MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Design rules<br />
Short-circuit currents<br />
Transformer<br />
In order to determine the short-circuit current across the terminals<br />
of a transformer, we need to know the short-circuit voltage (Usc %).<br />
c Usc % is defined in the following way:<br />
The short-circuit current depends on<br />
the type of equipment installed on<br />
the network (transformers,<br />
generators, motors, lines, etc).<br />
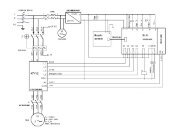
potentiometer<br />
U : 0 to Usc<br />
V<br />
primary<br />
secondary<br />
A<br />
I : 0 to Ir<br />
Example:<br />
c Transformer 20 <strong>MV</strong>A<br />
c Voltage 10 kV<br />
c Usc = 10 %<br />
c Upstream power: infinite<br />
Ir =<br />
Sr 20 000<br />
= = 1 150 A<br />
e U no-load e•10<br />
Isc =<br />
Ir<br />
=<br />
1 150<br />
= 11 500 A = 11.5 kA<br />
Usc 10÷100<br />
1 the voltage transformer is not powered: U = 0<br />
2 place the secondary in short-circuit<br />
3 gradually increase voltage U at the primary up to the rated current Ir in<br />
the transformer secondary circuit.<br />
The value U read across the primary is then equal to Usc<br />
c The short-circuit current, expressed in kA, is given by the following<br />
equation:<br />
Ir<br />
Isc =<br />
Usc<br />
<strong>Schneider</strong> <strong>Electric</strong><br />
Merlin Gerin <strong>MV</strong> <strong>design</strong> <strong>guide</strong><br />
13