TEchNOLOGy TRaNSFER MODEL - Javna agencija
TEchNOLOGy TRaNSFER MODEL - Javna agencija
TEchNOLOGy TRaNSFER MODEL - Javna agencija
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
KNOWLEDGE FOR BUSINESS IN BORDER REGIONS<br />
5<br />
Module 5: Technology Management<br />
Dr. Stefan Vorbach<br />
5.1 Learning objectives of the module<br />
Module 5 deals with technology management and in particular with the technology management process. In doing so, its aim is to<br />
provide a deeper understanding of basic theories in a) technological dynamics, b) technology assessment, c) technology foresight,<br />
d) technology related decisions and e) technology marketing. Aside from presenting theoretical concepts, methods and instruments<br />
with high potential to support technology related decision-making (like the technology roadmap, technology calendar, technology<br />
portfolio, Delphi study, scenario analysis, etc.) are also an integrated part of this module.<br />
5.2 Keywords<br />
Technology Management, Technological Dynamics, Disruptive Technology, Technology Assessment, Technology Portfolio, Technology<br />
Foresight Activities, Technology Roadmap, Technology Calendar, Technology Tree, Technology Radar, Delphi Study, Scenario<br />
Analysis, Technological Feasibility, Technology Marketing<br />
5.3 Technology and Technology Management in a nutshell<br />
5.3.1 Technology in the corporate setting<br />
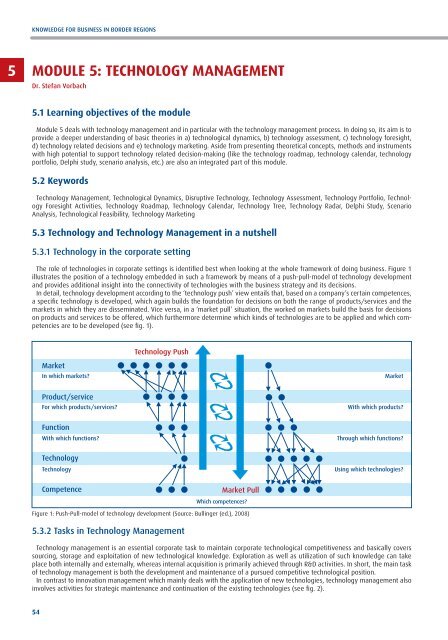
The role of technologies in corporate settings is identified best when looking at the whole framework of doing business. Figure 1<br />
illustrates the position of a technology embedded in such a framework by means of a push-pull-model of technology development<br />
and provides additional insight into the connectivity of technologies with the business strategy and its decisions.<br />
In detail, technology development according to the ‘technology push’ view entails that, based on a company’s certain competences,<br />
a specific technology is developed, which again builds the foundation for decisions on both the range of products/services and the<br />
markets in which they are disseminated. Vice versa, in a ‘market pull’ situation, the worked on markets build the basis for decisions<br />
on products and services to be offered, which furthermore determine which kinds of technologies are to be applied and which competencies<br />
are to be developed (see fig. 1).<br />
Figure 1: Push-Pull-model of technology development (Source: Bullinger (ed.), 2008)<br />
5.3.2 Tasks in Technology Management<br />
Technology management is an essential corporate task to maintain corporate technological competitiveness and basically covers<br />
sourcing, storage and exploitation of new technological knowledge. Exploration as well as utilization of such knowledge can take<br />
place both internally and externally, whereas internal acquisition is primarily achieved through R&D activities. In short, the main task<br />
of technology management is both the development and maintenance of a pursued competitive technological position.<br />
In contrast to innovation management which mainly deals with the application of new technologies, technology management also<br />
involves activities for strategic maintenance and continuation of the existing technologies (see fig. 2).<br />
54