genomewide characterization of host-pathogen interactions by ...
genomewide characterization of host-pathogen interactions by ...
genomewide characterization of host-pathogen interactions by ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Maren Depke<br />
Results<br />
Host Cell Gene Expression Pattern in an in vitro Infection Model<br />
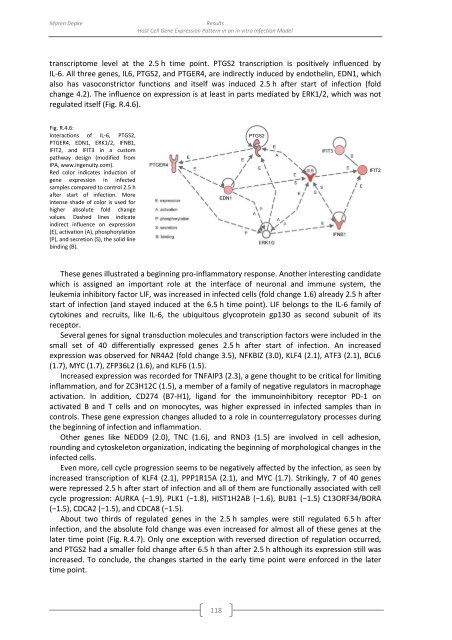
transcriptome level at the 2.5 h time point. PTGS2 transcription is positively influenced <strong>by</strong><br />
IL-6. All three genes, IL6, PTGS2, and PTGER4, are indirectly induced <strong>by</strong> endothelin, EDN1, which<br />
also has vasoconstrictor functions and itself was induced 2.5 h after start <strong>of</strong> infection (fold<br />
change 4.2). The influence on expression is at least in parts mediated <strong>by</strong> ERK1/2, which was not<br />
regulated itself (Fig. R.4.6).<br />
Fig. R.4.6:<br />
Interactions <strong>of</strong> IL-6, PTGS2,<br />
PTGER4, EDN1, ERK1/2, IFNB1,<br />
IFIT2, and IFIT3 in a custom<br />
pathway design (modified from<br />
IPA, www.ingenuity.com).<br />
Red color indicates induction <strong>of</strong><br />
gene expression in infected<br />
samples compared to control 2.5 h<br />
after start <strong>of</strong> infection. More<br />
intense shade <strong>of</strong> color is used for<br />
higher absolute fold change<br />
values. Dashed lines indicate<br />
indirect influence on expression<br />
(E), activation (A), phosphorylation<br />
(P), and secretion (S), the solid line<br />
binding (B).<br />
These genes illustrated a beginning pro-inflammatory response. Another interesting candidate<br />
which is assigned an important role at the interface <strong>of</strong> neuronal and immune system, the<br />
leukemia inhibitory factor LIF, was increased in infected cells (fold change 1.6) already 2.5 h after<br />
start <strong>of</strong> infection (and stayed induced at the 6.5 h time point). LIF belongs to the IL-6 family <strong>of</strong><br />
cytokines and recruits, like IL-6, the ubiquitous glycoprotein gp130 as second subunit <strong>of</strong> its<br />
receptor.<br />
Several genes for signal transduction molecules and transcription factors were included in the<br />
small set <strong>of</strong> 40 differentially expressed genes 2.5 h after start <strong>of</strong> infection. An increased<br />
expression was observed for NR4A2 (fold change 3.5), NFKBIZ (3.0), KLF4 (2.1), ATF3 (2.1), BCL6<br />
(1.7), MYC (1.7), ZFP36L2 (1.6), and KLF6 (1.5).<br />
Increased expression was recorded for TNFAIP3 (2.3), a gene thought to be critical for limiting<br />
inflammation, and for ZC3H12C (1.5), a member <strong>of</strong> a family <strong>of</strong> negative regulators in macrophage<br />
activation. In addition, CD274 (B7-H1), ligand for the immunoinhibitory receptor PD-1 on<br />
activated B and T cells and on monocytes, was higher expressed in infected samples than in<br />
controls. These gene expression changes alluded to a role in counterregulatory processes during<br />
the beginning <strong>of</strong> infection and inflammation.<br />
Other genes like NEDD9 (2.0), TNC (1.6), and RND3 (1.5) are involved in cell adhesion,<br />
rounding and cytoskeleton organization, indicating the beginning <strong>of</strong> morphological changes in the<br />
infected cells.<br />
Even more, cell cycle progression seems to be negatively affected <strong>by</strong> the infection, as seen <strong>by</strong><br />
increased transcription <strong>of</strong> KLF4 (2.1), PPP1R15A (2.1), and MYC (1.7). Strikingly, 7 <strong>of</strong> 40 genes<br />
were repressed 2.5 h after start <strong>of</strong> infection and all <strong>of</strong> them are functionally associated with cell<br />
cycle progression: AURKA (−1.9), PLK1 (−1.8), HIST1H2AB (−1.6), BUB1 (−1.5) C13ORF34/BORA<br />
(−1.5), CDCA2 (−1.5), and CDCA8 (−1.5).<br />
About two thirds <strong>of</strong> regulated genes in the 2.5 h samples were still regulated 6.5 h after<br />
infection, and the absolute fold change was even increased for almost all <strong>of</strong> these genes at the<br />
later time point (Fig. R.4.7). Only one exception with reversed direction <strong>of</strong> regulation occurred,<br />
and PTGS2 had a smaller fold change after 6.5 h than after 2.5 h although its expression still was<br />
increased. To conclude, the changes started in the early time point were enforced in the later<br />
time point.<br />
118