Technical Notes: 1 The Specificity of the microCompass ... - Lonza
Technical Notes: 1 The Specificity of the microCompass ... - Lonza
Technical Notes: 1 The Specificity of the microCompass ... - Lonza
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Technical</strong> <strong>Notes</strong>: 1<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Specificity</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Assay<br />
Introduction<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> System is a rapid microbial detection system<br />
that can provide quantitative results in four hours. Both<br />
filterable and non-filterable samples can be tested for a variety<br />
<strong>of</strong> applications. <strong>The</strong> technology is based upon amplification <strong>of</strong><br />
ribosomal RNA using real-time, reverse transcriptase PCR. <strong>The</strong><br />
<strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit for total viable count (TVC) is<br />
designed to detect all viable bacteria present in a test sample.<br />
<strong>The</strong> kit contains primers and a probe that match ribosomal 16S<br />
RNA sequences universally found in all bacteria (Gram positive,<br />
Gram negative, spores, aerobic and anaerobic bacteria).<br />
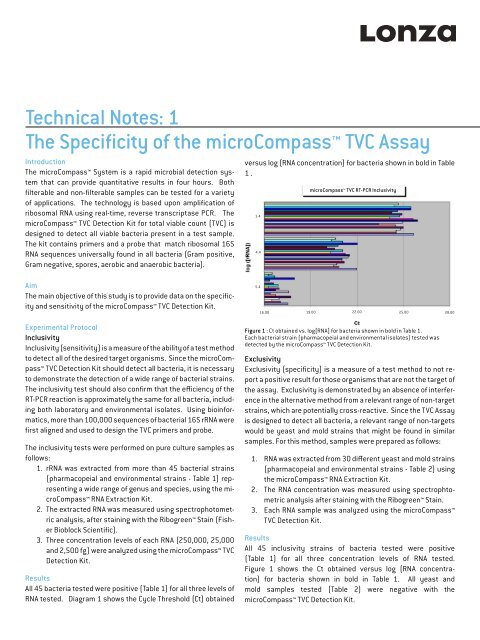
versus log (RNA concentration) for bacteria shown in bold in Table<br />
1 .<br />
3.4<br />
4.4<br />
<strong>microCompass</strong> TVC RT-PCR Inclusivity<br />
Aim<br />
<strong>The</strong> main objective <strong>of</strong> this study is to provide data on <strong>the</strong> specificity<br />
and sensitivity <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit.<br />
Experimental Protocol<br />
Inclusivity<br />
Inclusivity (sensitivity) is a measure <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> ability <strong>of</strong> a test method<br />
to detect all <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> desired target organisms. Since <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong><br />
TVC Detection Kit should detect all bacteria, it is necessary<br />
to demonstrate <strong>the</strong> detection <strong>of</strong> a wide range <strong>of</strong> bacterial strains.<br />
<strong>The</strong> inclusivity test should also confirm that <strong>the</strong> efficiency <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
RT-PCR reaction is approximately <strong>the</strong> same for all bacteria, including<br />
both laboratory and environmental isolates. Using bioinformatics,<br />
more than 100,000 sequences <strong>of</strong> bacterial 16S rRNA were<br />
first aligned and used to design <strong>the</strong> TVC primers and probe.<br />
<strong>The</strong> inclusivity tests were performed on pure culture samples as<br />
follows:<br />
1. rRNA was extracted from more than 45 bacterial strains<br />
(pharmacopeial and environmental strains - Table 1) representing<br />
a wide range <strong>of</strong> genus and species, using <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong><br />
RNA Extraction Kit.<br />
2. <strong>The</strong> extracted RNA was measured using spectrophotometric<br />
analysis, after staining with <strong>the</strong> Ribogreen Stain (Fisher<br />
Bioblock Scientific).<br />
3. Three concentration levels <strong>of</strong> each RNA (250,000, 25,000<br />
and 2,500 fg) were analyzed using <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> TVC<br />
Detection Kit.<br />
Results<br />
All 45 bacteria tested were positive (Table 1) for all three levels <strong>of</strong><br />
RNA tested. Diagram 1 shows <strong>the</strong> Cycle Threshold (Ct) obtained<br />
5.4<br />
16.00 19.00 22.00 25.00 28.00<br />
Figure 1 : Ct obtained vs. log[RNA] for bacteria shown in bold in Table 1.<br />
Each bacterial strain (pharmacopeial and environmental isolates) tested was<br />
detected by <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit.<br />
Exclusivity<br />
Exclusivity (specificity) is a measure <strong>of</strong> a test method to not report<br />
a positive result for those organisms that are not <strong>the</strong> target <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> assay. Exclusivity is demonstrated by an absence <strong>of</strong> interference<br />
in <strong>the</strong> alternative method from a relevant range <strong>of</strong> non-target<br />
strains, which are potentially cross-reactive. Since <strong>the</strong> TVC Assay<br />
is designed to detect all bacteria, a relevant range <strong>of</strong> non-targets<br />
would be yeast and mold strains that might be found in similar<br />
samples. For this method, samples were prepared as follows:<br />
1. RNA was extracted from 30 different yeast and mold strains<br />
(pharmacopeial and environmental strains - Table 2) using<br />
<strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> RNA Extraction Kit.<br />
2. <strong>The</strong> RNA concentration was measured using spectrophtometric<br />
analysis after staining with <strong>the</strong> Ribogreen Stain.<br />
3. Each RNA sample was analyzed using <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong><br />
TVC Detection Kit.<br />
Results<br />
All 45 inclusivity strains <strong>of</strong> bacteria tested were positive<br />
(Table 1) for all three concentration levels <strong>of</strong> RNA tested.<br />
Figure 1 shows <strong>the</strong> Ct obtained versus log (RNA concentration)<br />
for bacteria shown in bold in Table 1. All yeast and<br />
mold samples tested (Table 2) were negative with <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit.
<strong>microCompass</strong> <strong>Technical</strong> <strong>Notes</strong> 1<br />
Table 1 : Bacteria tested strains list (Data shown in Diagram 1 for bacteria in bold)<br />
Organism Group Organism Species Source<br />
Endospore-forming Gram<br />
positive Bacillus<br />
Gram positive Coccus<br />
Gram negative<br />
Bacillus<br />
Non–spore-forming<br />
Gram positive Bacillus<br />
Contact Information<br />
Bacillus circulans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Bacillus licheniformis,<br />
(ES)<br />
Bacillus cereus, (CIP 78.3)<br />
Bacillus pumilus,<br />
(ES)<br />
Bacillus marocanus,<br />
(ES)<br />
Bacillus subtilis, (ATCC 6633)<br />
Paenibacillus pabuli,<br />
(Unknown)<br />
Clostridium sporogenes (CIP 79.39)<br />
Staphylococcus aureus, (ATCC 6538)<br />
Micrococcus luteus, (CIP A 270 T)<br />
Micrococcus lylae,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus hominis,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus warneri,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus arlettae,<br />
(ES)<br />
Staphylococcus carnosus,<br />
(ES)<br />
Macrococcus bovicus,<br />
(ES)<br />
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (CIP 104411)<br />
Escherichia coli, (ATCC 8739)<br />
Salmonella abony, (NCTC 6017/CIP 80.39)<br />
Serratia marcescens, (NCTC 10211)<br />
Pantoea agglomerans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Klebsiella spp, (SD 54.19)<br />
Enterobacter gergoviae (SD 53.21)<br />
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (ATCC 9027)<br />
Pseudomonas fluorescens, (ATCC 13525)<br />
Burkholderia cepacia, (CIP 80.24)<br />
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia,<br />
(ES)<br />
Pseudomonas stuzeri,<br />
(ES)<br />
Acidovorax delafieldii,<br />
(ES)<br />
Burkholderia multivorans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Bordetella hinzii,<br />
(ES)<br />
Brevundimonas vesicularis, (CIP 101035)<br />
Flavobacterium jonhsoniae,<br />
(ES)<br />
Delftia acidovorans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Ralstonia picketii<br />
(ES)<br />
Flavimonas oryzihabitans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Fusobacterium nucleatum, (CIP 1011303)<br />
Bacteroides fragilis,<br />
(Unknown)<br />
Prevotella denticola,<br />
(Unknown)<br />
Porphyromonas gingivalis, (CIP 103683)<br />
Methylobacterium spp<br />
(ES)<br />
Rothia dentocariosa,<br />
(ES)<br />
Corynebacterium afermentans,<br />
(ES)<br />
Tsukamurella inchonensis,<br />
(ES)<br />
Mycobacterium spp,<br />
(ES)<br />
Tsukamurella paurometabola,<br />
(ES)<br />
Propionibacterium acnes,<br />
(ES)<br />
Actinomyces bovis, (CIP 103258)<br />
Bifidobacterium bifidum, (CIP 56.7)<br />
Bifidobacterium longun (CIP 64.62)<br />
Discussion and Conclusion<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit allows detection <strong>of</strong> a broad<br />
range <strong>of</strong> bacterial strains, including aerobic and anaerobic bacteria,<br />
endospore-forming and non–spore-forming Gram positive Bacillus,<br />
Gram positive Coccus, Gram negative Bacillus, Enterobacteriaceae<br />
and Non-Enterobacteriaceae. In this study, <strong>the</strong> <strong>microCompass</strong><br />
TVC Detection Kit was found to have 100% inclusivity/sensitivity<br />
for detecting a wide range <strong>of</strong> bacterial strains and 100% exclusivity/specificity<br />
for non-bacterial strains. Regardless <strong>of</strong> bacterial<br />
source-species <strong>the</strong> relative efficiency <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> RT-PCR results were<br />
<strong>the</strong> same levels <strong>of</strong> detection. It can <strong>the</strong>refore be concluded that <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>microCompass</strong> TVC Detection Kit is a rapid, sensitive and specific<br />
test for <strong>the</strong> quantitative detection <strong>of</strong> bacteria in a wide variety <strong>of</strong><br />
samples, providing results in hours, versus several days for conventional<br />
reference methods.<br />
Table 2 : Yeasts and Molds tested strains list<br />
Organism<br />
Group<br />
Yeasts<br />
Molds<br />
Organism<br />
Species<br />
Source<br />
Candida albicans, ATCC 10231<br />
Candida tropicalis, ATCC 201380<br />
Candida kefyr, ATCC 2512<br />
Candida krusei, ATCC 6258<br />
Debaryomyces polymorphus, ATCC 18577<br />
Pichia fermentans, ATCC 28789<br />
Rhodotorula glutinis, ATCC 16740<br />
Aspergillus oryzae, ATCC 10124<br />
Aspergillus niger, CIP 1431-83<br />
Aspergillus fumigatus,<br />
ES<br />
Botrytis cinerea, ATCC 11542<br />
Cladosporium cladosporioides,<br />
UMIP 1232.80<br />
Cladosporium sphaerospermum<br />
Penz,<br />
ES<br />
Aspergillus repens, ATCC 48521<br />
Organism<br />
Species<br />
Source<br />
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ES<br />
Torulaspora delbrueckii, ATCC 204289<br />
Zygosaccharomyces rouxii, UMIP 2021.92<br />
Kluyveromyces yarrowii, ATCC 200789<br />
Cryptococcus terreus, ATCC 11799<br />
Pichia pastoris, ATCC 204414<br />
Kluyveromyces lactis ATCC 8563<br />
Fusarium oxysporum, ATCC 16322<br />
Geotrichum candidum, ATCC 34614<br />
Monascus purpureus, ATCC 16365<br />
Penicillium roquefortii, UMIP 1404.82<br />
Penicillium chrysogenum, ES<br />
Rhizopus stolonifer, UMIP 1583.85<br />
Trichoderma viride, ATCC 26802<br />
Tricho<strong>the</strong>cium roseum, ATCC 8685<br />
Verticillium dahliae ATCC 16535<br />
1.) Ct/Cp (Cycle Threshold/Crossing Point) is <strong>the</strong> number <strong>of</strong> RT-PCR cycles required to detect a<br />
flourescent signal above <strong>the</strong> background. Ct/Cp is inversely proportional to <strong>the</strong> starting concentration<br />
<strong>of</strong> target in <strong>the</strong> sample, i.e. <strong>the</strong> lower <strong>the</strong> Ct/Cp, <strong>the</strong> higher <strong>the</strong> concentration <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> sample.<br />
2.) RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription -Polymerase Chain Reaction) RT converts RNA to amplifiable DNA.<br />
Once <strong>the</strong> DNA strand is built, it is <strong>the</strong>n amplified by PCR.<br />
North America<br />
Customer Service: 800-638-8174<br />
<strong>Technical</strong> Service: 800-521-0390<br />
E-mail:<br />
biotechserv@lonza.com<br />
Online Ordering: www.lonza.com<br />
Europe<br />
Customer Service: 00 32 87 321 687<br />
<strong>Technical</strong> Service: 00 32 87 321 688<br />
E-mail:<br />
techsup.europe@lonza.com<br />
or techsup.uk@lonza.com<br />
Online Ordering: www.lonza.com<br />
International<br />
Contact your local <strong>Lonza</strong> Distributor<br />
Customer Service: 301-898-7025, ext. 2322<br />
Fax: 301-845-8291<br />
E-mail:<br />
biotechserv@lonza.com<br />
International Offices<br />
Australia 61 3 9550 0883<br />
Austria 0800 201 538<br />
Belgium 00 32 87 321 687<br />
Denmark 45 43 56 74 00<br />
France 0800 91 19 81<br />
Germany 0800 182 52 87<br />
India 91 22 6697 2883<br />
Italy 0039 0363 45710<br />
<strong>The</strong> Ne<strong>the</strong>rlands 0800 022 4525<br />
Spain 34 902 531 366<br />
Sweden 020 140 4410<br />
Switzerland 0800 83 86 20<br />
United Kingdom 44 118 979 5234<br />
<strong>Lonza</strong> Walkersville, Inc.<br />
Walkersville, MD 21793<br />
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.<br />
Ribogreen is a trademark <strong>of</strong> Molecular Probes.<br />
Unless o<strong>the</strong>rwise noted, all trademarks herein are marks <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> <strong>Lonza</strong> Group or its affiliates.<br />
© Copyright 2008, <strong>Lonza</strong> Walkersville, Inc.<br />
All rights reserved.<br />
TB-TVC 05/08