Download File
Download File Download File
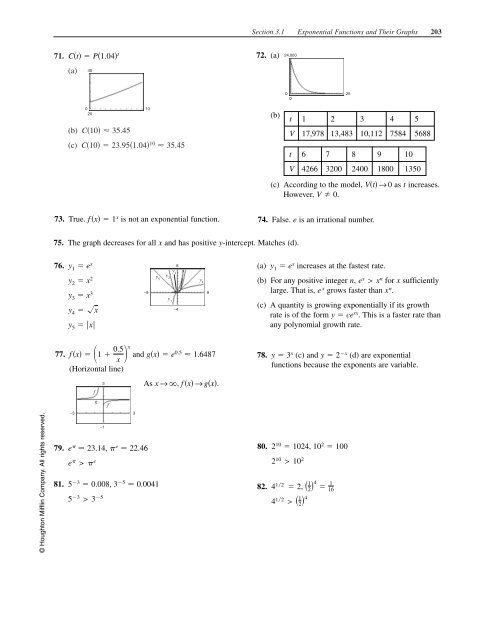
Section 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 203 71. Ct P1.04 t 72. (a) 24,000 (a) 40 0 25 0 (b) 0 20 C10 35.45 (c) C10 23.951.04 10 35.45 10 (b) t V t 1 2 3 4 5 17,978 13,483 10,112 7584 5688 6 7 8 9 10 V 4266 3200 2400 1800 1350 (c) According to the model, Vt → 0 as t increases. However, V 0. 73. True. f x 1 x is not an exponential function. 74. False. e is an irrational number. 75. The graph decreases for all x and has positive y-intercept. Matches (d). 76. y 8 1 e x (a) y y 1 e x increases at the fastest rate. 1 y 2 x 2 y y 5 2 y4 (b) For any positive integer n, e x > x n y 3 x 3 −9 9 large. That is, e x grows faster than y 3 y 4 x y 5 x −4 for x sufficiently x n . (c) A quantity is growing exponentially if its growth rate is of the form y ce rx . This is a faster rate than any polynomial growth rate. © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 77. f x 1 0.5 and gx e 0.5 1.6487 x x 78. y 3 x (c) and y 2 x (d) are exponential functions because the exponents are variable. (Horizontal line) 79. 81. 3 f g f −3 3 −1 e > e As x →, f x → gx. e 23.14, e 22.4680. 5 3 0.008, 3 5 0.0041 82. 5 3 > 3 5 2 10 1024, 10 2 100 2 10 > 10 2 4 12 2, 1 2 4 1 16 4 12 > 1 2 4
204 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 83. f has an inverse because f is one-to-one. y 5x 7 x 5y 7 x 7 5y f 1 x 1 5x 7 84. f is one-to-one, so it has an inverse. f x 2 3 x 5 2 y 2 3 x 5 2 x 2 3 y 5 2 x 5 2 2 3 y 3 2x 5 2 y f 1 x 3 2 x 15 4 85. f has an inverse because f is one-to-one. 86. f is not one-to-one, so it does not have an inverse. y 3 x 8 x 3 y 8 x 3 y 8 x 3 8 y f 1 x x 3 8 87. f x 2x x 7 Vertical asymptote: x 7 Horizontal asymptote: y 2 Intercept: 0, 0 12 10 8 6 4 2 −4 −2 y 6 8 10 12 14 16 x −4 −6 −8 88. f x x2 3 x 1 x 1 4 x 1 y Slant asymptote: y x 1 Vertical asymptote: x 1 Intercept: 0, 3 89. Answers will vary. −10 −8 −6 −4 −2 2 2 4 6 8 10 x © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
- Page 1 and 2: CHAPTER 3 Exponential and Logarithm
- Page 3 and 4: 194 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 5 and 6: 196 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 7 and 8: 198 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 9 and 10: 200 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 11: 202 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 15 and 16: 206 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 17 and 18: 208 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 19 and 20: 210 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 21 and 22: 212 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 23 and 24: 214 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 25 and 26: 216 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 27 and 28: 218 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 29 and 30: 220 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 31 and 32: 222 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 33 and 34: 224 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 35 and 36: 226 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 37 and 38: 228 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 39 and 40: 230 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 41 and 42: 232 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 43 and 44: 234 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 45 and 46: 236 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 47 and 48: 238 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 49 and 50: 240 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 51 and 52: 242 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 53 and 54: 244 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 55 and 56: 246 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 57 and 58: 248 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 59 and 60: 250 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
- Page 61 and 62: 252 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logar
Section 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 203<br />
71.<br />
Ct P1.04 t<br />
72. (a)<br />
24,000<br />
(a)<br />
40<br />
0 25<br />
0<br />
(b)<br />
0<br />
20<br />
C10 35.45<br />
(c) C10 23.951.04 10 35.45<br />
10<br />
(b)<br />
t<br />
V<br />
t<br />
1 2 3 4 5<br />
17,978 13,483 10,112 7584 5688<br />
6 7 8 9 10<br />
V<br />
4266 3200 2400 1800 1350<br />
(c) According to the model, Vt → 0 as t increases.<br />
However, V 0.<br />
73. True. f x 1 x is not an exponential function.<br />
74. False. e is an irrational number.<br />
75. The graph decreases for all x and has positive y-intercept. Matches (d).<br />
76.<br />
y 8<br />
1 e x (a) y<br />
y 1 e x increases at the fastest rate.<br />
1<br />
y 2 x 2<br />
y y<br />
5 2<br />
y4<br />
(b) For any positive integer n, e x > x n<br />
y 3 x 3<br />
−9<br />
9<br />
large. That is, e x grows faster than<br />
y 3<br />
y 4 x<br />
y 5 x <br />
−4<br />
for x sufficiently<br />
x n .<br />
(c) A quantity is growing exponentially if its growth<br />
rate is of the form y ce rx . This is a faster rate than<br />
any polynomial growth rate.<br />
© Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.<br />
77. f x 1 0.5 and gx e 0.5 1.6487<br />
x x<br />
78. y 3 x (c) and y 2 x (d) are exponential<br />
functions because the exponents are variable.<br />
(Horizontal line)<br />
79.<br />
81.<br />
3<br />
f<br />
g<br />
f<br />
−3<br />
3<br />
−1<br />
e<br />
><br />
<br />
e<br />
As x →, f x → gx.<br />
e<br />
23.14, e<br />
22.4680.<br />
5 3 0.008, 3 5 0.0041 82.<br />
5 3 > 3 5<br />
2 10 1024, 10 2 100<br />
2 10 > 10 2<br />
4 12 2, 1 2 4 1 16<br />
4 12 > 1 2 4