Integrating MEG, EEG and fMRI data
Integrating MEG, EEG and fMRI data
Integrating MEG, EEG and fMRI data
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
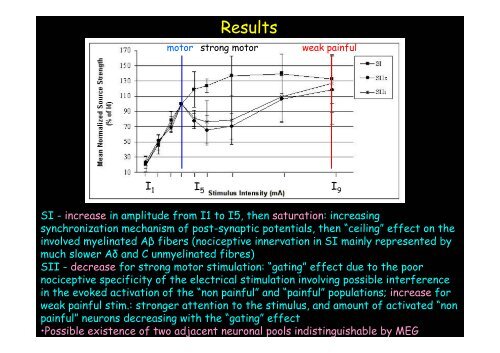
Results<br />
motor strong motor weak painful<br />
I 1 I 5<br />
I 9<br />
SI - increase in amplitude from I1 to I5, then saturation: increasing<br />
synchronization mechanism of post-synaptic potentials, then “ceiling” effect on the<br />
involved myelinated Aβ fibers (nociceptive innervation in SI mainly represented by<br />
much slower Aδ <strong>and</strong> C unmyelinated fibres)<br />
SII - decrease for strong motor stimulation: “gating” effect due to the poor<br />
nociceptive specificity of the electrical stimulation involving possible interference<br />
in the evoked activation of the “non painful” <strong>and</strong> “painful” populations; increase for<br />
weak painful stim.: stronger attention to the stimulus, <strong>and</strong> amount of activated “non<br />
painful” neurons decreasing with the “gating” effect<br />
•Possible existence of two adjacent neuronal pools indistinguishable by <strong>MEG</strong>