MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Design rules<br />
Short-circuit power<br />
E<br />
Example 1:<br />
25 kA at an operating voltage of 11 kV<br />
R<br />
Zcc<br />
Icc<br />
L<br />
A<br />
U<br />
Zs<br />
Introduction<br />
c The short-circuit power depends directly on the network configuration<br />
and the impedance of its components:<br />
lines, cables, transformers, motors... through which the short-circuit<br />
current passes.<br />
c It is the maximum power that the network can provide to an installation<br />
during a fault, expressed in <strong>MV</strong>A or in kA rms for a given operating<br />
voltage.<br />
Ssc = e • U • Isc<br />
B<br />
U : operating voltage (kV)<br />
Isc : short-circuit current (kA rms.) Ref: following pages<br />
The short-circuit power can be assimilated to an apparent power.<br />
c The customer generally imposes the value of short-circuit power on us<br />
because we rarely have the information required to calculate it.<br />
Determination of the short-circuit power requires analysis of the power<br />
flows feeding the short-circuit in the worst possible case.<br />
Possible sources are:<br />
c Network incomer via power transformers.<br />
c Generator incomer.<br />
c Power feedback due to rotary sets (motors, etc);<br />
or via <strong>MV</strong>/LV transformaters.<br />
63 kV<br />
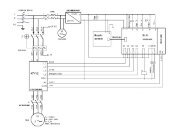
Example 2:<br />
c Feedback via LV Isc5 is only<br />
possible if the transformer (T4)<br />
is powered by another source.<br />
c Three sources are flowing in the<br />
switchboard (T1-A-T2)<br />
v circuit breaker D1 (s/c at A)<br />
Isc1 + Isc2 + Isc3 + Isc4 + Isc5<br />
v circuit breaker D2 (c/c at B)<br />
Isc1 + Isc2 + Isc3 + Isc4 + Isc5<br />
v circuit breaker D3 (c/c at C)<br />
Isc1 + Isc2 + Isc3 + Isc4 + Isc5<br />
T1<br />
A<br />
T2<br />
Isc1 Isc2 Isc3<br />
A B C<br />
D1<br />
D2<br />
D3<br />
10 kV<br />
D6<br />
MT<br />
D4 D5 D7<br />
T3<br />
M<br />
Isc5<br />
Isc4<br />
BT<br />
BT<br />
T4<br />
MT<br />
We have to calculate each of the Isc currents.<br />
<strong>Schneider</strong> <strong>Electric</strong><br />
Merlin Gerin <strong>MV</strong> <strong>design</strong> <strong>guide</strong><br />
11