Slides - Åbo Akademi
Slides - Åbo Akademi Slides - Åbo Akademi
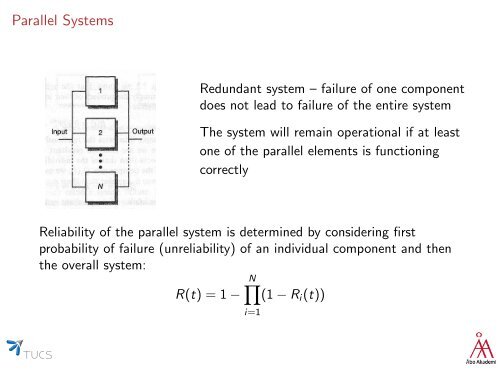
Parallel Systems Redundant system – failure of one component does not lead to failure of the entire system The system will remain operational if at least one of the parallel elements is functioning correctly Reliability of the parallel system is determined by considering first probability of failure (unreliability) of an individual component and then the overall system: N∏ R(t) = 1 − (1 − R i (t)) i=1
Series-Parallel Combinations The most common in practice. Any systems may be simplified, i.e., reduced to a single component A series-parallel arrangement: (a) The original arrangement (b) The result of combining parallel modules (c) The result of combining the series modules The overall reliability of the system is represented by that of module 13
- Page 1 and 2: Software Safety Lecture 8: System R
- Page 3 and 4: Reliability Definition Reliability:
- Page 5 and 6: Safety-critical Systems • Pervasi
- Page 7 and 8: Hardware Failures The system is sai
- Page 9 and 10: Failure Rate (ctd.) Classification
- Page 11 and 12: Most Important Distributions Discre
- Page 13 and 14: Reliability Parameters MTTF: Mean T
- Page 15 and 16: Exponential Distribution The distri
- Page 17 and 18: MTTF Example A system with a consta
- Page 19 and 20: Example: Failure Rate Calculation F
- Page 21: Series Systems Such a configuration
- Page 25 and 26: M-of-N Arrangement A system consist
- Page 27 and 28: Failure rate The term failure inten
- Page 29 and 30: Design diversity Each variant of so
Parallel Systems<br />
Redundant system – failure of one component<br />
does not lead to failure of the entire system<br />
The system will remain operational if at least<br />
one of the parallel elements is functioning<br />
correctly<br />
Reliability of the parallel system is determined by considering first<br />
probability of failure (unreliability) of an individual component and then<br />
the overall system:<br />
N∏<br />
R(t) = 1 − (1 − R i (t))<br />
i=1