Report
Report
Report
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
14 QUANTIFICATION OF BENEFITS FROM ECONOMIC COOPERATION IN SOUTH ASIA<br />
1.9). This is mainly due to the free trade agreement<br />
between the two nations, its geographical proximity,<br />
free current account convertibility between its currency<br />
and Indian rupees and generous grants from India.<br />
Table 1.9 Top Export Markets of Bhutan<br />
(in Million Nu), 2000–03<br />
Countries 2000 2001 2002 2003<br />
India 4376.95 4700.47 5153.78 5188.23<br />
Bangladesh 164.72 222.38 222.97 120.83<br />
Nepal 28.44 41.51 32.79 14.19<br />
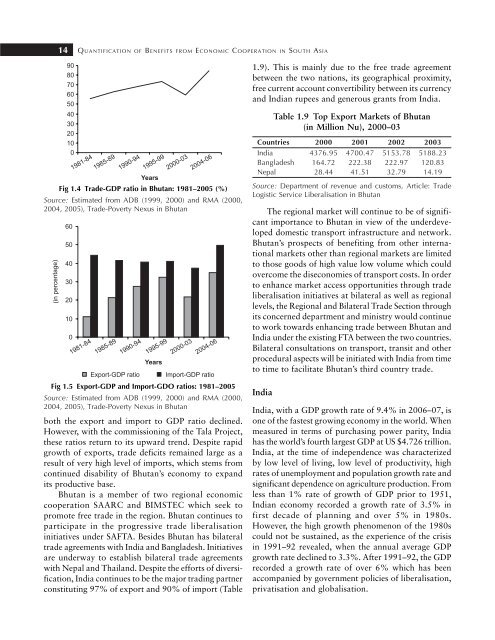
Fig 1.4 Trade-GDP ratio in Bhutan: 1981–2005 (%)<br />
Source: Estimated from ADB (1999, 2000) and RMA (2000,<br />
2004, 2005), Trade-Poverty Nexus in Bhutan<br />
Fig 1.5 Export-GDP and Import-GDO ratios: 1981–2005<br />
Source: Estimated from ADB (1999, 2000) and RMA (2000,<br />
2004, 2005), Trade-Poverty Nexus in Bhutan<br />
both the export and import to GDP ratio declined.<br />
However, with the commissioning of the Tala Project,<br />
these ratios return to its upward trend. Despite rapid<br />
growth of exports, trade deficits remained large as a<br />
result of very high level of imports, which stems from<br />
continued disability of Bhutan’s economy to expand<br />
its productive base.<br />
Bhutan is a member of two regional economic<br />
cooperation SAARC and BIMSTEC which seek to<br />
promote free trade in the region. Bhutan continues to<br />
participate in the progressive trade liberalisation<br />
initiatives under SAFTA. Besides Bhutan has bilateral<br />
trade agreements with India and Bangladesh. Initiatives<br />
are underway to establish bilateral trade agreements<br />
with Nepal and Thailand. Despite the efforts of diversification,<br />
India continues to be the major trading partner<br />
constituting 97% of export and 90% of import (Table<br />
Source: Department of revenue and customs, Article: Trade<br />
Logistic Service Liberalisation in Bhutan<br />
The regional market will continue to be of significant<br />
importance to Bhutan in view of the underdeveloped<br />
domestic transport infrastructure and network.<br />
Bhutan’s prospects of benefiting from other international<br />
markets other than regional markets are limited<br />
to those goods of high value low volume which could<br />
overcome the diseconomies of transport costs. In order<br />
to enhance market access opportunities through trade<br />
liberalisation initiatives at bilateral as well as regional<br />
levels, the Regional and Bilateral Trade Section through<br />
its concerned department and ministry would continue<br />
to work towards enhancing trade between Bhutan and<br />
India under the existing FTA between the two countries.<br />
Bilateral consultations on transport, transit and other<br />
procedural aspects will be initiated with India from time<br />
to time to facilitate Bhutan’s third country trade.<br />
India<br />
India, with a GDP growth rate of 9.4% in 2006–07, is<br />
one of the fastest growing economy in the world. When<br />
measured in terms of purchasing power parity, India<br />
has the world’s fourth largest GDP at US $4.726 trillion.<br />
India, at the time of independence was characterized<br />
by low level of living, low level of productivity, high<br />
rates of unemployment and population growth rate and<br />
significant dependence on agriculture production. From<br />
less than 1% rate of growth of GDP prior to 1951,<br />
Indian economy recorded a growth rate of 3.5% in<br />
first decade of planning and over 5% in 1980s.<br />
However, the high growth phenomenon of the 1980s<br />
could not be sustained, as the experience of the crisis<br />
in 1991–92 revealed, when the annual average GDP<br />
growth rate declined to 3.3%. After 1991–92, the GDP<br />
recorded a growth rate of over 6% which has been<br />
accompanied by government policies of liberalisation,<br />
privatisation and globalisation.