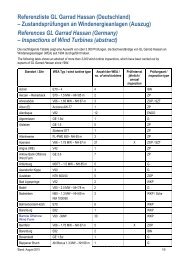
energize oil & gas – issue 01-2013 - GL Group
energize oil & gas – issue 01-2013 - GL Group
energize oil & gas – issue 01-2013 - GL Group
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
integrity composite repairs<br />
selecting variables that predicted the most conservative<br />
stress:<br />
Smallest bend radius: 1.5 D selected<br />
Tightest angle: 90° selected<br />
Corrosion patch to be located on the bend intrados<br />
Furthermore the following simplified assumptions were<br />
made:<br />
Internal corrosion was not considered a credible threat<br />
as the network transports sweet, dry natural <strong>gas</strong>, therefore<br />
only external defects were considered.<br />
The corrosion patch was limited to the minimum<br />
size specified for the short-term survival spool test in<br />
ISO 24817 Annex C (0.5D × 0.25D), using a maximum<br />
defect depth equal to 80 per cent of the wall thickness.<br />
The composite material was modelled as a single layer<br />
with anisotropic properties, perfectly bonded to the<br />
bend.<br />
A pressure load was applied to all internal surfaces of<br />
the model and pressure end loads were applied to represent<br />
the pipe being “capped off”. Additional loading<br />
was not considered in the current scope due to the temporary<br />
nature of the repair.<br />
The material properties were based on manufacturer<br />
specifications. The local coordinate axes in FEA were defined<br />
to represent the bidirectional fabric orientations<br />
(0° and 90° to the roll direction of the fabric, i.e. bend<br />
circumferential and axial directions).<br />
loaded in a direction other than that for which it is designed.<br />
However, it is noted that both manufacturers employ<br />
trained personnel to perform the repairs, rather than<br />
selling the repair technology to third parties. This provides<br />
confidence in the repair method and helps to justify the<br />
assumptions made above.<br />
Repair Thickness<br />
ISO 24817-2<strong>01</strong>1 Annex C specifies an equation for the<br />
minimum required repair thickness for the short-term spool<br />
survival test. This applies to straight pipe. Section 6.5.10.3<br />
Figure 3. Example<br />
of FE mesh for<br />
corrosion<br />
patch on<br />
bend.<br />
Note that it is an inherent assumption that the fabric is<br />
applied so that the directional assumptions are correct.<br />
Composite fibre strength can be seriously compromised if<br />
Figure 4. Example of failure<br />
predicted for unrepaired bend<br />
(150 NB model illustrated, at<br />
95.8 bars applied pressure).<br />
38 energıze