.66<br />
( )<br />
0.089 • 70 4<br />
f = 406 Hz<br />
f is outside of the values that have to be avoided, in other words<br />
42 to 58 Hz and 80 to 115 Hz:<br />
The solution is OK<br />
In conclusion<br />
The busbars chosen, i.e. 2 bars of 10 • 1 cm<br />
per phase, are suitable for an Ir = 2 500 A and<br />
Ith = 31.5 kA 3 sec.<br />
<strong>Schneider</strong> <strong>Electric</strong><br />
Merlin Gerin <strong>MV</strong> <strong>design</strong> <strong>guide</strong><br />
37