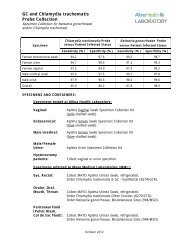
Human (Granulocytic) Anaplasmosis (HGA ... - Allina Health
Human (Granulocytic) Anaplasmosis (HGA ... - Allina Health
Human (Granulocytic) Anaplasmosis (HGA ... - Allina Health
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Infected individuals may be asymptomatic. Symptoms/signs of the disease may include hemolysis,<br />
high fever, chills, muscle aches/arthralgias, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite,<br />
nausea and vomiting. More extreme expressions of disease include hypotension, hepatic<br />
dysfunction, renal failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation, multiorgan failure and<br />
death.<br />
Supportive laboratory findings may include hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, and elevated LFTs.<br />
Treatment:<br />
According to the CDC, most patients who are asymptompatic do not require treatment. Early<br />
diagnosis and treatment of symptomatic patients may reduce the length of illness and severity<br />
of disease. CDC recommendations include assistance from infectious disease specialists<br />
and antimicrobial drugs: Atovaquone + azithromycin for mild to moderate cases or<br />
Clindamycin + quinine for severe cases, usually for 7-10 days, although repeat treatment or<br />
monitoring of parasitemia may be necessary for some patients (immunocompromised, for<br />
example). Please see CDC or MDH web sites for dosing recommendations.<br />
Additionally, those patients with severe illness may require or benefit from supportive care<br />
such as: vasopressors, antipyretics, blood transfusions, exchange transfusions, dialysis, and<br />
mechanical ventilation.<br />
Laboratory Diagnosis:<br />
Bear in mind that some patients may be simultaneously infected with more than one tickborne<br />
infection.<br />
7