LIFE01200604005 Shri Somnath Ghosh - Homi Bhabha National ...
LIFE01200604005 Shri Somnath Ghosh - Homi Bhabha National ...
LIFE01200604005 Shri Somnath Ghosh - Homi Bhabha National ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
14 S. <strong>Ghosh</strong> et al. / Mutation Research 716 (2011) 10–19<br />
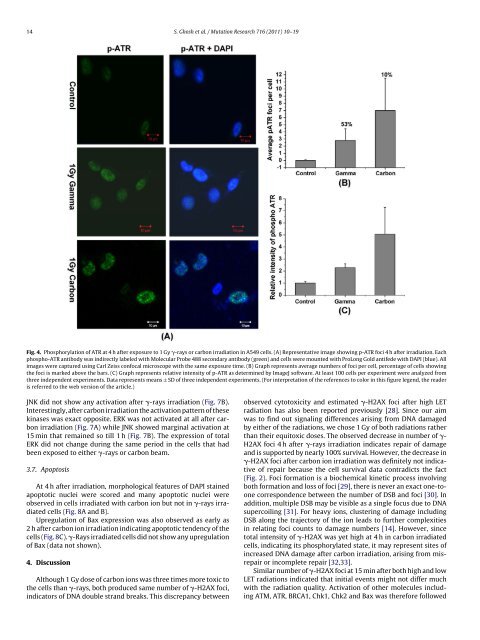
Fig. 4. Phosphorylation of ATR at 4 h after exposure to 1 Gy -rays or carbon irradiation in A549 cells. (A) Representative image showing p-ATR foci 4 h after irradiation. Each<br />
phospho-ATR antibody was indirectly labeled with Molecular Probe 488 secondary antibody (green) and cells were mounted with ProLong Gold antifede with DAPI (blue). All<br />
images were captured using Carl Zeiss confocal microscope with the same exposure time. (B) Graph represents average numbers of foci per cell, percentage of cells showing<br />
the foci is marked above the bars. (C) Graph represents relative intensity of p-ATR as determined by ImageJ software. At least 100 cells per experiment were analyzed from<br />
three independent experiments. Data represents means ± SD of three independent experiments. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader<br />
is referred to the web version of the article.)<br />
JNK did not show any activation after -rays irradiation (Fig. 7B).<br />
Interestingly, after carbon irradiation the activation pattern of these<br />
kinases was exact opposite. ERK was not activated at all after carbon<br />
irradiation (Fig. 7A) while JNK showed marginal activation at<br />
15 min that remained so till 1 h (Fig. 7B). The expression of total<br />
ERK did not change during the same period in the cells that had<br />
been exposed to either -rays or carbon beam.<br />
3.7. Apoptosis<br />
At 4 h after irradiation, morphological features of DAPI stained<br />
apoptotic nuclei were scored and many apoptotic nuclei were<br />
observed in cells irradiated with carbon ion but not in -rays irradiated<br />
cells (Fig. 8A and B).<br />
Upregulation of Bax expression was also observed as early as<br />
2 h after carbon ion irradiation indicating apoptotic tendency of the<br />
cells (Fig. 8C). -Rays irradiated cells did not show any upregulation<br />
of Bax (data not shown).<br />
4. Discussion<br />
Although 1 Gy dose of carbon ions was three times more toxic to<br />
the cells than -rays, both produced same number of -H2AX foci,<br />
indicators of DNA double strand breaks. This discrepancy between<br />
observed cytotoxicity and estimated -H2AX foci after high LET<br />
radiation has also been reported previously [28]. Since our aim<br />
was to find out signaling differences arising from DNA damaged<br />
by either of the radiations, we chose 1 Gy of both radiations rather<br />
than their equitoxic doses. The observed decrease in number of -<br />
H2AX foci 4 h after -rays irradiation indicates repair of damage<br />
and is supported by nearly 100% survival. However, the decrease in<br />
-H2AX foci after carbon ion irradiation was definitely not indicative<br />
of repair because the cell survival data contradicts the fact<br />
(Fig. 2). Foci formation is a biochemical kinetic process involving<br />
both formation and loss of foci [29], there is never an exact one-toone<br />
correspondence between the number of DSB and foci [30]. In<br />
addition, multiple DSB may be visible as a single focus due to DNA<br />
supercoiling [31]. For heavy ions, clustering of damage including<br />
DSB along the trajectory of the ion leads to further complexities<br />
in relating foci counts to damage numbers [14]. However, since<br />
total intensity of -H2AX was yet high at 4 h in carbon irradiated<br />
cells, indicating its phosphorylated state, it may represent sites of<br />
increased DNA damage after carbon irradiation, arising from misrepair<br />
or incomplete repair [32,33].<br />
Similar number of -H2AX foci at 15 min after both high and low<br />
LET radiations indicated that initial events might not differ much<br />
with the radiation quality. Activation of other molecules including<br />
ATM, ATR, BRCA1, Chk1, Chk2 and Bax was therefore followed