Annual Report 2010-2011 - Gammon India
Annual Report 2010-2011 - Gammon India
Annual Report 2010-2011 - Gammon India
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
126<br />
Capital work in progress represents the costs incurred on project activity till completion of the project. It includes all direct material, labour and<br />
sub-contracting costs and those indirect costs related to constructions that are identifiable with or allocable to the project including borrowing<br />
costs.<br />
Depreciation and Amortization<br />
<strong>India</strong>n Operations<br />
Depreciation for the accounting period is provided on:<br />
(a) Straight Line Method, for assets purchased after 2-4-1987, at the rates and in the manner specified in Schedule XIV to the Companies Act,<br />
1956.<br />
(b) Written Down Value Method, for assets acquired on or prior to 2-4-1987, at the rates as specified in Schedule XIV to the Companies Act,<br />
1956.<br />
(c) Depreciation on revalued component of the assets is withdrawn from the Revaluation Reserve.<br />
(d) The depreciation on assets used for construction has been treated as period cost.<br />
(e) The Infrastructure Projects Assets are amortized over a period of the rights given under the various Concession Agreements to which they<br />
relate.<br />
(f) Expenses incurred by the Company on periodic maintenance (required to be incurred by it in the 5 th , 10 th and 15 th year as per the Contract<br />
with NHAI) are capitalised on the completion of said activity as the same enhances the useful life of the project. These costs are amortised<br />
over the period up to which the next periodic maintenance is due. The periodic maintenance of 15 th year is written off over the balance<br />
concession period.<br />
Overseas Operations<br />
Depreciation is charged on a straight line basis over the useful life of the assets or as prescribed as per the relevant local laws of such country.<br />
Where the asset being depreciated is made up of distinctly identifiable elements, whose useful life significantly differs from that of the other<br />
parts the depreciation is provided separately in accordance with the component approach.<br />
The estimated useful lives of the assets for calculating depreciation are as follows:<br />
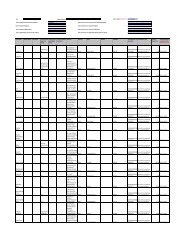
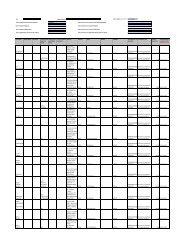
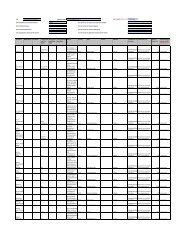
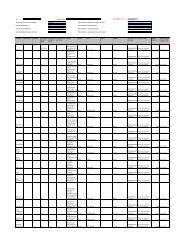
ASSET From To<br />
Building 20 Years 40 Years<br />
Plant & Machinery 3 Years 20 Years<br />
Computer 3 Years 7 Years<br />
Furniture & Fixtures 3 Years 10 Years<br />
Office Equipment 2 Years 15 Years<br />
Motor Vehicles 3 Years 8 Years<br />
Temporary Site Office 2 Years 8 Years<br />
Intangible Assets<br />
Intangible assets are amortised over the period of the useful life of the rights and it begins when the asset is available for use. Intangible assets<br />
of infinite useful lives are not amortized but subject to impairment test, on an annual basis.<br />
Intangible assets are represented by non-monetary elements, identifiable and lacking physical consistency, controllable and capable of generating<br />
future economic benefits. These elements are recorded at purchase and/or production cost, inclusive of any directly attributable expenses for<br />
preparing the asset for use, net of accumulated amortisation and any impairment losses.<br />
Intangible assets also represents the concession rights in relation to toll roads to collect toll fees for improvement, operations and maintenance,<br />
rehabilitation and strengthening of existing 2 lane road and widening to 4 lane divided carriageway from Km. 539.500 to Km. 440.000 (Vadape-<br />
Gonde Section) of NH-3 on Build, Operate and Transfer (BOT) basis in the State of Maharashtra. Such costs include all construction costs<br />
including sub-contract costs and other costs attributable to the said project asset including borrowing costs and the proportionate cash payout<br />
(negative grant) at the end of concession period to NHAI.<br />
Concession rights are amortised on the pro-rata basis of Actual Tollable Traffic volume for the period over the Total Projected Tollable Traffic<br />
volume over the Toll Periods granted for the Project. The projections for the Total Traffic Volume are based on the <strong>Report</strong> of Independent<br />
Professionals for this purpose. The Volume of Traffic is reviewed on periodic intervals for its consistency and appropriateness. If the Right to<br />
Collect Toll being amortised is revised on account of the material change in the Projected Traffic Volume arising out of the periodic review, the<br />
amortization would be revised accordingly.<br />
9. Impairment of Assets<br />
On annual basis Company makes an assessment of any indicator that may lead to impairment of assets. An asset is treated as impaired when<br />
the carrying cost of asset exceeds its recoverable value. Recoverable amount is higher of an asset’s net selling price and its value in use. Value<br />
in use is the present value of estimated future cash flows expected to arise from the continuing use of an asset and from its disposal at the end<br />
of its useful life.<br />
An impairment loss is charged to the Profit and Loss Account in the year in which an asset is identified as impaired. The impairment loss<br />
recognized in prior accounting period is reversed if there has been a change in the estimate of recoverable amount.<br />
A NNUAL R EPORT I <strong>2010</strong>/11