Characteristics: Triac - nptel
Characteristics: Triac - nptel
Characteristics: Triac - nptel
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
A<br />
A<br />
A<br />
I A<br />
G<br />
p<br />
n -<br />
p<br />
n + n +<br />
K<br />
(a)<br />
p<br />
J 1<br />
n -<br />
J 2<br />
p<br />
n -<br />
G<br />
J 2<br />
J 3 p<br />
n +<br />
K<br />
(b)<br />
J 3<br />
i C2<br />
(α 2 ) Q 2<br />
I K<br />
K<br />
(c)<br />
Q 1 (α 1 )<br />
i C1<br />
I G<br />
G<br />
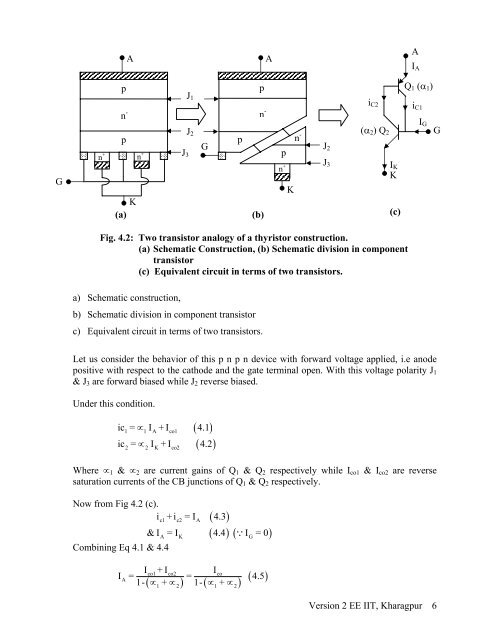
Fig. 4.2: Two transistor analogy of a thyristor construction.<br />
(a) Schematic Construction, (b) Schematic division in component<br />
transistor<br />
(c) Equivalent circuit in terms of two transistors.<br />
a) Schematic construction,<br />
b) Schematic division in component transistor<br />
c) Equivalent circuit in terms of two transistors.<br />
Let us consider the behavior of this p n p n device with forward voltage applied, i.e anode<br />
positive with respect to the cathode and the gate terminal open. With this voltage polarity J 1<br />
& J 3 are forward biased while J 2 reverse biased.<br />
Under this condition.<br />
2 2 K co2<br />
( )<br />
( )<br />
ic<br />
1= ∝1I A+ I<br />
co1<br />
4.1<br />
ic = ∝ I + I 4.2<br />
Where ∝ 1 & ∝ 2 are current gains of Q 1 & Q 2 respectively while I co1 & I co2 are reverse<br />
saturation currents of the CB junctions of Q 1 & Q 2 respectively.<br />
Now from Fig 4.2 (c).<br />
i<br />
c1<br />
+ i<br />
c2<br />
= I<br />
A ( 4.3)<br />
& I<br />
A<br />
= I<br />
K ( 4.4 ) ( ∵ I<br />
G<br />
= 0)<br />
Combining Eq 4.1 & 4.4<br />
I +I I<br />
( )<br />
co1 co2 co<br />
I<br />
A<br />
= = 4.5<br />
1- ( ∝1+ ∝2) 1- ( ∝1+<br />
∝2)<br />
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 6