- Page 1 and 2: NOVEL APPROACHES TO EXPRESSION AND
- Page 3 and 4: TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Page 5 and 6: 2.2.3 Statistical Analyses ........
- Page 7 and 8: 5.3 RESULTS .......................
- Page 9 and 10: Furthermore, automated software was
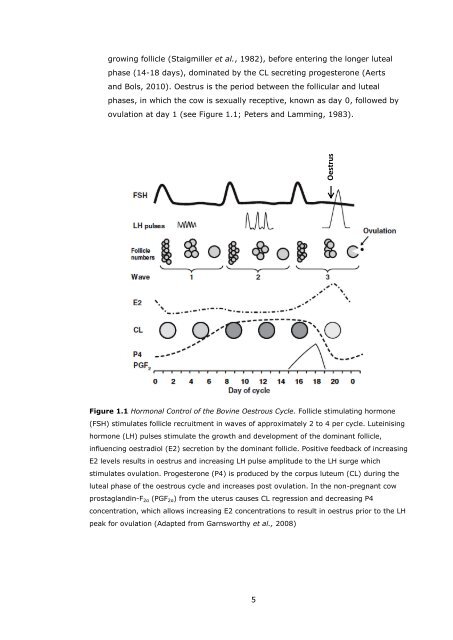
- Page 11 and 12: LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1.1 Hormonal
- Page 13 and 14: LIST OF TABLES Table 1.1 Trends in
- Page 15 and 16: LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS ˚ ˚C μM 2D
- Page 17 and 18: CHAPTER 1 - Introduction & Literatu
- Page 19: the past 50 years and duration of o
- Page 23 and 24: ecomes the main inhibitor of FSH an
- Page 25 and 26: calf at 40-50 days post partum; inv
- Page 27 and 28: al., 2006). However, aged sperm hav
- Page 29 and 30: can occur within 2-3 days, but if t
- Page 31 and 32: educes the incidence of problem cow
- Page 33 and 34: oestradiol, the LH surge and ovulat
- Page 35 and 36: The secondary signs of oestrus can
- Page 37 and 38: There are also changes in normal be
- Page 39 and 40: engage in more natural behaviours i
- Page 41 and 42: 1983). Exact explanations and mecha
- Page 43 and 44: 2006) and disruption of LH secretio
- Page 45 and 46: 1.4.3.2 Milk Yield and Nutrition Di
- Page 47 and 48: influence the ability of the ovary
- Page 49 and 50: cyclicity can be delayed if dietary
- Page 51 and 52: indication for the optimal time to
- Page 53 and 54: calving), 3) pre-breeding heat date
- Page 55 and 56: 1.5.2 Physiological Changes Physiol
- Page 57 and 58: 1.5.2.3 Body and Milk Temperature T
- Page 59 and 60: physical activity and stage of the
- Page 61 and 62: caused by the general environment t
- Page 63 and 64: may be gained. This is because data
- Page 65 and 66: In summary the objective was to for
- Page 67 and 68: diet, with concentrates at milking.
- Page 69 and 70: oestrus was defined as 3 consecutiv
- Page 71 and 72:
The interaction between parity and
- Page 73 and 74:
individual oestrus was not signific
- Page 75 and 76:
Table 2.4 The effects of the intera
- Page 77 and 78:
(361 vs. 578 points, respectively,
- Page 79 and 80:
oestrous expression with increasing
- Page 81 and 82:
the blood (Sangsritavong et al., 20
- Page 83 and 84:
CHAPTER 3 - Single Nucleotide Polym
- Page 85 and 86:
population owing to previous select
- Page 87 and 88:
Table 3.1 Cont. Follicle Stimulatin
- Page 89 and 90:
3.2.4 Sequencing of DNA in the Labo
- Page 91 and 92:
was achieved. PCR products were rem
- Page 93 and 94:
3.4 DISCUSSION The objectives of th
- Page 95 and 96:
fertility and oestrous expression.
- Page 97 and 98:
CHAPTER 4 - Development of a Novel
- Page 99 and 100:
In summary UWB seems a good option
- Page 101 and 102:
Initial tests were carried out to i
- Page 103 and 104:
Therefore this demonstrates that X
- Page 105 and 106:
which is most important for achievi
- Page 107 and 108:
Figure 4.9 Horizontal - Vertical Di
- Page 109 and 110:
that UWB is matching the ‘truth
- Page 111 and 112:
mounting cow. For example height ch
- Page 113 and 114:
Backpack 1 st put on in AI stalls E
- Page 115 and 116:
Cows’ behaviour was assessed at 5
- Page 117 and 118:
or that the cows were in an area of
- Page 119 and 120:
plane, but mostly in achieving high
- Page 121 and 122:
Develop techniques for analysis of
- Page 123 and 124:
in elastic silicone moulded over a
- Page 125 and 126:
and time of mount, duration of moun
- Page 127 and 128:
observed matched with increases in
- Page 129 and 130:
5.3 RESULTS Results demonstrate pos
- Page 131 and 132:
Figure 5.2 Graph showing mounting b
- Page 133 and 134:
Table 5.1 Results from POC 2 showin
- Page 135 and 136:
Table 5.3 Efficiency and accuracy o
- Page 137 and 138:
oestrus and oestrus it is clear to
- Page 139 and 140:
P4 Concentration, ng/ml P4 Concentr
- Page 141 and 142:
P4 Concentration, ng/ml P4 Concentr
- Page 143 and 144:
P4 Concentration, ng/ml P4 Concentr
- Page 145 and 146:
P4 Concentration, ng/ml P4 Concentr
- Page 147 and 148:
Activity Activity Activity Activity
- Page 149 and 150:
Activity Activity Activity Activity
- Page 151 and 152:
Activity Activity Activity Activity
- Page 153 and 154:
5.4 DISCUSSION The aim of this work
- Page 155 and 156:
averaged 70% which was lower than t
- Page 157 and 158:
when the cows lie down, especially
- Page 159 and 160:
the level of oestrous activity was
- Page 161 and 162:
technology larger herds must be mon
- Page 163 and 164:
monitoring could also monitor non-l
- Page 165 and 166:
antennae which could affect accurac
- Page 167 and 168:
predispose cows to illness e.g. met
- Page 169 and 170:
CHAPTER 6 - Overall Discussion & Co
- Page 171 and 172:
oestrus, h 2 =0.27 (Lovendahl et al
- Page 173 and 174:
The final section of this thesis de
- Page 175 and 176:
ate. By using UWB in a commercial s
- Page 177 and 178:
provides an insight the potential o
- Page 179 and 180:
BLOWEY, R. (2005) Factors associate
- Page 181 and 182:
ovine gonadotrophin releasing hormo
- Page 183 and 184:
GINTHER, O. J., KOT, K., KULICK, L.
- Page 185 and 186:
associated with embryonic survival
- Page 187 and 188:
ody condition at parturition on end
- Page 189 and 190:
Signs in a 24-h Tie-Stalled Dairy H
- Page 191 and 192:
SHERMAN, E. L., NKRUMAH, J. D., MUR
- Page 193 and 194:
Influence of negative energy balanc