Facing China's Coal Future - IEA
Facing China's Coal Future - IEA
Facing China's Coal Future - IEA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
© OECD/<strong>IEA</strong> 2012 <strong>Facing</strong> China’s <strong>Coal</strong> <strong>Future</strong><br />
Prospects and Challenges for Carbon Capture and Storage<br />
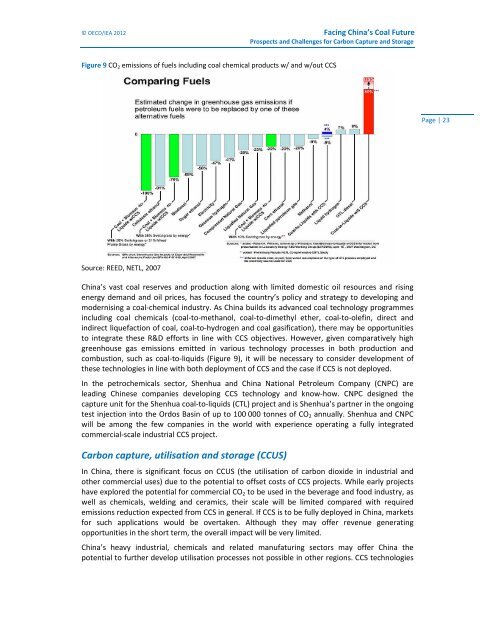
Figure 9 CO 2 emissions of fuels including coal chemical products w/ and w/out CCS<br />
Page | 23<br />
Source: REED, NETL, 2007<br />
China’s vast coal reserves and production along with limited domestic oil resources and rising<br />
energy demand and oil prices, has focused the country’s policy and strategy to developing and<br />
modernising a coal‐chemical industry. As China builds its advanced coal technology programmes<br />
including coal chemicals (coal‐to‐methanol, coal‐to‐dimethyl ether, coal‐to‐olefin, direct and<br />
indirect liquefaction of coal, coal‐to‐hydrogen and coal gasification), there may be opportunities<br />
to integrate these R&D efforts in line with CCS objectives. However, given comparatively high<br />
greenhouse gas emissions emitted in various technology processes in both production and<br />
combustion, such as coal‐to‐liquids (Figure 9), it will be necessary to consider development of<br />
these technologies in line with both deployment of CCS and the case if CCS is not deployed.<br />
In the petrochemicals sector, Shenhua and China National Petroleum Company (CNPC) are<br />
leading Chinese companies developing CCS technology and know‐how. CNPC designed the<br />
capture unit for the Shenhua coal‐to‐liquids (CTL) project and is Shenhua’s partner in the ongoing<br />
test injection into the Ordos Basin of up to 100 000 tonnes of CO 2 annually. Shenhua and CNPC<br />
will be among the few companies in the world with experience operating a fully integrated<br />
commercial‐scale industrial CCS project.<br />
Carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS)<br />
In China, there is significant focus on CCUS (the utilisation of carbon dioxide in industrial and<br />
other commercial uses) due to the potential to offset costs of CCS projects. While early projects<br />
have explored the potential for commercial CO 2 to be used in the beverage and food industry, as<br />
well as chemicals, welding and ceramics, their scale will be limited compared with required<br />
emissions reduction expected from CCS in general. If CCS is to be fully deployed in China, markets<br />
for such applications would be overtaken. Although they may offer revenue generating<br />
opportunities in the short term, the overall impact will be very limited.<br />
China’s heavy industrial, chemicals and related manufaturing sectors may offer China the<br />
potential to further develop utilisation processes not possible in other regions. CCS technologies