The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
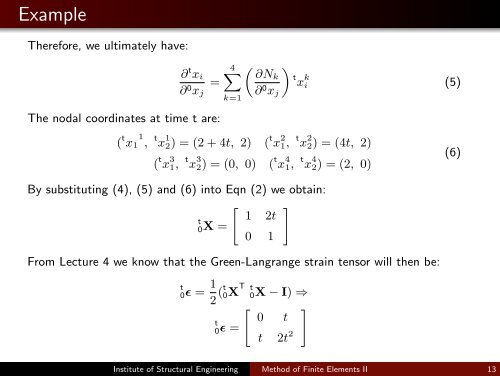
Example<br />
<strong>The</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e, we ultimately have:<br />
∂ t x i<br />
∂ 0 x j<br />
=<br />
<strong>The</strong> nodal coordinates at time t are:<br />
4∑<br />
k=1<br />
( ) ∂Nk t x k<br />
∂ 0 i (5)<br />
x j<br />
( t x 1<br />
1<br />
, t x 1 2) = (2 + 4t, 2) ( t x 2 1, t x 2 2) = (4t, 2)<br />
( t x 3 1, t x 3 2) = (0, 0) ( t x 4 1, t x 4 2) = (2, 0)<br />
(6)<br />
By substituting (4), (5) <strong>and</strong> (6) into Eqn (2) we obtain:<br />
[ ]<br />
t 1 2t<br />
0X =<br />
0 1<br />
From Lecture 4 we know that <strong>the</strong> Green-Langrange strain tensor will <strong>the</strong>n be:<br />
t<br />
0ɛ = 1 2 (t 0X T t 0X − I) ⇒<br />
[ ]<br />
t 0 t<br />
0ɛ =<br />
t 2t 2<br />
Institute <strong>of</strong> Structural Engineering <strong>Method</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Finite</strong> <strong>Element</strong>s II 13