Preventive Resettlement of Populations at Risk of Disaster - GFDRR
Preventive Resettlement of Populations at Risk of Disaster - GFDRR
Preventive Resettlement of Populations at Risk of Disaster - GFDRR
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
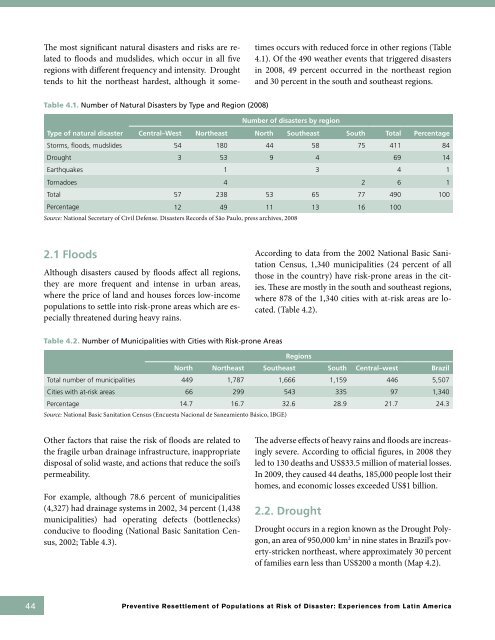
The most significant n<strong>at</strong>ural disasters and risks are rel<strong>at</strong>ed<br />
to floods and mudslides, which occur in all five<br />
regions with different frequency and intensity. Drought<br />
tends to hit the northeast hardest, although it sometimes<br />
occurs with reduced force in other regions (Table<br />
4.1). Of the 490 we<strong>at</strong>her events th<strong>at</strong> triggered disasters<br />
in 2008, 49 percent occurred in the northeast region<br />
and 30 percent in the south and southeast regions.<br />
Table 4.1. Number <strong>of</strong> N<strong>at</strong>ural <strong>Disaster</strong>s by Type and Region (2008)<br />
Number <strong>of</strong> disasters by region<br />
Type <strong>of</strong> n<strong>at</strong>ural disaster Central–West Northeast North Southeast South Total Percentage<br />
Storms, floods, mudslides 54 180 44 58 75 411 84<br />
Drought 3 53 9 4 69 14<br />
Earthquakes 1 3 4 1<br />
Tornadoes 4 2 6 1<br />
Total 57 238 53 65 77 490 100<br />
Percentage 12 49 11 13 16 100<br />
Source: N<strong>at</strong>ional Secretary <strong>of</strong> Civil Defense. <strong>Disaster</strong>s Records <strong>of</strong> São Paulo, press archives, 2008<br />
2.1 Floods<br />
Although disasters caused by floods affect all regions,<br />
they are more frequent and intense in urban areas,<br />
where the price <strong>of</strong> land and houses forces low-income<br />
popul<strong>at</strong>ions to settle into risk-prone areas which are especially<br />
thre<strong>at</strong>ened during heavy rains.<br />
According to d<strong>at</strong>a from the 2002 N<strong>at</strong>ional Basic Sanit<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
Census, 1,340 municipalities (24 percent <strong>of</strong> all<br />
those in the country) have risk-prone areas in the cities.<br />
These are mostly in the south and southeast regions,<br />
where 878 <strong>of</strong> the 1,340 cities with <strong>at</strong>-risk areas are loc<strong>at</strong>ed.<br />
(Table 4.2).<br />
Table 4.2. Number <strong>of</strong> Municipalities with Cities with <strong>Risk</strong>-prone Areas<br />
Regions<br />
North Northeast Southeast South Central–west Brazil<br />
Total number <strong>of</strong> municipalities 449 1,787 1,666 1,159 446 5,507<br />
Cities with <strong>at</strong>-risk areas 66 299 543 335 97 1,340<br />
Percentage 14.7 16.7 32.6 28.9 21.7 24.3<br />
Source: N<strong>at</strong>ional Basic Sanit<strong>at</strong>ion Census (Encuesta Nacional de Saneamiento Básico, IBGE)<br />
Other factors th<strong>at</strong> raise the risk <strong>of</strong> floods are rel<strong>at</strong>ed to<br />
the fragile urban drainage infrastructure, inappropri<strong>at</strong>e<br />
disposal <strong>of</strong> solid waste, and actions th<strong>at</strong> reduce the soil’s<br />
permeability.<br />
For example, although 78.6 percent <strong>of</strong> municipalities<br />
(4,327) had drainage systems in 2002, 34 percent (1,438<br />
municipalities) had oper<strong>at</strong>ing defects (bottlenecks)<br />
conducive to flooding (N<strong>at</strong>ional Basic Sanit<strong>at</strong>ion Census,<br />
2002; Table 4.3).<br />
The adverse effects <strong>of</strong> heavy rains and floods are increasingly<br />
severe. According to <strong>of</strong>ficial figures, in 2008 they<br />
led to 130 de<strong>at</strong>hs and US$33.5 million <strong>of</strong> m<strong>at</strong>erial losses.<br />
In 2009, they caused 44 de<strong>at</strong>hs, 185,000 people lost their<br />
homes, and economic losses exceeded US$1 billion.<br />
2.2. Drought<br />
Drought occurs in a region known as the Drought Polygon,<br />
an area <strong>of</strong> 950,000 km 2 in nine st<strong>at</strong>es in Brazil’s poverty-stricken<br />
northeast, where approxim<strong>at</strong>ely 30 percent<br />
<strong>of</strong> families earn less than US$200 a month (Map 4.2).<br />
44 <strong>Preventive</strong> <strong>Resettlement</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Popul<strong>at</strong>ions</strong> <strong>at</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Disaster</strong>: Experiences from L<strong>at</strong>in America