Thesis-PDF - IAP/TU Wien
Thesis-PDF - IAP/TU Wien
Thesis-PDF - IAP/TU Wien
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
6.2 AFM data and cell features<br />
Below some images in AFM xy-mode are presented. They clearly demonstrate the<br />
convenience of Atomic Force Microscopy as a tool for high resolution imaging of<br />
E. gracilis cells. AFM data could be acquired of various features of the Euglena<br />
gracilis cell, including cell walls, mucus excretion pellicle pores, crystalline cell<br />
parts and new surface features not previously reported or visible on SEM/TEM<br />
images available in the literature.<br />
Fusing pellicle strips<br />
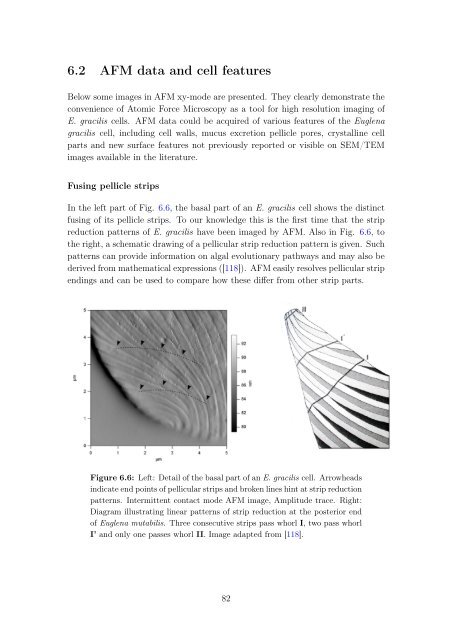
In the left part of Fig. 6.6, the basal part of an E. gracilis cell shows the distinct<br />
fusing of its pellicle strips. To our knowledge this is the first time that the strip<br />
reduction patterns of E. gracilis have been imaged by AFM. Also in Fig. 6.6, to<br />
the right, a schematic drawing of a pellicular strip reduction pattern is given. Such<br />
patterns can provide information on algal evolutionary pathways and may also be<br />
derived from mathematical expressions ([118]). AFM easily resolves pellicular strip<br />
endings and can be used to compare how these differ from other strip parts.<br />
Figure 6.6: Left: Detail of the basal part of an E. gracilis cell. Arrowheads<br />
indicate end points of pellicular strips and broken lines hint at strip reduction<br />
patterns. Intermittent contact mode AFM image, Amplitude trace. Right:<br />
Diagram illustrating linear patterns of strip reduction at the posterior end<br />
of Euglena mutabilis. Three consecutive strips pass whorl I, two pass whorl<br />
I’ and only one passes whorl II. Image adapted from [118].<br />
82