Etude de la combustion de gaz de synthèse issus d'un processus de ...
Etude de la combustion de gaz de synthèse issus d'un processus de ... Etude de la combustion de gaz de synthèse issus d'un processus de ...
Chapter 2 Biomass Gas Drying Pyrolysis Reduction Oxidation Grate Oxidant Figure 2.3 – Updraft gasifier Ashs tel-00623090, version 1 - 13 Sep 2011 The advantages of updraft gasification are: - simple, low cost process; - able to handle biomass with a high moisture and high inorganic content; - proven technology. The primary disadvantage of updraft gasification is: - syngas contains 10-20% tar by weight, requiring extensive syngas cleanup before engine, turbine or synthesis applications. Downdraft Downdraft gasification also known as co-current-flow gasification is simple, reliable and proven for certain fuels. The downdraft gasifier has the same mechanical configuration as the updraft gasifier except that the oxidant and product gases flow down the reactor, in the same direction as the biomass. A major difference is that this process can combust up to 99 % of the tars formed (Reed and Das, 1988). Low moisture biomass (
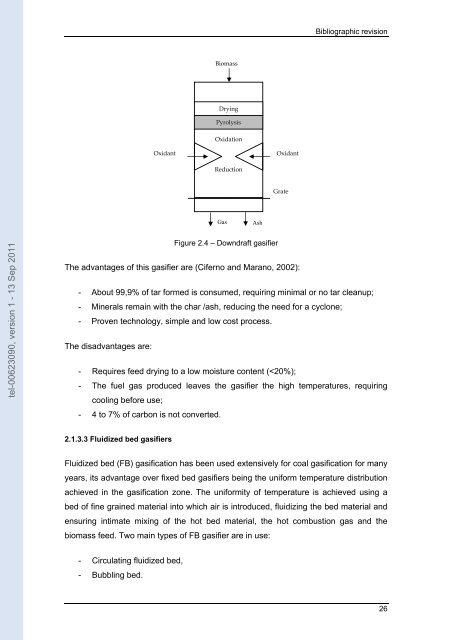
Bibliographic revision Biomass Drying Pyrolysis Oxidation Oxidant Oxidant Reduction Grate Gas Ash tel-00623090, version 1 - 13 Sep 2011 Figure 2.4 – Downdraft gasifier The advantages of this gasifier are (Ciferno and Marano, 2002): - About 99,9% of tar formed is consumed, requiring minimal or no tar cleanup; - Minerals remain with the char /ash, reducing the need for a cyclone; - Proven technology, simple and low cost process. The disadvantages are: - Requires feed drying to a low moisture content (
- Page 1 and 2: THÈSE Pour l’obtention du Grade
- Page 3 and 4: Acknowledgements Acknowledgements T
- Page 5 and 6: Résumé __________________________
- Page 7 and 8: Nomenclature Nomenclature Roman tel
- Page 9 and 10: Nomenclature Subscripts tel-0062309
- Page 11 and 12: Contents tel-00623090, version 1 -
- Page 13 and 14: Contents 6.4. SYNGAS FUELLED-ENGINE
- Page 15 and 16: Introduction CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
- Page 17 and 18: Introduction proves to have higher
- Page 19 and 20: Introduction Chapter 3 - Experiment
- Page 21 and 22: Bibliographic revision CHAPTER 2 BI
- Page 23 and 24: Bibliographic revision point today
- Page 25 and 26: Bibliographic revision - Boudouard
- Page 27: Bibliographic revision Table 2.1 -
- Page 31 and 32: Bibliographic revision Circulating
- Page 33 and 34: Bibliographic revision or eliminate
- Page 35 and 36: Bibliographic revision established
- Page 37 and 38: Bibliographic revision Hydrogen Hyd
- Page 39 and 40: Bibliographic revision of low moist
- Page 41 and 42: Bibliographic revision scrubbing an
- Page 43 and 44: Bibliographic revision suggests tha
- Page 45 and 46: Bibliographic revision 1 d( δ A) 1
- Page 47 and 48: Bibliographic revision Since n is
- Page 49 and 50: Bibliographic revision 2 ( rsr ) 2
- Page 51 and 52: Bibliographic revision This evoluti
- Page 53 and 54: Bibliographic revision The burning
- Page 55 and 56: Bibliographic revision δVG = − a
- Page 57 and 58: Bibliographic revision 2 1 − −
- Page 59 and 60: Bibliographic revision where the su
- Page 61 and 62: Bibliographic revision the stretche
- Page 63 and 64: Bibliographic revision burning velo
- Page 65 and 66: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 67 and 68: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 69 and 70: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 71 and 72: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 73 and 74: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 75 and 76: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
- Page 77 and 78: Experimental set ups and diagnostic
Bibliographic revision<br />
Biomass<br />
Drying<br />
Pyrolysis<br />
Oxidation<br />
Oxidant<br />
Oxidant<br />
Reduction<br />
Grate<br />
Gas<br />
Ash<br />
tel-00623090, version 1 - 13 Sep 2011<br />
Figure 2.4 – Downdraft gasifier<br />
The advantages of this gasifier are (Ciferno and Marano, 2002):<br />
- About 99,9% of tar formed is consumed, requiring minimal or no tar cleanup;<br />
- Minerals remain with the char /ash, reducing the need for a cyclone;<br />
- Proven technology, simple and low cost process.<br />
The disadvantages are:<br />
- Requires feed drying to a low moisture content (