Frayer Model (PDF)
Frayer Model (PDF)
Frayer Model (PDF)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
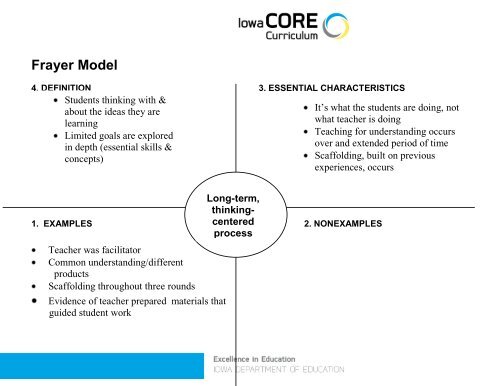
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Students thinking with &<br />
about the ideas they are<br />
learning<br />
Limited goals are explored<br />
in depth (essential skills &<br />
concepts)<br />
It’s : what the students are doing, not<br />
what teacher is doing<br />
Teaching for understanding occurs<br />
over and extended period of time<br />
Scaffolding, built on previous<br />
experiences, occurs<br />
Long-term,<br />
thinkingcentered<br />
1. EXAMPLES<br />
process<br />
2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
Teacher was facilitator<br />
Common understanding/different<br />
products<br />
Scaffolding throughout three rounds<br />
Evidence of teacher prepared materials that<br />
guided student work
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Assessment about deep understanding<br />
occurs throughout the learning process<br />
from beginning to end to guide instruction<br />
and student learning, giving specific detail<br />
about how to move to the next step<br />
Ongoing : criteria, feedback, reflection<br />
teacher teacher<br />
developed student<br />
st. constructed peers<br />
guides student & guides teacher<br />
Learning<br />
Rich, ongoing<br />
1. EXAMPLES 2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
assessment<br />
Students-review resource cards to select<br />
the right info<br />
End of unit for grading<br />
Peer to peer discussions of reading & questions<br />
Teaching without assessment<br />
Check for understanding(ask ? of table groups)<br />
Make list of materials<br />
Should we allow them to come in?<br />
El Salvador-symbolism in project<br />
Instruction
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Conceptual models that<br />
demonstrate understanding<br />
Assisting : students in solving<br />
nonroutine problems that ask them to<br />
apply new ideas in unexpected ways<br />
Imaginistic, intuitive & evocative<br />
representations to support students<br />
understandings<br />
Powerful<br />
1. EXAMPLES<br />
representations<br />
2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
Songs, poetry, skits,<br />
3D models<br />
Formal dictionary<br />
definitions of concepts<br />
Notational representations<br />
(i.e. I=E/R)
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Be aware of developmental stages but<br />
don’t limit expectations of individual<br />
students<br />
Awareness : of developmental factors/characteristics<br />
No rigid conceptions of what students can & cannot<br />
do at certain ages<br />
Development is not linear-students grow in complex<br />
ways<br />
Understand complexity is a critical variable<br />
Allowing for multiple entry points in your lessons<br />
and assessments<br />
Pay heed to<br />
developmental<br />
1. EXAMPLES factors<br />
2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
Different tasks & different roles<br />
Scaffolding of cognitive complexity<br />
Most resources involved reading<br />
Personalized & situational; authentic individual<br />
Tasks not assigned for specific reasons<br />
assessment<br />
Projects show varied levels of complexity;<br />
challenges each student at their level<br />
Move beyond knowing to understanding &<br />
evaluating when they answered questions at<br />
personal level
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Unpack the structure & logic of<br />
the disciplines taught<br />
To induct students into the<br />
discipline is to teach students<br />
how people in the discipline<br />
logically think to create new<br />
understanding<br />
The discipline : works toward a system of<br />
thought<br />
Performance of understanding<br />
Teaching specific thinking skills in one<br />
discipline needs to purposefully more<br />
toward Teach for Transfer<br />
Induct students<br />
into the discipline<br />
1. EXAMPLES 2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
Introducing students to the<br />
thinking & resources a<br />
social scientist uses<br />
Gave students the resources<br />
Low level thinking skills<br />
Recitation of facts as the performance
<strong>Frayer</strong> <strong>Model</strong><br />
4. DEFINITION 3. ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Helping student to cultivate<br />
mental habits to make<br />
connections from one context to<br />
another<br />
Explicit : teaching for transfer in an authentic<br />
manner. It is interdisciplinary authentic<br />
tasks that reach beyond the traditional<br />
boundaries of the discipline.<br />
Teach for<br />
1. EXAMPLES<br />
transfer<br />
2. NONEXAMPLES<br />
Lesson was designed with transfer in<br />
mind given in embedded in all aspects<br />
of the lesson literature, music, art integrated<br />
in lesson